如果你也在 怎样代写multi-level modeling:nested这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。multi-level modeling:nested多层次模型(也称为分层线性模型、线性混合效应模型、混合模型、嵌套数据模型、随机系数、随机效应模型、随机参数模型或分割图设计)是在一个以上层次上变化的参数的统计模型。这些模型可以被看作是线性模型(尤其是线性回归)的概括,尽管它们也可以扩展到非线性模型。在有了足够的计算能力和软件之后,这些模型变得更加流行了。
multi-level modeling:nested多层次模型特别适合于研究设计,即参与者的数据被组织在一个以上的层次(即嵌套数据)。分析单位通常是个人(较低层次),他们被嵌套在背景/总体单位(较高层次)中。虽然多层次模型中最低层次的数据通常是个人,但也可以研究个人的重复测量。因此,多层次模型为重复测量的单变量或多变量分析提供一种替代的分析类型。此外,多水平模型还可以用来替代方差分析,在方差分析中,因变量的分数在测试处理差异之前会根据协变量(如个体差异)进行调整。多水平模型能够分析这些实验,而不需要方差分析所要求的回归斜率的同质性假设。
my-assignmentexpert™multi-level modeling:nested作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的multi-level modeling:nested作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此multi-level modeling:nested作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在multi-level modeling:nested代写方面经验极为丰富,各种multi-level modeling:nested相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的multi-level modeling:nested及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考|Semantic Closure
Closure concepts play a prominent role in systems theory where may be used to identify or define the whole system in correlation with its environment and to allow the autonomy of the systems.
Significant is the relation between self-adaptivity, cognitivity, intelligence and different notions of closure as encountered in systems theory: closure to efficient cause (Rosen 1991), organizational closure (Maturana and Varela 1992), catalytic closure (Kauffman S. 1993), semantic closure (Pattee 1995), and operational closure (Luhmann 1995).
These definitions refer to different facets of complexity.
For example, a system is considered catalitically closed just in case every product of the system is also a catalyst in the system (Kauffman S. 1993).
Closure does not mean that the considered system is not in contact with its environment or with other systems. Rather the term closure refers to the closed loop which connects the whole structures and the functions of individual, elementary entities or levels.
In a significant investigation of closure applicable to both real and artificial life, Pattee pointed out that the complex evolutions, requires a two-level complementary description of the material and symbolic aspects of events (Pattee 1995,2000 ). Life involves a semantically closed organization between symbolic records and dynamical constraints. Symbols, as discrete functional switchingstates, are seen in all evolvable systems in form of codes, and at the core of all neural systems in the form of informational mechanisms that switch behavior. Symbolic information as that contained in genotype has no intrinsic meaning outside the context of an entire symbol systems as well as the material organization that interprets the symbol for a specific function such as construction, classification control and communication. Self-reference that has evolvability potential is an autonomous closure between the dynamics-physical laws of the material aspects and the constraints-syntactic rules of the symbolic aspects of a physical organization. Pattee refers to this condition as “semantic closure” or more recently as “semiotic closure” (Rocha 2001). Semantic closure requires a separate symbolic description (genotype, design, and software) and material embodiment (phenotype, machine, and computer). The symbolic description must be capable of generating the material embodiment. Finally, the material embodiment must be capable of re-generating the symbolic description with the possibility of mutation. Cariani $(1989,2001)$ evaluated the semantic closure principle relation with the design of devices with emergent semantic functions. Self-modification and selfconstruction of own categories were recognized as important to the symbol-matter problem and as a requirement for semantically adaptive devices or evolvable ones. Temporal codes and neural pulse codes that use the time patterns of spikes to encode information appeared as potential tool for evolvable devices and for brain study.
