如果你也在 怎样代写r语言r project这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。r语言r projectR是一种用于统计计算和图形的编程语言,由R核心团队和R统计计算基金会支持。R由统计学家Ross Ihaka和Robert Gentleman创建,在数据挖掘者和统计学家中被用于数据分析和开发统计软件。用户已经创建了软件包来增强R语言的功能。根据用户调查和对学术文献数据库的研究,R是数据挖掘中最常用的编程语言之一。截至2022年3月,R在衡量编程语言普及程度的TIOBE指数中排名第11位。
r语言r project官方的R软件环境是GNU软件包中的一个开源自由软件环境,在GNU通用公共许可证下提供。它主要是用C、Fortran和R本身(部分自我托管)编写的。预编译的可执行文件提供给各种操作系统。R有一个命令行界面。也有多个第三方图形用户界面,如RStudio,一个集成开发环境,和Jupyter,一个笔记本界面。
my-assignmentexpert™r语言r projects作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的r语言r project作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此r语言r project作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在统计Statistics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在r语言r project代写方面经验极为丰富,各种r语言r project相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的r语言r project及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
统计代写|r语言代考r project代写|Conceptual Preparation
Logic of Statistical Inference
The main use of statistical modeling is to help us answer substantive research questions by making statistical inferences regarding a population of subjects through the use of sample data. The notion of population refers to the universe of all subjects of interest to an analyst, and sample refers to a subset, ideally a randomly selected subset, of the population. When it is not feasible to collect data on the whole population of interest, statistical inference based on sample information becomes necessary. In a nutshell, we use sample data to compute sample statistics in order to estimate the attributes or parameters of the population and then draw inferences about them in a probabilistic manner.
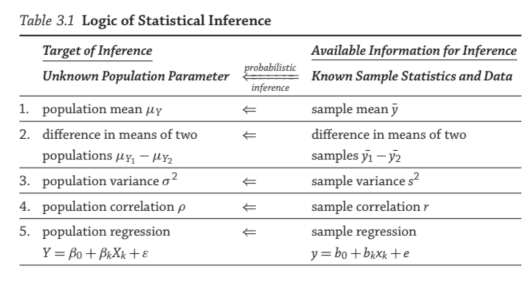
What population attributes are we interested in? Table $3.1$ illustrates some population parameters one could estimate and draw inferences about via corresponding sample statistics. In this chapter, we will study how to make inferences about a population mean and the difference between the population means of two groups; in the next chapters, we will learn about population correlation and regression coefficient.
Statistical inference informs us about population attributes based on sample data. That is, it informs us about the likelihood of sample statistics capturing population parameters. In other words, we use available sample information in the right column of Table $3.1$ to guess unknown population attributes, referred to as parameters, in the left column of Table $3.1$, in a probabilistic manner. The validity of statistical inference depends on whether a sample is randomly drawn from a population and whether the relevant assumptions about sample statistics and population parameters are satisfied.
统计代写|r语言代考r project代写|Two Methods of Statistical Inference
We often use two methods to make statistical inferences from known sample information to unknown population parameters. The first method is to test a hypothesis regarding a hypothetical population parameter value in a probabilistic manner, and the second method involves constructing a confidence interval around the sample estimate to make a probabilistic prediction about an unknown population parameter. Hence, the two inferential methods are related but distinct.
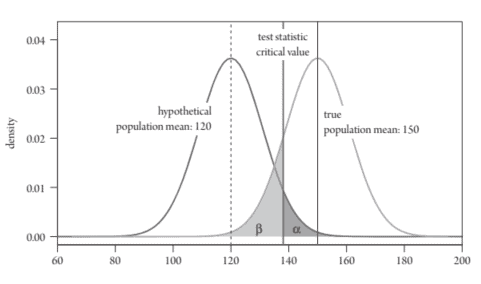
Here we illustrate their conceptual differences and related concepts using an example, leaving more technical details for later sections. Assume a student named Joe, who is contemplating whether to take an introductory statistics course STAT101, is interested in the average student grade in this course to aid his decision. Also assume that on a $0-200$ grading scale, the average course grade has a true population mean of 150 (just above C) and population standard deviation of 11 , both of which are unknown to Joe. Since Joe does not have information on the grades of all students in the universe of past and future STAT101 classes, he cannot compute the true population average grade and thus, does not know it is 150 . Joe, however, would like to know what the population average grade might be, based on some sample information. The undergraduate advisor in the department draws a random sample of 45 students based on records of past STAT101 classes and tells Joe that the sample has an average of 140 and standard deviation of 12 . How can Joe use the available information to make an educated guess, or rather statistical inference, about the population average grade in STAT101?
In Joe’s case, the task of statistical inference is to use the sample information (e.g., sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size) to infer about the population mean in a probabilistic manner. To make a long story short, the conceptual or mathematical foundation of Joe’s inference is as follows. If resources permit us to collect repeated random samples from past records and obtain as many mean values as the number of samples, then we will find the following pattern: if the sample size is large enough, the plot of the many sample means follows a bell-shaped normal distribution curve, with the mean of the many sample means coinciding with the true population mean. This bell-shaped normal distribution curve is the probability distribution of the sample mean, which is called the sampling distribution of the sample mean. The property that if the sample size is large enough, the sampling distribution of the sample mean is approximately normal can be demonstrated mathematically. This property allows us to conduct hypothesis testing and construct a confidence interval about the population mean in a probabilistic manner. So even if Joe cannot obtain repeated samples himself, he can use the one sample provided by the advisor and the property of the sampling distribution of the sample mean to make statistical inferences.
统计代写|R语言代考R PROJECT代写|Data Preparation
For data preparation, we should have completed the following tasks:
- Clean the workspace in $\mathrm{R}$ by removing all objects.
