如果你也在为遇到的matlab相关的难题发愁,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。MATLAB®将为迭代分析和设计过程而调整的桌面环境与直接表达矩阵和阵列数学的编程语言相结合。它包括用于创建脚本的实时编辑器,这些脚本将代码、输出和格式化文本结合在可执行的笔记本中。
- 专业构建
MATLAB工具箱是专业开发的,经过严格的测试,并有完整的文件记录。 - 拥有互动式应用程序
MATLAB应用程序让您看到不同的算法是如何与您的数据一起工作的。迭代直到您得到您想要的结果,然后自动生成一个MATLAB程序来重现或自动完成您的工作。 - 以及扩展的能力
只需稍加修改代码,就可以将您的分析扩展到集群、GPU和云上运行。不需要重写你的代码或学习大数据编程和内存外技术。
my-assignmentexpert™ matlab作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的matlab作业代写作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此matlab作业代写作业代写的价格不固定。通常在matlab专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在matlab作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在matlab作业代写方面经验极为丰富,各种matlab作业代写相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的matlab作业代写及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 数据分析
- 数值与符号计算
- 工程与科学绘图
- 控制系统设计
- 航天工业
- 汽车工业
- 生物医学工程
- 语音处理
运筹学代写
数学代写|matlab作业代写|Stochastic DP for Finite Time Horizons
Like other functional equations, most notably differential equations, we need boundary conditions to solve it. In our case, the natural solution process goes backward in time, starting from the terminal condition
$$
V_{T}\left(\mathbf{s}{T}\right)=F{T}\left(\mathbf{s}{T}\right) \quad \forall \mathbf{s}{T}
$$
i.e., the value of the terminal state is given by function $F_{T}(\cdot)$. If we do not assign any value to the terminal state, then $V_{T}(\cdot) \equiv 0$. This is certainly the case in deterministic problems with a fixed terminal state.
Then, we find the value function at each time instant by a recursive unfolding of Bellman’s equation. At the last decision time instant, $t=T-1$, we should solve the single-stage problem
$$
\begin{aligned}
V_{T-1}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-1}\right)=\underset{\mathbf{x}{T-1} \in \mathcal{X}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-1}\right)}{\operatorname{opt}}{& f{T-1}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-1}, \mathbf{x}{T-1}\right)+\
\left.\gamma \mathbb{E}\left[V_{T}\left(g_{T}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-1}, \mathbf{x}{T-1}, \boldsymbol{\xi}{T}\right)\right) \mid \mathbf{s}{T-1}, \mathbf{x}{T-1}\right]\right} \end{aligned} $$ for every possible state $\mathbf{s}{T-1}$. This is a static, but not myopic problem, since the terminal value function $V_{T}(\cdot)$ also accounts for the effect of the last decision $\mathbf{x}{T-1}$ on the terminal state. By solving it for every state $\mathbf{s}{T-1}$, we build the value function $V_{T-1}(\cdot)$. Then, unfolding the recursion backward in time, we find the value function $V_{T-2}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-2}\right)$, and so on, down to $V{1}\left(\mathbf{s}{1}\right)$. Finally, given the initial state $\mathbf{s}{0}$, we find the first optimal decision by solving the single-stage problem
$$
V_{0}\left(\mathbf{s}{0}\right)=\underset{\mathbf{x}{0} \in \mathcal{X}\left(\mathbf{s}{0}\right)}{\operatorname{opt}}\left{f{0}\left(\mathbf{s}{0}, \mathbf{x}{0}\right)+\gamma \mathbb{E}\left[V_{1}\left(g_{1}\left(\mathbf{s}{0}, \mathbf{x}{0}, \xi_{1}\right)\right) \mid \mathbf{s}{0}, \mathbf{x}{0}\right]\right}
$$
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|Stochastic DP for Infinite Time Horizons
The recursive form of Eq. (1.22) needs to be adjusted when coping with an infinitehorizon problem like
$$
\text { opt } \mathbb{E}\left[\sum_{t=0}^{+\infty} \gamma^{t} f\left(\mathbf{s}{t}, \mathbf{x}{t}\right)\right]
$$
where we assume that immediate costs are bounded and $\gamma<1$, so that the series converges to a finite value. ${ }^{27}$ In this case, we typically drop the subscript $t$ from the immediate contribution, as well as from the state-transition function
