如果你也在 怎样代写电路设计Intro to circuit design这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。电路设计Intro to circuit design一个简单的电路由电阻器、电容器、电感器、晶体管、二极管和集成电路组成。这些基本的电子元件是由导电线连接的。电流可以很容易地在这些导线之间流动,以便使电子元件处于工作状态。
电路设计Intro to circuit design过程从规格书开始,规格书说明了成品设计必须提供的功能,但没有指出如何实现这些功能。最初的规格书基本上是对客户希望成品电路实现的技术上的详细描述,可以包括各种电气要求,如电路将接收什么信号,必须输出什么信号,有什么电源,允许消耗多少功率。规格书还可以(通常也是如此)设定设计必须满足的一些物理参数,如尺寸、重量、防潮性、温度范围、热输出、振动容限和加速度容限等。
my-assignmentexpert™ 电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在电子工程Electrical Engineering作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的电子工程Electrical Engineering代写服务。我们的专家在电路设计Intro to circuit design代写方面经验极为丰富,各种电路设计Intro to circuit design相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的电路设计Intro to circuit design及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考|Training
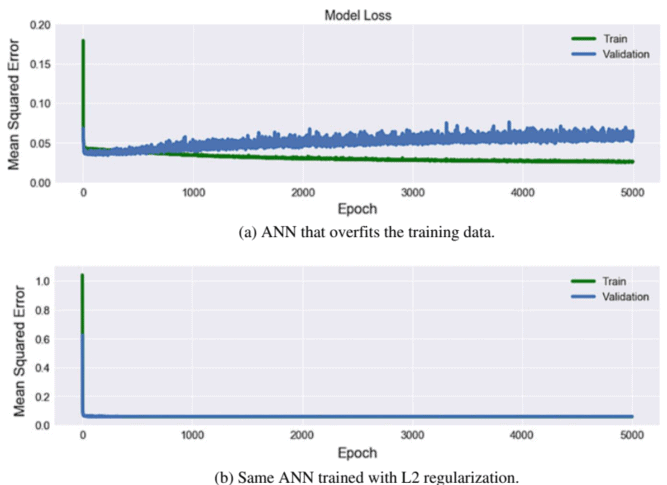
When training a supervised learning model, the main goal is to achieve an optimal generalization of unseen data. When a model achieves low error on training data but performs much worse on test data, we say that the model has overfit. This means that the model has caught very specific features of the training data, but did not really learn the general patterns. The best way to evaluate this behavior is through error analysis.
Test error is also commonly referred to as generalization error because it reflects the error of the model when generalized to previously unseen data. When we have simple models and abundant data, we expect the generalization error to resemble the training error. When we work with more complex models and fewer examples, we expect the training error to go down but the generalization gap to grow. Some factors that may affect generalization error are: the number of hyper-parameters, the values taken by them, and the number of training examples.
Model complexity is governed by many factors, and its definition is not straightforward. For example, a model with more parameters might be considered more complex. A model whose parameters can take a wider range of values might be more complex. Often with neural networks, it is common to think of a model that takes more training steps as more complex, and one subject to early stopping as less complex. Complexity is no exact science, though, but it can be loosely defined by models that can readily explain arbitrary facts, whereas models that only have a limited expressive power but still manage to explain the data well are probably closer to the truth.
$L_{2}$ regularization was used in the models proposed in this chapter, as seen in (4.6). This is a technique that helps overcoming overfitting and is a regularization term that is added to the loss function in order to prevent coefficients to fit perfectly and undergeneralize.
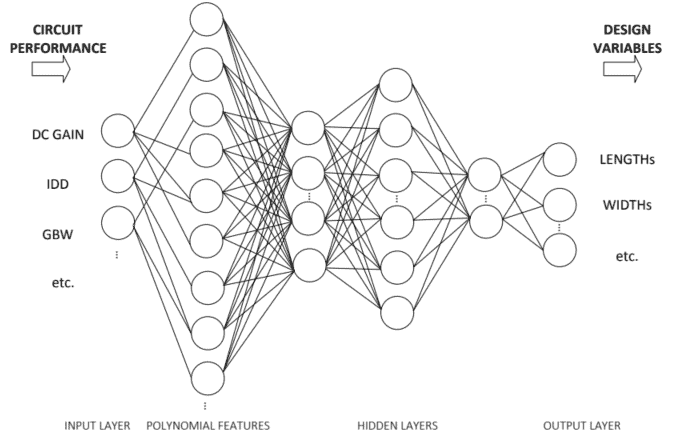
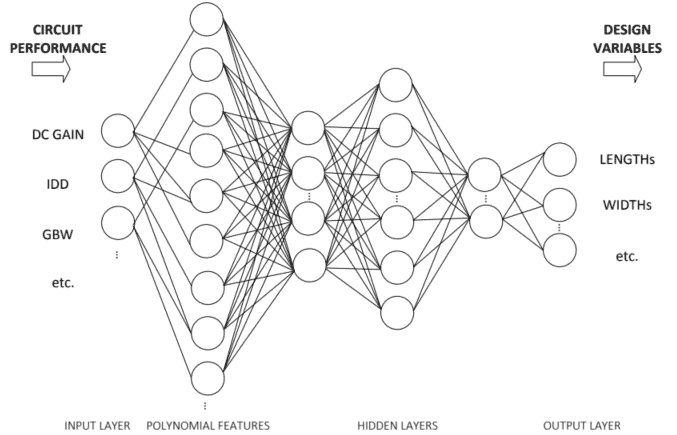
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考|Using the ANN for Circuit Sizing
Obtaining a sized circuit from the ANN is done using (4.3) $P$ times, with $\Gamma$ replaced by $-\Gamma$; i.e., we ask the model to predict a set of $P$ sizing solutions for target circuit performances that are better than the desired specifications. In case not all performance figures used to train the model are specified, then the corresponding component in the diagonal random matrix $\Delta$ should be a random value in the range of $[-1,1]$. For instance, if the target specifications are gain bandwidth product (GBW) over $30 \mathrm{MHz}$ and current consumption (IDD) under $300 \mu \mathrm{A}$, and the model was trained with DC gain, GBW, and IDD. A set of circuit performances given to the ANN could be, e.g., ${(50 \mathrm{~dB}, 35 \mathrm{MHz}, 290 \mu \mathrm{A}),(75 \mathrm{~dB}, 30 \mathrm{MHz}, 285 \mu \mathrm{A}),(60 \mathrm{~dB}, 37 \mathrm{MHz}, 250 \mu \mathrm{A})$, $\ldots(90 \mathrm{~dB}, 39 \mathrm{MHz}, 210 \mu \mathrm{A})}$.
