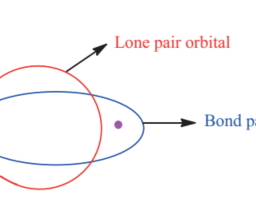
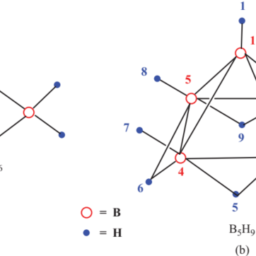
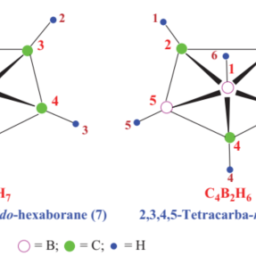
如果你也在 怎样代写无机化学inorganic chemistry这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。无机化学inorganic chemistry涉及到无机和有机金属化合物的合成和行为。这个领域涵盖了非碳基的化合物,这些化合物是有机化学的主题。这两门学科之间的区别远非绝对,因为有机金属化学的分支学科有很多重叠。它在化学工业的各个方面都有应用,包括催化、材料科学、颜料、表面活性剂、涂料、药物、燃料和农业。
无机化学inorganic chemistry许多无机化合物是离子化合物,由阳离子和阴离子通过离子键连接组成。盐(属于离子化合物)的例子有氯化镁MgCl2,它由镁的阳离子Mg2+和氯的阴离子Cl-组成;或氧化钠Na2O,它由钠的阳离子Na+和氧化阴离子O2-组成。在任何盐中,离子的比例是这样的:电荷相互抵消,因此大部分化合物是电中性的。离子由其氧化状态描述,其形成的难易程度可以从电离电位(阳离子)或从母元素的电子亲和力(阴离子)推断出来。
my-assignmentexpert™ 无机化学inorganic chemistry作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的无机化学inorganic chemistry作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此无机化学inorganic chemistry作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在化学Chemical作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的无机化学inorganic chemistry代写服务。我们的专家在化学Chemical代写方面经验极为丰富,各种无机化学inorganic chemistry相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的无机化学inorganic chemistry及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
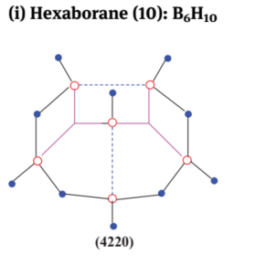
化学代写|无机化学作业代写INORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|Benzene (C6H6)
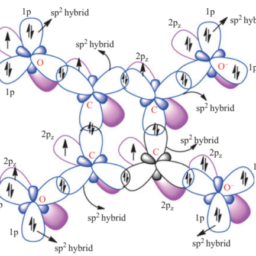
Benzene is an example of cyclic molecule. It is a regular hexagon (Figure 2.38) with bond angle of $120^{\circ}$.The hybridization scheme (Figure 2.39) shows that each carbon undergoes sp ${ }^{2}$ hybridization during the formation of molecule. The three $\mathrm{sp}^{2}$ hybrid orbitals on each carbon form $3 \sigma$ bonds, bond angle being $120^{\circ}$.
Each $\mathrm{C}$ atom is still left with a $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$-orbital $\perp \mathrm{r}$ to the plane of the benzene $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ $\sigma$-skeleton. All the $12(6 \mathrm{C}$ and $6 \mathrm{H})$ atoms are co-planar, with the same $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ bond distance of $1.39 \AA$ which is intermediate between ethylene $(1.33 \AA$ ) and ethane (1.54 $\AA$ ).
The formation of delocalized $\pi$-bonding in benzene can be understood as follows:
(i) Total skeleton electrons in benzene involved in $\sigma$ – and $\pi$-bonding apart from C-H $\sigma$-bonds $=6 \times 4-6=18 \mathrm{e}$.(ii) The six $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals (one on each C) interact to give $6 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs, three bonding and three anti-bonding. The six different modes of combination of $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals giving $6 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$
(iii) It is notable that the $+$ and – sign in Figure $2.40$ denote the signs of the top lobes of various $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals involved. (iv) The six $\pi$-electrons of the molecules go to occupy three bonding orbitals $\pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs $\left(\boldsymbol{\pi}{\mathbf{D} 1}, \boldsymbol{\pi}{\mathbf{D} 2}\right.$ and $\pi_{\mathrm{D} 3}$ ) while antibonding MOs $\pi_{\mathbf{D} 4}, \pi_{\mathrm{D} 5}$ and $\boldsymbol{\pi}_{\mathrm{D} 6}$ remain vacant. $\sigma \mathrm{L}^{\star}$ also remain vacant.
