如果你也在 怎样代写线性代数Linear Algebra这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。线性代数Linear Algebra是数学的一个分支,涉及到矢量空间和线性映射。它包括对线、面和子空间的研究,也涉及所有向量空间的一般属性。
线性代数Linear Algebra也被用于大多数科学和工程engineering领域,因为它可以对许多自然现象进行建模Mathematical model,并对这些模型进行高效计算。对于不能用线性代数建模的非线性系统Nonlinear system,它经常被用来处理一阶first-order approximations近似。
my-assignmentexpert™ 线性代数linear algebra作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的线性代数linear algebra作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于线性代数linear algebra作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此线性代数linear algebra作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在线性代数linear algebra作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的线性代数linear algebra代写服务。我们的专家在线性代数linear algebra代写方面经验极为丰富,各种线性代数linear algebra相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的线性代数linear algebra及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 数值分析
- 高等线性代数
- 矩阵论
- 优化理论
- 线性规划
- 逼近论
线性代数作业代写linear algebra代考|linear equations
A linear equation in $n$ unknowns $x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}$ is an equation of the form
$$
a_{1} x_{1}+a_{2} x_{2}+\cdots+a_{n} x_{n}=b,
$$
where $a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{n}, b$ are given real numbers.
For example, with $x$ and $y$ instead of $x_{1}$ and $x_{2}$, the linear equation $2 x+3 y=6$ describes the line passing through the points $(3,0)$ and $(0,2)$.
Similarly, with $x, y$ and $z$ instead of $x_{1}, x_{2}$ and $x_{3}$, the linear equation $2 x+3 y+4 z=12$ describes the plane passing through the points $(6,0,0),(0,4,0),(0,0,3)$.
A system of $m$ linear equations in $n$ unknowns $x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}$ is a family of linear equations
$$
\begin{aligned}
a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}+\cdots+a_{1 n} x_{n} &=b_{1} \
a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}+\cdots+a_{2 n} x_{n} &=b_{2} \
& \vdots \
a_{m 1} x_{1}+a_{m 2} x_{2}+\cdots+a_{m n} x_{n} &=b_{m} .
\end{aligned}
$$
We wish to determine if such a system has a solution, that is to find out if there exist numbers $x_{1}, x_{2}, \cdots, x_{n}$ which satisfy each of the equations simultaneously. We say that the system is consistent if it has a solution. Otherwise the system is called inconsistent.
Note that the above system can be written concisely as
$$
\sum_{j=1}^{n} a_{i j} x_{j}=b_{i}, \quad i=1,2, \cdots, m .
$$
The matrix
$$
\left[\begin{array}{cccc}
a_{11} & a_{12} & \cdots & a_{1 n} \
a_{21} & a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2 n} \
\vdots & & & \vdots \
a_{m 1} & a_{m 2} & \cdots & a_{m n}
\end{array}\right]
$$
is called the coefficient matrix of the system, while the matrix
$$
\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}
a_{11} & a_{12} & \cdots & a_{1 n} & b_{1} \
a_{21} & a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2 n} & b_{2} \
\vdots & & & \vdots & \vdots \
a_{m 1} & a_{m 2} & \cdots & a_{m n} & b_{m}
\end{array}\right]
$$
is called the augmented matrix of the system.
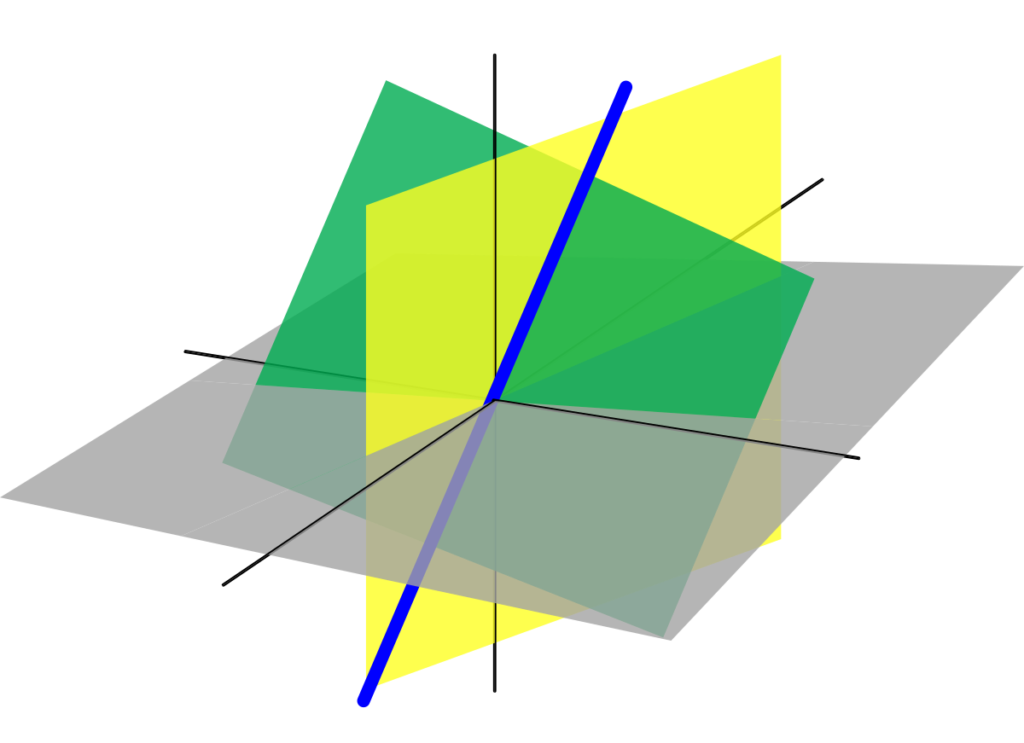
Geometrically, solving a system of linear equations in two (or three) unknowns is equivalent to determining whether or not a family of lines (or planes) has a common point of intersection.
