数学代写| Undefined Values 离散代考
离散数学在计算领域有广泛的应用,例如密码学、编码理论、 形式方法, 语言理论, 可计算性, 人工智能, 理论 数据库和软件的可靠性。 离散数学的重点是理论和应用,而不是为了数学本身而研究数学。 一切算法的基础都是离散数学一切加密的理论基础都是离散数学
编程时候很多奇怪的小技巧(特别是所有和位计算相关的东西)核心也是离散数学
其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
离散数学代写
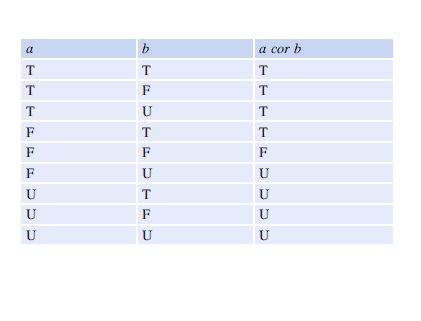
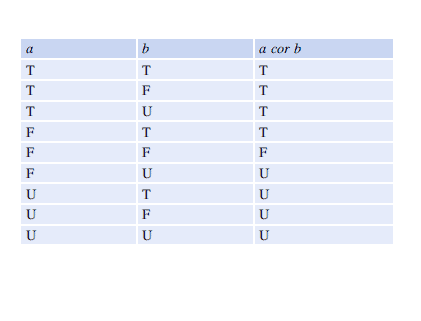
Parnas’s approach to logic is based on classical two-valued logic, and his philosophy is that truth-values should be true or false only, ${ }^{4}$ and that there is no third logical value. It is an extension to predicate calculus to deal with partial functions. The evaluation of a logical expression yields the value ‘true’ or ‘false’ irrespective of the assignment of values to the variables in the expression. This allows the expression: $(y=\sqrt{x})) \vee(y=\sqrt{-} x)$, that is undefined in classical logic to yield the value true.
The advantages of his approach are that no new symbols are introduced into the logic and that the logical connectives retain their traditional meaning. This makes it easier for engineers and computer scientists to understand, as it is closer to their intuitive understanding of logic.
The meaning of predicate expressions is given by first defining the meaning of the primitive expressions. These are then used as the building blocks for predicate expressions. The evaluation of a primitive expression $R_{j}(V)$ (where $V$ is a comma-separated set of terms with some elements of $V$ involving the application of partial functions) is false if the value of an argument of a function used in one of the terms of $V$ is not in the domain of that function. ${ }^{5}$ The following examples (Tables $16.1$ and $16.2$ ) should make this clearer:
These primitive expressions are used to build the predicate expressions, and the standard logical connectives are used to yield truth-values for the predicate expression. Parnas logic is defined in detail in [4].
The power of Parnas logic may be seen by considering a tabular expressions example [4]. The table below specifies the behaviour of a program that searches the array $B$ for the value $x$. It describes the properties of the values of ‘ $j$ ‘ and ‘present’.
There are two cases to be considered (Fig. 16.4):
- There is an element in the array with the value of $x$
- There is no such element in the array with the value of $x$.
Clearly, from the example above the predicate expressions $\exists i, \mathrm{~B}[i]=x$ and $\neg(\exists i, B[i]=x)$ are defined. One disadvantage of the Parnas approach is that some However, these relational operators are then constructed from primitive operators. Further, the axiom of reflection does not hold in the logic.
$\overline{{ }^{4} \text { It seems strange to assign the value false to the primitive predicate calculus expression } y={ }^{1 /} 0 \text {. }$ ${ }^{5}$ The approach avoids the undefined logical value (\) and preserves the two-valued logic.
图论代考
Parnas 的逻辑方法基于经典的二值逻辑,他的哲学是真值应该是真或假,${ }^{4}$,并且没有第三个逻辑值。它是处理偏函数的谓词演算的扩展。逻辑表达式的评估产生值“真”或“假”,而与表达式中变量的值分配无关。这允许表达式:$(y=\sqrt{x})) \vee(y=\sqrt{-} x)$,它在经典逻辑中未定义,以产生值 true。
他的方法的优点是没有在逻辑中引入新的符号,并且逻辑连接词保留了它们的传统意义。这使工程师和计算机科学家更容易理解,因为它更接近于他们对逻辑的直观理解。
谓词表达式的含义是通过首先定义原始表达式的含义来给出的。然后将它们用作谓词表达式的构建块。如果参数的值,则原始表达式 $R_{j}(V)$(其中 $V$ 是逗号分隔的一组术语,其中 $V$ 的某些元素涉及偏函数的应用)的评估为假在 $V$ 的一个术语中使用的函数不在该函数的域中。 ${ }^{5}$ 以下示例(表 $16.1$ 和 $16.2$ )应该更清楚地说明这一点:
这些原始表达式用于构建谓词表达式,标准逻辑连接词用于产生谓词表达式的真值。 Parnas 逻辑在 [4] 中有详细定义。
通过考虑表格表达式示例 [4],可以看出 Parnas 逻辑的强大功能。下表指定了在数组 $B$ 中搜索值 $x$ 的程序的行为。它描述了“$j$”和“present”的值的属性。
有两种情况需要考虑(图 16.4):
1.数组中有一个元素的值为$x$
- 数组中不存在值为$x$ 的元素。
显然,从上面的例子中,谓词表达式 $\exists i, \mathrm{~B}[i]=x$ 和 $\neg(\exists i, B[i]=x)$ 被定义了。 Parnas 方法的一个缺点是一些但是,这些关系运算符是从原始运算符构造的。此外,反射公理在逻辑中不成立。
$\overline{{ }^{4} \text { 将值 false 分配给原始谓词演算表达式似乎很奇怪 } y={ }^{1 /} 0 \text {。 }$ ${ }^{5}$ 该方法避免了未定义的逻辑值(\)并保留了二值逻辑

数学代写| DISCRETE MATHEMATICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
抽象代数代考
抽象代数就是一门概念繁杂的学科,我们最重要的一点我想并不是掌握多少例子。即便是数学工作者也不会刻意记住Jacobson环、正则环这类东西,重要的是你要知道这门学科的基本工具和基本手法,对概念理解了没有,而这一点不需要用例子来验证,只需要看看你的理解和后续概念是否相容即可。
矩阵论代考matrix theory
数学,矩阵理论是一门研究矩阵在数学上的应用的科目。矩阵理论本来是线性代数的一个小分支,但其后由于陆续在图论、代数、组合数学和统计上得到应用,渐渐发展成为一门独立的学科。
密码学代考
密码学是研究编制密码和破译密码的技术科学。 研究密码变化的客观规律,应用于编制密码以保守通信秘密的,称为编码学;应用于破译密码以获取通信情报的,称为破译学,总称密码学。 电报最早是由美国的摩尔斯在1844年发明的,故也被叫做摩尔斯电码。
- Cryptosystem
- A system that describes how to encrypt or decrypt messages
- Plaintext
- Message in its original form
- Ciphertext
- Message in its encrypted form
- Cryptographer
- Invents encryption algorithms
- Cryptanalyst
- Breaks encryption algorithms or implementations
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。