化学代写|无机化学作业代写inorganic chemistry代考|Cyclopentadienyl radical (C5H5·)
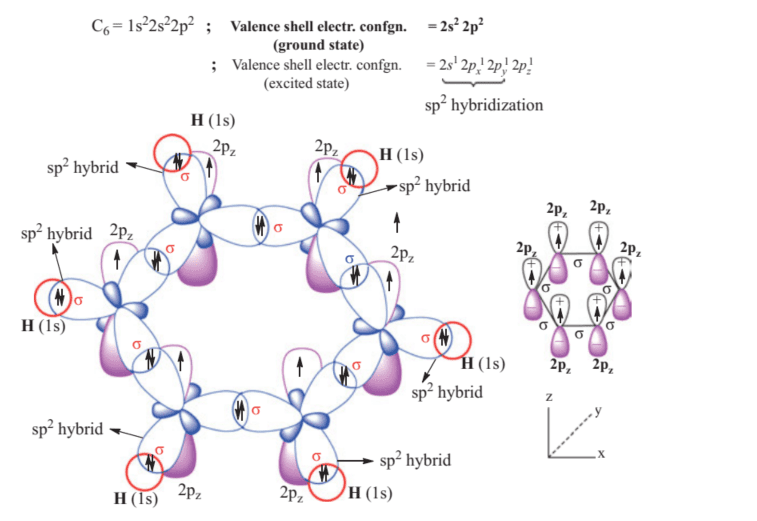
It is a regular pentagon with bond angle of $120^{\circ}$ (Figure $2.42$ ). Similar to benzene, the MO treatment of this radical envisages/considers that each carbon undergoes $\mathrm{sp}^{2}$ hybridization during its formation. The five $\mathrm{sp}^{2}$ hybrid orbitals on each carbon form $5 \sigma$ bonds, bond angle being $120^{\circ}$. However, each $C$ atom is still left with a $2 \mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$-orbital $\perp \mathrm{r}$ to the plane of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C} \sigma$-skeleton (Figure $\left.2.43\right)$. All the $10(5 \mathrm{C}$ and $5 \mathrm{H})$ atoms are co-planar, with the same $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ bond distance of $1.39 \AA$ which is intermediate between ethylene ( $1.33 \AA$ ) and ethane (1.54 A).
The formation of delocalized $\pi$-bonding in cyclopentadienyl radical can be understood as follows:
(v) Total skeleton electrons in $\mathrm{C}{5} \mathrm{H}{5}$ radical involved in $\sigma$ – and $\pi$-bonding apart from $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \sigma$-bonds $=5 \times 4-5=15 \mathrm{e}$.
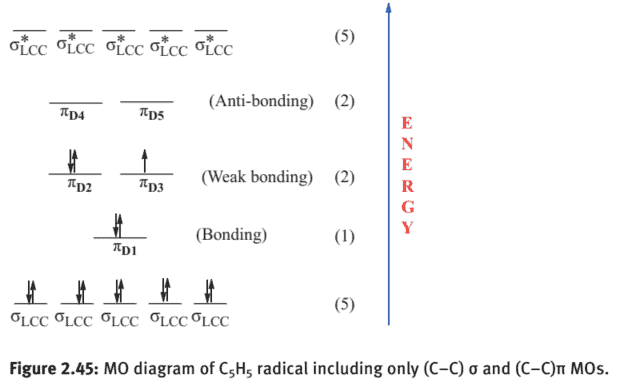
(vi) The five $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals (one on each $\mathrm{C}$ ) interact to give $5 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs., three bonding and 2 anti-bonding. The five different modes of combination of $2 \mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals giving $5 \pi \mathrm{D}$ MOs can be viewed as shown in Figure $2.44$.
C-C bond order in $\mathrm{C}{5} \mathrm{H}{5}$ radical
Bond order of C-C bond
$$
\begin{aligned}
&=\frac{\text { No. of bonding electrons }(\sigma+\pi, \text { both })-\text { No. of antibonding electrons }}{2 \times \text { No. of bonding centres }} \
&=\frac{{10(\sigma)+5(\pi)}}{2 \times 5}=\frac{15}{10} \
&=1.5
\end{aligned}
$$
Thus, in cyclopentadienyl radical, the $C-C$ bond is neither one nor two. In fact, there are five $\sigma$-bonds and five $\pi$-electrons $(2.5 \pi$-bonds), which are delocalized over all the five $\sigma$-bonds. Hence, the bond order of $C-C$ is $1.5$.