- Create a project folder to hold the original Penn World Table data, program, and output files.
- Create a well-documented R program to read the original dataset into $R$.
- Inspect imported data to make sure the original data is imported into $R$ properly.
- Clean possible data problems.
- Create a new dataset using a subset of the original dataset.
- Create new variables for later use.
- Install add-on packages needed.
Using what we learned in the previous two chapters, we must first use $R$ to clean the workspace, set up our project folder, read data into $\mathrm{R}$, inspect and clean imported data, install and load packages needed in this chapter, and prepare the data for analysis. All the tasks conducted below and related $R$ code have been covered in the previous chapter. This chapter will use the following add-on packages: DataCombine, ggplot2, Rmisc, and stargazer; readers should use install. packages (“DataCombine”), for example, to install these packages for once first. At the end of data preparation, we will have saved the cleaned dataset into a new $\mathrm{R}$ dataset “pwt7g” in the project folder.
R语言代写
统计代写|R语言代考R PROJECT代写|CONCEPTUAL PREPARATION
统计推断的逻辑
统计建模的主要用途是通过使用样本数据对受试者群体进行统计推断,从而帮助我们回答实质性研究问题。总体的概念是指分析师感兴趣的所有对象的宇宙,样本是指总体的子集,理想情况下是随机选择的子集。当收集整个感兴趣人群的数据不可行时,基于样本信息的统计推断变得必要。简而言之,我们使用样本数据来计算样本统计量,以估计总体的属性或参数,然后以概率的方式对其进行推断。
我们对哪些人口属性感兴趣?桌子3.1说明了一些人口参数,人们可以通过相应的样本统计数据来估计和推断。在本章中,我们将研究如何推断总体均值以及两组总体均值之间的差异;在接下来的章节中,我们将学习人口相关性和回归系数。
统计推断告诉我们基于样本数据的人口属性。也就是说,它告诉我们样本统计数据捕获总体参数的可能性。换句话说,我们使用表格右栏中的可用样本信息3.1猜测未知的人口属性,称为参数,在表的左列3.1,以概率的方式。统计推断的有效性取决于样本是否是从总体中随机抽取的,以及是否满足样本统计量和总体参数的相关假设。
统计代写|R语言代考R PROJECT代写|TWO METHODS OF STATISTICAL INFERENCE
我们经常使用两种方法从已知样本信息到未知总体参数进行统计推断。第一种方法是以概率方式检验关于假设总体参数值的假设,第二种方法涉及围绕样本估计构建置信区间,以对未知总体参数进行概率预测。因此,这两种推理方法是相关的,但又是不同的。
在这里,我们通过一个示例来说明它们的概念差异和相关概念,将更多技术细节留给后面的部分。假设一个名叫乔的学生正在考虑是否参加统计入门课程 STAT101,他对这门课程的学生平均成绩感兴趣,以帮助他做出决定。还假设在0−200评分标准,平均课程成绩的真实人口平均值为 150j在s吨一种b这在和C和 11 的总体标准差,乔不知道这两者。由于 Joe 没有过去和未来 STAT101 班级中所有学生的成绩信息,因此他无法计算真实的总体平均成绩,因此不知道它是 150 。然而,Joe 想根据一些样本信息了解总体平均成绩可能是多少。该系的本科生导师根据过去 STAT101 课程的记录随机抽取 45 名学生样本,并告诉 Joe 该样本的平均值为 140 ,标准差为 12 。Joe 如何使用可用信息对 STAT101 中的总体平均成绩做出有根据的猜测,或者更确切地说是统计推断?
在 Joe 的案例中,统计推断的任务是使用样本信息和.G.,s一种米pl和米和一种n,s一种米pl和s吨一种nd一种rdd和在一世一种吨一世这n,一种nds一种米pl和s一世和和以概率的方式推断总体均值。长话短说,Joe 推理的概念或数学基础如下。如果资源允许我们从过去的记录中收集重复的随机样本并获得与样本数量一样多的平均值,那么我们将发现以下模式:如果样本量足够大,则多样本均值的图呈钟形形正态分布曲线,多个样本均值的均值与真实总体均值一致。这条钟形的正态分布曲线就是样本均值的概率分布,称为样本均值的抽样分布。如果样本量足够大,样本均值的抽样分布近似正态分布的性质可以用数学来证明。该属性使我们能够进行假设检验并以概率方式构建关于总体均值的置信区间。所以即使 Joe 自己无法获得重复样本,他也可以利用 Advisor 提供的一个样本以及样本均值的抽样分布的性质进行统计推断。
统计代写|R语言代考R PROJECT代写|DATA PREPARATION
对于数据准备,我们应该完成以下任务:
- 清洁工作区R通过删除所有对象。
- 创建一个项目文件夹来保存原始的 Penn World Table 数据、程序和输出文件。
- 创建一个有据可查的 R 程序以将原始数据集读入R.
- 检查导入的数据以确保将原始数据导入R适当地。
- 清理可能的数据问题。
- 使用原始数据集的子集创建新数据集。
- 创建新变量以供以后使用。
- 安装所需的附加包。
使用我们在前两章中学到的东西,我们必须首先使用R清理工作区,设置我们的项目文件夹,将数据读入R,检查和清理导入的数据,安装和加载本章需要的包,并准备数据进行分析。以下和相关的所有任务R代码在上一章已经讲过了。本章将使用以下附加包:DataCombine、ggplot2、Rmisc 和 stargazer;读者应该使用安装。包“D一种吨一种C这米b一世n和”,例如,首先安装这些软件包一次。在数据准备结束时,我们会将清理后的数据集保存到一个新的R项目文件夹中的数据集“pwt7g”。

统计代写|r语言代考r project代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