线性代数作业代写linear algebra代考|THE FIELD AXIOMS
- $(a+b)+c=a+(b+c)$ for all $a, b, c$ in $F$;
- $(a b) c=a(b c)$ for all $a, b, c$ in $F$;
- $a+b=b+a$ for all $a, b$ in $F$;
- $a b=b a$ for all $a, b$ in $F$;
- there exists an element 0 in $F$ such that $0+a=a$ for all $a$ in $F$;
- there exists an element 1 in $F$ such that $1 a=a$ for all $a$ in $F$;
- to every $a$ in $F$, there corresponds an additive inverse $-a$ in $F$, satisfying
$$
a+(-a)=0
$$ - to every non-zero $a$ in $F$, there corresponds a multiplicative inverse $a^{-1}$ in $F$, satisfying
$$
a a^{-1}=1 ;
$$ - $a(b+c)=a b+a c$ for all $a, b, c$ in $F$;
- $0 \neq 1$.
With standard definitions such as $a-b=a+(-b)$ and $\frac{a}{b}=a b^{-1}$ for $b \neq 0$, we have the following familiar rules:
$$
\begin{aligned}
-(a+b) &=(-a)+(-b), \quad(a b)^{-1}=a^{-1} b^{-1} \
-(-a) &=a, \quad\left(a^{-1}\right)^{-1}=a ; \
-(a-b) &=b-a, \quad\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^{-1}=\frac{b}{a} \
\frac{a}{b}+\frac{c}{d} &=\frac{a d+b c}{b d} \
\frac{a}{b} \frac{c}{d} &=\frac{a c}{b d} ; \
\frac{a b}{a c} &=\frac{b}{c}, \frac{a}{\left(\frac{b}{c}\right)}=\frac{a c}{b} \
-(a b) &-(-a) b-a(-b) \
-\left(\frac{a}{b}\right) &=\frac{-a}{b}=\frac{a}{-b} \
0 a &=0 ; \
(-a)^{-1} &=-\left(a^{-1}\right) .
\end{aligned}
$$
Fields which have only finitely many elements are of great interest in many parts of mathematics and its applications, for example to coding theory. It is easy to construct fields containing exactly $p$ elements, where $p$ is a prime number. First we must explain the idea of modular addition and modular multiplication. If $a$ is an integer, we define $a(\bmod p)$ to be the least remainder on dividing a by $p$ : That is, if $a=b p+r$, where $b$ and $r$ are integers and $0 \leq r<p$, then $a(\bmod p)=r$.

线性代数作业代写LINEAR ALGEBRA代考|LINEAR EQUATIONS
一个线性方程n未知数X1,X2,⋯,Xn是形式的方程
一种1X1+一种2X2+⋯+一种nXn=b,
在哪里一种1,一种2,…,一种n,b给定实数。
例如,与X和和代替X1和X2, 线性方程2X+3和=6描述通过点的线(3,0)和(0,2).
同样,与X,和和和代替X1,X2和X3, 线性方程2X+3和+4和=12描述通过点的平面(6,0,0),(0,4,0),(0,0,3).
一个系统米线性方程组n未知数X1,X2,⋯,Xn是一族线性方程
一种11X1+一种12X2+⋯+一种1nXn=b1 一种21X1+一种22X2+⋯+一种2nXn=b2 ⋮ 一种米1X1+一种米2X2+⋯+一种米nXn=b米.
我们希望确定这样的系统是否有解决方案,即找出是否存在数字X1,X2,⋯,Xn同时满足每个方程。如果系统有解,我们说系统是一致的。否则称系统不一致。
注意上面的系统可以简写为
∑j=1n一种一世jXj=b一世,一世=1,2,⋯,米.