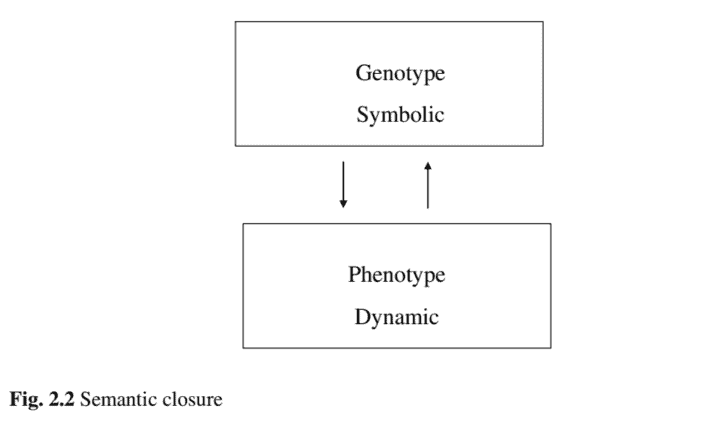
Fig. $2.2$ illustrates the concept of semantic closure for genetic systems. Two levels are considered, the genotype and the phenotype. The genotype initiates the dynamics, while the phenotype is developed by genome iterated dynamics. The environment determines the stability and reproductive activity of the genome.
In model categorification terms, the symbolic system is at a higher level category relative to the dynamic system. The model for symbols involves “other than real”, that is “non-standard” fields.
数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考|Two Levels Modeling
The transition from one level to multiple level modeling appears to be simple, in principle.
To describe evolution in emergent hierarchical systems, one replaces the parameters of the accepted models or theorems for “real” field systems by the “non-standard” field counterparts, and one sees at least in some cases meaningful general models, and true statements for the emergent complex systems that results.
Fig. $2.3$ shows a two-levels architecture. Notice that the two levels are supposed to have different categorical organization. In some cases there appear discrepancies and this is the indication of significantly new phenomena.
In a more general context this is the general problem of closure between the experiment and theory in scientific or engineering modeling. One considers as a natural approach in science or engineering, to start from phenomena to which one may associate formal mathematical frames. Then, the predictions are tested empirically. It is a succession of theoretical and testing steps. The evolution back and forth between models and testing results, changing things on the one side and checking the effect on the other side, forms the basis of science and engineering methods. It may be a difference in language, that is in the algebraic frames for modeling and testing models and this represent one of the challenges for closure.
The closure between experiment and theory for scientific and engineering modeling may appears as the closure of “real” field relative to “other than real” fields for models or theorems. The closure request is the need for both types of models to have a complete view for emergent complexity.
One has to make additional modifications and reinterpretations to obtain physically and mathematically adequate complete or semantically closed theories.
Required by closure methodology is an analysis involving both real-valued and “other than real” valued functions. This explains the fact that, during the PSM study, both the real valued probabilities and “other than real” that is “nonstandard” probabilities continue to be associated. The attention was focused on problems not on purity of methods, surely inappropriate to the objective of study, the emergence of multi-level complexity. It should be a clear cut between mathematical frames for different categories but the natural complexity has neither pure real, nor pure “other than real” fabric. Understanding complexity should involve, real frames interacting with “other than real” ones, at different levels not privileging any one in particular.
One might ask why to support non-standard or categorification frames in the study of complexity. After all there are numerous studies of complexity that make use of real field analysis only. The involvement of non-standard and higher categories frame in PSM is not motivated by the tendency to construct unusual frames that may appears to a certain extent novel and unexpected as theories, but is imposed by the PSM objective to understand and built evolvable systems that is systems that go beyond the learning and adaptability level and may be evolvable and capable to take autonomous and creative control of their environment. The semantic advantage of making use of “other than real” frames, of higher categories in close relation with real ones is the decisive enhancement for multilevel system responsiveness, evolvability and autonomy.
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|Integrative Closure
Integrative closure appeared as the direct consequence of mutual restrictedness or exclusiveness of the new levels relative to the previous ones, and of the finite number of levels to be considered. Integrative closure approach is not looking for an identity between the philosophical and mathematical categorical viewpoints but for a structural analogy and a general methodology shared by different domains as knowledge organization, ontological problem solving or technological developments (Iordache 2010).
Significant examples of structural analogy, parallelism and recapitulation in the field of mathematics and physics have been presented by Piaget and Garcia (1989).
