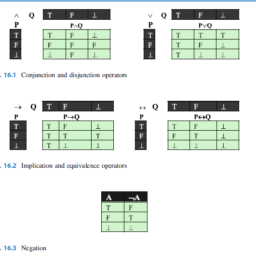
数学代写| Public Key Systems 代考
离散数学在计算领域有广泛的应用,例如密码学、编码理论、 形式方法, 语言理论, 可计算性, 人工智能, 理论 数据库和软件的可靠性。 离散数学的重点是理论和应用,而不是为了数学本身而研究数学。 一切算法的基础都是离散数学一切加密的理论基础都是离散数学
编程时候很多奇怪的小技巧(特别是所有和位计算相关的东西)核心也是离散数学
其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
离散数学代写
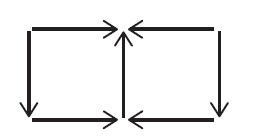
A public key cryptosystem (Fig. 10.7) is an asymmetric key system where there is a separate key $e_{k}$ for encryption and $d_{k}$ decryption with $e_{k} \neq d_{k}$. Martin Hellman and Whitfield Diffie invented it in 1976 . The fact that a person is able to encrypt a
\begin{tabular}{l|l|}
\hline Table. & $10.3$ DES encryption \
\hline Step & Description \
\hline 1 & Expansion of the 32 -bit half block to 48 bits (by duplicating half of the bits) \
\hline 2 & The 48 -bit result is combined with a 48 bit subkey of the secret key using an XOR operation \
\hline 3 & The 48 -bit result is broken in to $8 * 6$ bits and passed through 8 substitution boxes to yield $8 * 4=32$ bits (This is the core part of the encryption algorithm) \
\hline 4 & The 32 -bit output is re-arranged according to a fixed permutation \
\hline
\end{tabular}$10.5$ Public Key Systems
Table. $10.5$ Advantages and disadvantages of public key cryptosystems
\begin{tabular}{l|l|}
Advantages & Disadvantages \
\hline Only the private key needs to be kept secret & Public keys must be authenticated \
\hline The distribution of keys for encryption is convenient, & It is slow and uses more computer \
as everyone publishes their public key and the & resources \
private key is kept private & \
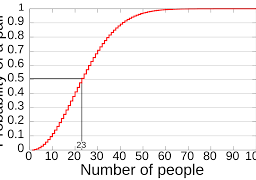
It provides message authentication as it allows the & Security Compromise is possible (if \
use of digital signatures (which enables the recipient & private key is compromised) \
to verify that the message is really from the particular & \
sender) & The sender encodes with the private key that is known only to sender. The receiver decodes with the public key and therefore knows that the message is from the sender \
\hline Detection of tampering (digital signatures enable the receiver to detect whether message was altered in transit) & Loss of private key may be irreparable (unable to decrypt messages) \
\hline Provides for non-repudiation & \
\hline
\end{tabular}
compute problem for large $n$ since there is no efficient algorithm to factorize a large integer into its prime factors (integer factorization problem).
compute problem f a large integer into
(ii) The function $f_{g, N}: x \rightarrow g^{x}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ is a one way function since it is easy to compute. However, the inverse function $f^{-1}$ is difficult to compute as there is no efficient method to determine $x$ from the knowledge of $g^{x}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ and $g$ and $\mathrm{N}$ (the discrete logarithm problem).
(iii) The function $f_{k, N}: x \rightarrow x^{k}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ (where $\mathrm{N}=p q$ and $p$ and $q$ are primes) and $k k^{\prime \prime} \equiv 1(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ is a trapdoor function. It is easy to compute but the inverse of $f$ (the $k^{\text {th }}$ root modulo $\mathrm{N}$ ) is difficult to compute. However, if the trapdoor $k^{\prime}$ is given then $f$ can easily be inverted as $\left(x^{k}\right)^{k^{\prime}} \equiv x(\bmod \mathrm{N})$
10.5.1 RSA Public Key Cryptosystem
Rivest, Shamir and Adleman proposed a practical public key cryptosystem (RSA) based on primality testing and integer factorization in the late $1970 \mathrm{~s}$. The RSA algorithm was filed as a patent (Patent No. 4,405, 829) at the U.S. Patent Office in December 1977. The RSA public key cryptosystem is based on the following assumptions:
- It is straightforward to find two large prime numbers.
- The integer factorization problem is infeasible for large numbers.