无机化学代写
化学代写|无机化学作业代写INORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|BENZENEC6H6
苯是环状分子的一个例子。它是一个正六边形F一世G你r和2.38与键角120∘.杂交方案F一世G你r和2.39表明每个碳经历 sp2分子形成过程中的杂交。他们三个sp2每个碳形式上的杂化轨道3σ键,键角为120∘.
每个C原子仍然留下一个p和-轨道⊥r到苯的平面C−C σ-骨骼。一切12(6C和6H)原子是共面的,具有相同的C−C键距1.39\AA介于乙烯之间(1.33\AA) 和乙烷1.54$\AA$.
离域的形成圆周率苯中的-键合可以理解如下:
Each $\mathrm{C}$ atom is still left with a $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$-orbital $\perp \mathrm{r}$ to the plane of the benzene $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ $\sigma$-skeleton. All the $12(6 \mathrm{C}$ and $6 \mathrm{H})$ atoms are co-planar, with the same $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ bond distance of $1.39 \AA$ which is intermediate between ethylene $(1.33 \AA$ ) and ethane (1.54 $\AA$ ).
The formation of delocalized $\pi$-bonding in benzene can be understood as follows:
(i) Total skeleton electrons in benzene involved in $\sigma$ – and $\pi$-bonding apart from C-H $\sigma$-bonds $=6 \times 4-6=18 \mathrm{e}$.(ii) The six $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals (one on each C) interact to give $6 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs, three bonding and three anti-bonding. The six different modes of combination of $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals giving $6 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$
(iii) It is notable that the $+$ and – sign in Figure $2.40$ denote the signs of the top lobes of various $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals involved. (iv) The six $\pi$-electrons of the molecules go to occupy three bonding orbitals $\pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs $\left(\boldsymbol{\pi}{\mathbf{D} 1}, \boldsymbol{\pi}{\mathbf{D} 2}\right.$ and $\pi_{\mathrm{D} 3}$ ) while antibonding MOs $\pi_{\mathbf{D} 4}, \pi_{\mathrm{D} 5}$ and $\boldsymbol{\pi}_{\mathrm{D} 6}$ remain vacant. $\sigma \mathrm{L}^{\star}$也保持空缺。
化学代写|无机化学作业代写INORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|CYCLOPENTADIENYL RADICALC5H5·
它是一个正五边形,键角为120∘ $120^{\circ}$ (Figure $2.42$ ). Similar to benzene, the MO treatment of this radical envisages/considers that each carbon undergoes $\mathrm{sp}^{2}$ hybridization during its formation. The five $\mathrm{sp}^{2}$ hybrid orbitals on each carbon form $5 \sigma$ bonds, bond angle being $120^{\circ}$. However, each $C$ atom is still left with a $2 \mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$-orbital $\perp \mathrm{r}$ to the plane of $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C} \sigma$-skeleton (Figure $\left.2.43\right)$. All the $10(5 \mathrm{C}$ and $5 \mathrm{H})$ atoms are co-planar, with the same $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C}$ bond distance of $1.39 \AA$ which is intermediate between ethylene ( $1.33 \AA$ ) and ethane (1.54 A)
离域的形成圆周率-环戊二烯基中的键合可以理解如下:
(v) Total skeleton electrons in $\mathrm{C}{5} \mathrm{H}{5}$ radical involved in $\sigma$ – and $\pi$-bonding apart from $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H} \sigma$-bonds $=5 \times 4-5=15 \mathrm{e}$.
(vi) The five $2 \mathrm{p}{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals (one on each $\mathrm{C}$ ) interact to give $5 \pi{\mathrm{D}}$ MOs., three bonding and 2 anti-bonding. The five different modes of combination of $2 \mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{z}}$ orbitals giving $5 \pi \mathrm{D}$ MOs can be viewed as shown in Figure $2.44$.
C-C bond order in $\mathrm{C}{5} \mathrm{H}{5}$ radical
Bond order of C-C bond
$$
\begin{aligned}
&=\frac{\text { No. of bonding electrons }(\sigma+\pi, \text { both })-\text { No. of antibonding electrons }}{2 \times \text { No. of bonding centres }} \
&=\frac{{10(\sigma)+5(\pi)}}{2 \times 5}=\frac{15}{10} \
&=1.5
\end{aligned}
$$
Thus, in cyclopentadienyl radical, the $C-C$ bond is neither one nor two. In fact, there are five $\sigma$-bonds and five $\pi$-electrons $(2.5 \pi$-bonds), which are delocalized over all the five $\sigma$-bonds. Hence, the bond order of $C-C$ is $1.5$.

物化学代写|无机化学作业代写inorganic chemistry代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。