矩阵
[一种11一种12⋯一种1n 一种21一种22⋯一种2n ⋮⋮ 一种米1一种米2⋯一种米n]
称为系统的系数矩阵,而矩阵
[一种11一种12⋯一种1nb1 一种21一种22⋯一种2nb2 ⋮⋮⋮ 一种米1一种米2⋯一种米nb米]
称为系统的增广矩阵。
在几何上,求解具有两个(或三个)未知数的线性方程组等同于确定一系列线(或平面)是否具有共同的交点。
线性代数作业代写LINEAR ALGEBRA代考|THE FIELD AXIOMS
- (一种+b)+C=一种+(b+C)对所有人一种,b,C在F;
- (一种b)C=一种(bC)对所有人一种,b,C在F;
- 一种+b=b+一种对所有人一种,b在F;
- 一种b=b一种对所有人一种,b在F;
- 中存在元素 0F这样0+一种=一种对所有人一种在F;
- 中存在元素 1F这样1一种=一种对所有人一种在F;
- 对每个一种在F, 对应一个加法逆−一种在F, 满足
一种+(−一种)=0 - 对每个非零一种在F, 对应一个乘法逆一种−1在F, 满足
一种一种−1=1; - 一种(b+C)=一种b+一种C对所有人一种,b,C在F;
- 0≠1.只有有限多个元素的领域在数学的许多部分及其应用中都非常有趣,例如编码理论。构造精确包含的字段很容易p元素,其中p是一个素数。首先我们必须解释模加和模乘的概念。如果一种是一个整数,我们定义一种(反对p)是除以 a 的最小余数p: 也就是说,如果一种=bp+r, 在哪里b和r是整数和0≤r<p, 然后一种(反对p)=r.

微积分note Integer Multiples of Irrational Numbers 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
计量经济学代写
计量经济学是利用统计方法检验经济学理论的一种方法,它既不属于统计的范畴也不属于经济的范畴更像是一种经验科学。大家有专业的问题可以在my-assignmentexpert™ 这里答疑,多读一读,相关的基础性的东西,做一些统计和经济的基础知识的积累对于学习计量经济学这一门课程都是有很大帮助的。
统计作业代写
线性代数到底应该怎么学?
线代是一门逻辑性非常强的数学,非常注重对概念的深入理解,QS排名前200的大学普遍线性代数考试的题目80%以上都是证明题形式。而且初学的时候大家会觉得线代概念很乱很杂且环环相扣,学的时候经常要翻前面的东西。
在这种情况下,如何学好线性代数?如何保证线性代数能获得高分呢?
如何理清楚线代的概念,总结并且理解各个概念和定理之间的层次关系和逻辑关系是最关键的。具体实行方法和其他科目大同小异,书+记笔记+刷题,但这三个怎么用,在UrivatetaTA了解到的情况来说,我觉得大部分人对总结理解是不准确的,以下将说明我认为效率最高的的总结方法。
1.1 mark on book
【重点的误解】划重点不是书上粗体,更不是每个定义,线代概念这么多,很多朋友强迫症似的把每个定义整整齐齐用荧光笔标出来,然后整本书都是重点,那期末怎么复习呀。我认为需要标出的重点为
A. 不懂,或是生涩,或是不熟悉的部分。这点很重要,有的定义浅显,但证明方法很奇怪。我会将晦涩的定义,证明方法标出。在看书时,所有例题将答案遮住,自己做,卡住了就说明不熟悉这个例题的方法,也标出。
B. 老师课上总结或强调的部分。这个没啥好讲的,跟着老师走就对了
C. 你自己做题过程中,发现模糊的知识点
1.2 take note
记笔记千万不是抄书!!!我看到很多课友都是,抄老师的PPT,或者把书上的东西搬到笔记本上。有人可能觉得抄容易记起来,但数学不是背书嗷,抄一遍浪费时间且无用。我用我笔记的一小部分来说明怎么做笔记。
1.3 understand the relation between definitions
比如特征值,特征向量,不变子空间,Jordan blocks, Jordan stadard form的一堆定义和推论,看起来很难记,但搞懂他们之间的关系就很简单了
美本或者加拿大本科,如果需要期末考试之前突击线性代数,怎样可以效率最大化?
如果您是美本或者加拿大本科的学生,那么您的教材有很大概率是Sehldon Axler的linear algebra done right这本书,这本书通俗易懂的同时做到了只有300页的厚度,以几何的观点介绍了线性代数的所有基本且重要的内容.
从目录来看,这本书从linear vector space的定义讲起,引入线性代数这一主题,第二章开始将讨论范围限制在有限维的线性空间,这样做的好处是规避Zorn lemma的使用,在处理无穷维线性空间的过程中,取基不可避免的需要用到zorn lemma,第二章主要讲了independent set和basis的概念,同时引入了维数
前两章的内容可以看做是线性代数的启蒙阶段,理解了这两章就知道了线性代数研究的对象基本上是怎么回事,虽然还没有学任何non-trivial的内容,此时最重要的当然是linear vector space和independent set, basis, dimension的概念