公钥密码系统(图 10.7)是一个非对称密钥系统,其中有一个单独的密钥 $e_{k}$ 用于加密和 $d_{k}$ 解密,$e_{k} \neq d_{k}$。 Martin Hellman 和 Whitfield Diffie 于 1976 年发明了它。一个人能够加密一个事实
\开始{表格}{l|l|}
\hline 表。 & $10.3$ DES 加密 \
\hline 步骤和说明 \
\hline 1 & 将 32 位半块扩展为 48 位(通过复制一半位)\
\hline 2 & 使用 XOR 操作将 48 位结果与密钥的 48 位子密钥组合在一起
\hline 3 & 将 48 位结果分解为 $8 * 6$ 位并通过 8 个替换框得到 $8 * 4=32$ 位(这是加密算法的核心部分)\
\hline 4 & 32 位输出根据固定排列重新排列 \
\hline
\end{tabular}$10.5$ 公钥系统
桌子。 $10.5$ 公钥密码系统的优缺点
\开始{表格}{l|l|}
优点缺点 \
\hline 只有私钥需要保密 & 公钥必须经过身份验证 \
\hline 用于加密的密钥分配方便,& 速度慢,使用较多电脑 \
因为每个人都发布了他们的公钥和 & 资源 \
私钥保持私有 & \
它提供消息身份验证,因为它允许 & 安全妥协是可能的(如果 \
使用数字签名(这会使收件人和私钥受到损害)\
验证消息是否真的来自特定的 & \
发件人) & 发件人使用只有发件人知道的私钥进行编码。接收方使用公钥解码,因此知道消息来自发送方\
\hline 篡改检测(数字签名使接收方能够检测消息在传输过程中是否被更改)& 私钥丢失可能无法弥补(无法解密消息)\
\hline 提供不可否认性 & \
\hline
\end{表格}
计算大 $n$ 的问题,因为没有有效的算法将大整数分解为其素数(整数分解问题)。
计算问题 f 一个大整数到
(ii) 函数 $f_{g, N}: x \rightarrow g^{x}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ 是单向函数,因为它易于计算。然而,逆函数 $f^{-1}$ 很难计算,因为没有有效的方法来根据 $g^{x}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ 和 $ 的知识确定 $x$ g$ 和 $\mathrm{N}$(离散对数问题)。
(iii) 函数 $f_{k, N}: x \rightarrow x^{k}(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ (其中 $\mathrm{N}=pq$ and $p$ and $q$是素数),$kk^{\prime \prime} \equiv 1(\bmod \mathrm{N})$ 是陷门函数。它很容易计算,但 $f$ 的倒数($k^{\text {th }}$ 根模 $\mathrm{N}$ )很难计算。但是,如果给定陷门 $k^{\prime}$,则 $f$ 可以很容易地反转为 $\left(x^{k}\right)^{k^{\prime}} \equiv x(\ bmod \mathrm{N})$
10.5.1 RSA公钥密码系统
Rivest、Shamir 和 Adleman 在 1970 年后期提出了一种实用的公钥密码系统 (RSA),该系统基于素数测试和整数分解。 RSA 算法于 1977 年 12 月在美国专利局作为专利(专利号 4,405, 829)提交。RSA 公钥密码系统基于以下假设:
- 找到两个大素数很简单。
- 整数分解问题对于大数是不可行的。
图论代考
自然数 $\mathbb{N}$ 由数字 $\{1,2,3, \ldots\}$ 组成。整数 $\mathbb{Z}$ 由 $\{\ldots-2,-1,0,1,2, \ldots\}$ 组成。有理数 $\mathbb{Q}$ 由 $\left\{{ }^{p} /_{q}\right.$ 形式的所有数字组成,其中 $p$ 和 $q$ 是整数,$ \left.q \neq 0\right\}$。实数 $\mathbb{R}$ 被定义为有理数收敛序列的集合,它们是有理数的超集。它们包含有理数和无理数。复数 $\mathbb{C}$ 由 $\{a+bi$ 形式的所有数字组成,其中 $a, b \in \mathbb{R}$ 和 $i=\sqrt{-} 1\}美元。 毕达哥拉斯三元组(图 3.2)是满足毕达哥拉斯方程 $x^{2}+y^{2}=z^{2}$ 的三个整数的组合。有无数个这样的三元组,这种三元组的一个例子是 $3,4,5$,因为 $3^{2}+4^{2}=5^{2}$。 毕达哥拉斯学派发现了音乐和数字之间的数学关系,他们的哲学是数字隐藏在从音乐到科学和自然的一切事物中。这导致了他们的哲学,即“一切都是数字”。
数学代写| DISCRETE MATHEMATICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
抽象代数代考
抽象代数就是一门概念繁杂的学科,我们最重要的一点我想并不是掌握多少例子。即便是数学工作者也不会刻意记住Jacobson环、正则环这类东西,重要的是你要知道这门学科的基本工具和基本手法,对概念理解了没有,而这一点不需要用例子来验证,只需要看看你的理解和后续概念是否相容即可。
矩阵论代考matrix theory
数学,矩阵理论是一门研究矩阵在数学上的应用的科目。矩阵理论本来是线性代数的一个小分支,但其后由于陆续在图论、代数、组合数学和统计上得到应用,渐渐发展成为一门独立的学科。
密码学代考
密码学是研究编制密码和破译密码的技术科学。 研究密码变化的客观规律,应用于编制密码以保守通信秘密的,称为编码学;应用于破译密码以获取通信情报的,称为破译学,总称密码学。 电报最早是由美国的摩尔斯在1844年发明的,故也被叫做摩尔斯电码。
- Cryptosystem
- A system that describes how to encrypt or decrypt messages
- Plaintext
- Message in its original form
- Ciphertext
- Message in its encrypted form
- Cryptographer
- Invents encryption algorithms
- Cryptanalyst
- Breaks encryption algorithms or implementations
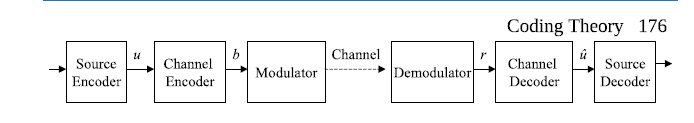
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。