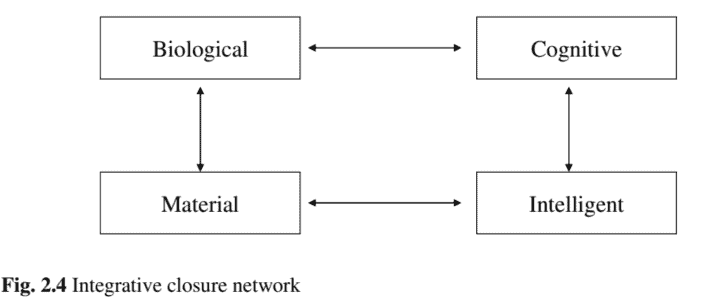
The starting idea for integrative closure was to reconsider the interrelated four main ontological levels in the study of nature: “material”, “biological”, “cognitive or psychological” and “intelligent or logical” (Hartmann 1952).
It was acknowledged that the hierarchical structures cannot serve as general models for multi-level knowledge organization. Facing complexity the task of knowledge integration remains pertinent.
Fig. $2.4$ shows an actualization of the integrative closure hypothesis as a network version of Hartmann’s four levels ontological hierarchy. The traditional hierarchical structure is closed and replaced by a network.
The integrative closure aims to make ends meets, for the four levels or realms, emphasizing the hypothetical interconnection between the Hartmann’s material and intelligent realms. An artificially or naturally evolvable system is supposed to cross the gap between these two levels.
Observe that a two-level modeling relation between material and intelligent realms could accomplish this closure task directly. For integrative closure the objective is not to reduce several interconnection steps to two-level interactions, as an attempt to achieve closure in the speediest manner. Contrary to these, integrative closure looks to the four interactions steps to facilitate the study and to take into account the necessary basic ingredients, as followed by the evolvable systems existing in nature.
多层线性模型代写
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|SEMANTIC CLOSURE
闭包概念在系统理论中发挥着重要作用,可用于识别或定义与其环境相关的整个系统并允许系统自治。
重要的是自适应性、认知性、智力和系统理论中遇到的不同闭合概念之间的关系:对有效原因的闭合R这s和n1991, 组织关闭米一种吨在r一种n一种一种nd在一种r和l一种1992, 催化关闭ķ一种在FF米一种n小号.1993, 语义闭包磷一种吨吨和和1995, 和操作关闭大号在H米一种nn1995.
这些定义涉及复杂性的不同方面。
例如,一个系统被认为是催化封闭的,以防系统的每个产品也是系统中的催化剂ķ一种在FF米一种n小号.1993.
关闭并不意味着所考虑的系统不与其环境或其他系统接触。相反,术语闭合指的是连接整个结构和单个基本实体或级别的功能的闭环。