The reasoning behind this sampling is that even if the ANN has properly learned the designs patterns present in the performances of the sizing solutions in the training data, when the performance trade-off implied by the target specifications being requested is not from the same distribution than the training data, the prediction of the ANN can be strongly and badly biased. While using the augmented dataset described in Sect. $4.2$ alleviates this bias, it is still better to sample the ANN this way. Another reason for this sampling is that a given set of predictions might not be accurate enough for some devices’ sizes. Specific values of design variables from the sizing output might be very far from the ones desired, and sampling is a good way to circumvent this problem.
The selection of solutions from the $P$ predictions of the ANN is done by simulating the predicted circuit sizing, and either: use a single value metric such as some figureof-merit (FoM) to select the most suitable solution or using some sort of Pareto dominance to present a set of solutions exploring the trade-off between specifications.
电路设计作业代写
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|TRAINING
在训练监督学习模型时,主要目标是实现未见数据的最佳泛化。当一个模型在训练数据上实现了低误差但在测试数据上表现更差时,我们说该模型有过拟合。这意味着该模型已经捕获了训练数据的非常具体的特征,但并没有真正学习到一般模式。评估此行为的最佳方法是通过错误分析。
测试误差通常也称为泛化误差,因为它反映了模型在泛化到以前看不见的数据时的误差。当我们有简单的模型和丰富的数据时,我们期望泛化误差类似于训练误差。当我们使用更复杂的模型和更少的示例时,我们预计训练误差会下降,但泛化差距会扩大。可能影响泛化误差的一些因素是:超参数的数量、它们所取的值以及训练示例的数量。
模型复杂性受许多因素控制,其定义并不简单。例如,具有更多参数的模型可能被认为更复杂。参数可以采用更广泛值的模型可能更复杂。通常对于神经网络,通常认为需要更多训练步骤的模型更复杂,而需要提前停止的模型不太复杂。然而,复杂性并不是一门精确的科学,但它可以通过可以轻松解释任意事实的模型进行松散定义,而表达能力有限但仍能很好地解释数据的模型可能更接近事实。
大号2本章提出的模型中使用了正则化,如4.6. 这是一种有助于克服过度拟合的技术,并且是添加到损失函数中的正则化项,以防止系数完美拟合和泛化不足。
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|USING THE ANN FOR CIRCUIT SIZING
从 ANN 获得一个大小的电路是使用4.3 磷次,与Γ取而代之−Γ; 即,我们要求模型预测一组磷为优于所需规格的目标电路性能确定尺寸解决方案。如果未指定用于训练模型的所有性能数据,则对角随机矩阵中的相应分量Δ应该是范围内的随机值[−1,1]. 例如,如果目标规格是增益带宽积G乙在超过30米H和和电流消耗一世DD在下面300μ一种, 模型使用 DC 增益、GBW 和 IDD 进行训练。赋予 ANN 的一组电路性能可以是,例如,(50 d乙,35米H和,290μ一种),(75 d乙,30米H和,285μ一种),(60 d乙,37米H和,250μ一种)$,$…(90 d乙,39米H和,210μ一种).
这种抽样背后的原因是,即使人工神经网络已经正确地学习了训练数据中尺寸解决方案的性能中存在的设计模式,当所请求的目标规范所暗示的性能折衷不是来自相同的分布时,在训练数据中,ANN 的预测可能会出现强烈和严重的偏差。在使用 Sect 中描述的增强数据集时。4.2减轻这种偏差,最好以这种方式对 ANN 进行采样。此采样的另一个原因是,对于某些设备的尺寸,一组给定的预测可能不够准确。尺寸输出中设计变量的具体值可能与期望值相差甚远,抽样是规避此问题的好方法。
从解决方案的选择磷ANN 的预测是通过模拟预测的电路尺寸来完成的,或者:使用单值度量,例如一些品质因数F这米选择最合适的解决方案或使用某种帕累托优势来呈现一组解决方案,探索规范之间的权衡。

电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。