$$
\mathbf{s}{t+1}=g\left(\mathbf{s}{t}, \mathbf{x}{t}, \xi{t+1}\right)
$$
i.e., we assume a stationary model. An infinite-horizon model may be of interest per se , or it can be a trick to avoid the need to specify a terminal state value function. In this case, the functional equation boils down to
$$
V(\mathbf{s})=\underset{\mathbf{x} \in \mathcal{X}(\mathbf{s})}{\operatorname{opt}}{f(\mathbf{s}, \mathbf{x})+\gamma \mathbb{E}[V(g(\mathbf{s}, \mathbf{x}, \boldsymbol{\xi}))]}
$$
where $\mathcal{X}(\mathbf{s})$ is the set of feasible decisions when we are in state s. The good news is that we need only one value function, rather than a value function for each time instant. The bad news is that now we have a value function defined as the fixed point of a possibly complicated operator, as we have $V(\mathbf{s})$ on both sides of the equation. Since we cannot just unfold the recursion, as we did in the finite-horizon case, we really have to solve a true functional equation. In general, an iterative method is needed to solve Eq. (1.28). $.^{28}$
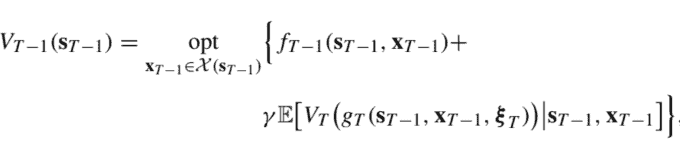
matlab代写
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|STOCHASTIC DP FOR FINITE TIME HORIZONS
与其他函数方程(尤其是微分方程)一样,我们需要边界条件来求解它。在我们的例子中,自然解过程在时间上倒退,从终止条件
$$
V_{T}\left(\mathbf{s} {T}\right)=F {T}\left(\mathbf{s } {T}\right) \quad \forall \mathbf{s} {T}
$$
即终端状态的值由函数给出F吨(⋅). 如果我们不给终端状态赋值,那么五吨(⋅)≡0. 在具有固定终端状态的确定性问题中肯定是这种情况。
然后,我们通过贝尔曼方程的递归展开找到每个时刻的价值函数。在最后的决策时刻,吨=吨−1,我们应该解决单阶段问题
for every possible state $\mathbf{s}{T-1}$. This is a static, but not myopic problem, since the terminal value function $V{T}(\cdot)$ also accounts for the effect of the last decision $\mathbf{x}{T-1}$ on the terminal state. By solving it for every state $\mathbf{s}{T-1}$, we build the value function $V_{T-1}(\cdot)$. Then, unfolding the recursion backward in time, we find the value function $V_{T-2}\left(\mathbf{s}{T-2}\right)$, and so on, down to $V{1}\left(\mathbf{s}{1}\right)$. Finally, given the initial state $\mathbf{s}{0}$, we find the first optimal decision by solving the single-stage problem
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|STOCHASTIC DP FOR INFINITE TIME HORIZONS
方程的递归形式。1.22在处理像
where we assume that immediate costs are bounded and $\gamma<1$, so that the series converges to a finite value. ${ }^{27}$ In this case, we typically drop the subscript $t$ from the immediate contribution, as well as from the state-transition function
$$
\mathbf{s}{t+1}=g\left(\mathbf{s}{t}, \mathbf{x}{t}, \xi{t+1}\right)
$$
i.e., we assume a stationary model. An infinite-horizon model may be of interest per se, or it can be a trick to avoid the need to specify a terminal state value function. In this case, the functional equation boils down to
$$
V(\mathbf{s})=\underset{\mathbf{x} \in \mathcal{X}(\mathbf{s})}{\operatorname{opt}}{f(\mathbf{s}, \mathbf{x})+\gamma \mathbb{E}[V(g(\mathbf{s}, \mathbf{x}, \boldsymbol{\xi}))]}
$$
在哪里X(s)是我们处于状态 s 时的一组可行决策。好消息是我们只需要一个价值函数,而不是每个时刻的价值函数。坏消息是,现在我们有一个价值函数定义为一个可能很复杂的运算符的不动点,因为我们有五(s)在等式的两边。由于我们不能仅仅展开递归,就像我们在有限范围的情况下所做的那样,我们真的必须求解一个真正的函数方程。一般来说,需要一种迭代方法来求解方程。1.28..28
统计代考
统计是汉语中的“统计”原有合计或汇总计算的意思。 英语中的“统计”(Statistics)一词来源于拉丁语status,是指各种现象的状态或状况。
数论代考
数论(number theory ),是纯粹数学的分支之一,主要研究整数的性质。 整数可以是方程式的解(丢番图方程)。 有些解析函数(像黎曼ζ函数)中包括了一些整数、质数的性质,透过这些函数也可以了解一些数论的问题。 透过数论也可以建立实数和有理数之间的关系,并且用有理数来逼近实数(丢番图逼近)
数值分析代考
数值分析NumericalAnalysis,又名“计算方法”,是研究分析用计算机求解数学计算问题的数值计算方法及其理论的学科。 它以数字计算机求解数学问题的理论和方法为研究对象,为计算数学的主体部分。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。