在对适用于真实生命和人造生命的封闭的重要调查中,帕蒂指出,复杂的演化需要对事件的物质和象征方面进行两级互补描述磷一种吨吨和和1995,2000. 生活涉及符号记录和动态约束之间的语义封闭组织。符号作为离散的功能切换状态,以代码的形式出现在所有可进化的系统中,并以切换行为的信息机制的形式出现在所有神经系统的核心。包含在基因型中的符号信息在整个符号系统以及为特定功能(如构造、分类控制和通信)解释符号的物质组织之外没有内在意义。具有进化潜力的自我参照是物质方面的动力学物理定律与物理组织的符号方面的约束句法规则之间的自主闭合。R这CH一种2001. 语义闭包需要单独的符号描述G和n这吨是p和,d和s一世Gn,一种nds这F吨在一种r和和物质体现pH和n这吨是p和,米一种CH一世n和,一种ndC这米p在吨和r. 符号描述必须能够产生物质体现。最后,物质体现必须能够重新生成具有突变可能性的象征性描述。卡里亚尼(1989,2001)评估了语义闭合原则与具有紧急语义功能的设备设计的关系。自身类别的自我修改和自我构建被认为对符号问题很重要,并且是语义自适应设备或可进化设备的要求。使用尖峰的时间模式来编码信息的时间代码和神经脉冲代码似乎是可进化设备和大脑研究的潜在工具。
如图。2.2说明了遗传系统语义闭合的概念。考虑两个水平,基因型和表型。基因型启动动力学,而表型由基因组迭代动力学发展。环境决定了基因组的稳定性和繁殖活动。
在模型分类术语中,符号系统相对于动态系统处于更高级别的类别。符号模型涉及“非真实”,即“非标准”字段。
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|TWO LEVELS MODELING
原则上,从一级建模到多级建模似乎很简单。
为了描述新兴层次系统的演变,人们用“非标准”领域对应物替换“真实”领域系统的公认模型或定理的参数,并且至少在某些情况下看到有意义的一般模型,以及对“真实”领域系统的真实陈述由此产生的新兴复杂系统。
如图。2.3显示了一个两级架构。请注意,这两个级别应该具有不同的分类组织。在某些情况下会出现差异,这是显着新现象的迹象。
在更一般的情况下,这是科学或工程建模中实验和理论之间的一般问题。人们认为这是科学或工程中的一种自然方法,从人们可能将正式数学框架与之联系起来的现象开始。然后,对预测进行实证检验。这是一系列理论和测试步骤。模型和测试结果之间的来回演变,一方面改变事物,另一方面检查效果,形成了科学和工程方法的基础。这可能是语言上的差异,即建模和测试模型的代数框架,这代表了闭包的挑战之一。
科学和工程建模的实验和理论之间的闭合可能表现为模型或定理相对于“非真实”场的“真实”场的闭合。关闭请求是两种类型的模型都需要对紧急复杂性有一个完整的视图。
人们必须进行额外的修改和重新解释,以获得物理上和数学上足够完整或语义上封闭的理论。
闭包方法需要进行涉及实值函数和“非实数”函数的分析。这解释了这样一个事实,即在 PSM 研究期间,实值概率和“非实数”即“非标准”概率继续相关联。注意力集中在问题上,而不是方法的纯度,肯定不适合研究的目标,出现了多层次的复杂性。不同类别的数学框架之间应该有明确的界限,但自然复杂性既没有纯粹的真实,也没有纯粹的“非真实”结构。理解复杂性应该涉及真实框架与“非真实”框架在不同级别上交互,而不是特别赋予任何一个特权。
有人可能会问,为什么在复杂性研究中支持非标准或分类框架。毕竟,有许多复杂性研究只使用了真实的现场分析。非标准和更高类别框架在 PSM 中的参与并非出于构建异常框架的倾向,这些框架在一定程度上可能看起来像理论一样新颖和出人意料,而是由 PSM 的目标强加于理解和构建可进化的系统,即超越学习和适应性水平的系统,可能是可进化的并且能够自主和创造性地控制其环境。使用与真实框架密切相关的更高类别的“非真实”框架的语义优势是多级系统响应性、可进化性和自主性的决定性增强。
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|INTEGRATIVE CLOSURE
整体闭合是新层次相对于先前层次的相互限制或排他性的直接结果,也是要考虑的层次数量有限的直接结果。综合封闭方法不是寻找哲学和数学分类观点之间的同一性,而是寻找结构类比和不同领域共享的一般方法论,如知识组织、本体问题解决或技术发展一世这rd一种CH和2010.
皮亚杰和加西亚提出了数学和物理学领域结构类比、平行和概括的重要例子1989.
整合闭合的出发点是重新考虑自然研究中相互关联的四个主要本体论层次:“物质的”、“生物的”、“认知的或心理的”和“智能的或逻辑的”H一种r吨米一种nn1952.
人们承认,层次结构不能作为多层次知识组织的通用模型。面对复杂性,知识整合的任务仍然是相关的。
如图。2.4显示了作为哈特曼四级本体层次的网络版本的综合闭包假设的实现。传统的层次结构是封闭的,被网络所取代。
综合封闭旨在为四个层次或领域实现收支平衡,强调哈特曼的物质领域和智能领域之间的假设互连。一个人为或自然可进化的系统应该跨越这两个层次之间的鸿沟。
观察到物质领域和智能领域之间的两级建模关系可以直接完成这个闭合任务。对于集成闭合,目标不是将几个互连步骤减少为两级交互,以尝试以最快的方式实现闭合。与这些相反,综合封闭着眼于四个相互作用步骤,以促进研究并考虑必要的基本成分,其次是自然界中存在的可进化系统。

数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。