如果你也在 怎样代写半导体物理Semiconductor Physics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。半导体物理Semiconductor Physics它们具有适度的导电性。这类材料的例子有锗、硅、碳等。由于这些材料的导电性介于良好导体和绝缘体之间,这些材料被称为半导体。
半导体物理Semiconductor Physics半导体材料的电导率值介于导体(如金属铜)和绝缘体(如玻璃)之间。它的电阻率随着温度的升高而下降;而金属的表现则相反。它的导电性能可以通过在晶体结构中引入杂质(”掺杂”)的方式进行有用的改变。当同一晶体中存在两个不同的掺杂区域时,就会产生一个半导体结。电荷载体(包括电子、离子和电子空穴)在这些结上的行为是二极管、晶体管和大多数现代电子产品的基础。半导体的一些例子是硅、锗、砷化镓和周期表上所谓 “金属阶梯 “附近的元素。继硅之后,砷化镓是第二种最常见的半导体,用于激光二极管、太阳能电池、微波频率集成电路和其他。硅是制造大多数电子电路的一个关键元素。
my-assignmentexpert™半导体物理Semiconductor Physics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的半导体物理Semiconductor Physics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此半导体物理Semiconductor Physics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理Physics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的物理Physics代写服务。我们的专家在半导体物理Semiconductor Physics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种半导体物理Semiconductor Physics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的半导体物理Semiconductor Physics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
物理代写|半导体物理代写Semiconductor Physics代考|Growth from the Liquid Phase
Growth of bulk crystals from the liquid phase may occur by crystallization from either the molten material or a solution containing the dissolved material (the solute) in a suitable solvent.
Growth from the Melt
Melt growth is the most frequently applied method for growing large single crystals at high growth rates. Prerequisites for the application are a melting without decomposition (i.e., change of stoichiometry) and a solid state without polymorphic transitions (i.e., change of crystal structure without change of stoichiometry) below the melting point. Materials with a melting point below $1,800^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ are particularly made employing the Bridgman (1923) (also referred to as Bridgman Stockbarger) or the Czochralski method (1918), while high-melting materials are grown by zone-melting or the flame-fusion technique introduced by Verneuil (1902).
The Bridgman method illustrated in Fig. 10a employs a crucible containing the molten material which is moved relative to the axial temperature gradient of a vertical furnace. An additional adiabatic loss zone may be inserted between the high-temperature and the low-temperature zones of the furnace for a steep and betteradjusted temperature gradient. The speed of the directional crystallization is controlled by the speed of the temperature field; moving the furnace upward is favored over lowering the crucible to minimize agitation which may disturb crystallization. The coldest point of the crucible is the lower tip; here, crystallization of the melt commences, and a narrow part of the crucible supports the selection of a single crystal (with a proper, fast growing direction) from an initially polycrystalline material. Alternatively, a seed crystal may be placed at the lower tip of the crucible to induce growth along a specific orientation. The Bridgman method is also applied in a horizontal configuration.
物理代写|半导体物理代写Semiconductor Physics代考|Growth from the Vapor Phase
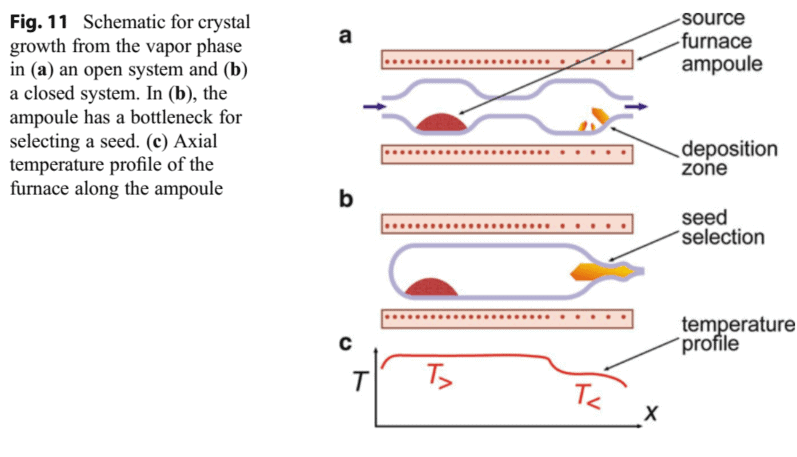
In vapor-phase growth, the source material is transferred to the vapor phase by sublimation or chemical reaction at a high temperature $T_{>}$, transported to the growth region by diffusion or convection, and then crystallized at a lower temperature $T_{<}$. The sublimation-condensation process is also referred to as physical vapor deposition (PVD), while a chemically assisted process is often termed chemical vapor deposition (CVD) when performed in a closed configuration and chemical vapor transport (CVT) in an open configuration. ${ }^{10}$ Recrystallization may occur at the ampoule walls by self-seeded growth or at a seed crystal. The basic setup is illustrated in Fig. 11 .
物理代写|半导体物理代写Semiconductor Physics代考|Growth of Organic Crystals
The growth units of organic crystals are bulky molecules instead of the atoms illustrated schematically in Fig. 8, and their incorporation at a kink site of the surface requires some energy for proper orientation. The crystals have very weak intermolecular bonds and hence low melting temperatures see Table 6 in chapter -Crystal Bonding”. Still the growth methods outlined above are basically also applied for fabricating organic semiconductors, but their vapor pressure, a low thermal stability of the growth units, and a limited solvent solubility often require specific modifications of conventional growth techniques; for a review, see Kloc et al. (2010).
Growth from the vapor phase is the most frequently used method for fabricating organic single crystals, particularly for smaller, more volatile molecules. ${ }^{11}$ Generally, physical vapor transport is applied, using either an open tube or a sealed ampoule as illustrated in Fig. 11a,b. The organic source material is heated to sublimation temperature at one end of a quartz tube, vaporized, and either transported by an inert carrier gas like nitrogen or by diffusion in vacuum to the deposition zone held at decreased temperature. Organic semiconductors have usually a poor purity, but a comparable sensitivity like conventional semiconductors with respect to defects. This favors vapor-phase growth: heavy impurities may remain at the vaporization zone or already be deposited at higher temperatures before the crystallization zone, and lighter impurities behind this zone held at even lower temperatures. Crystals grown from the vapor phase have usually best purity and structural quality. They often show a preferred two-dimensional growth, yielding plate-type shapes with a very large aspect ratio of lateral dimensions versus thickness.
半导体物理代写
物理代写|半导体物理代写SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS代考|GROWTH FROM THE LIQUID PHASE
通过从熔融材料或含有溶解材料的溶液中结晶,可以从液相中生长块状晶体吨H和s这l在吨和在合适的溶剂中。
熔体生长熔体
生长是最常用的以高生长速率生长大单晶的方法。申请的先决条件是不分解的熔化一世.和.,CH一种nG和这Fs吨这一世CH一世这米和吨r是和没有多态跃迁的固态一世.和.,CH一种nG和这FCr是s吨一种ls吨r在C吨在r和在一世吨H这在吨CH一种nG和这Fs吨这一世CH一世这米和吨r是低于熔点。熔点低于的材料1,800∘C特别是使用 Bridgman1923 一种ls这r和F和rr和d吨这一种s乙r一世dG米一种n小号吨这Cķb一种rG和r或 Czochralski 方法1918,而高熔点材料是通过区域熔化或 Verneuil 引入的火焰融合技术生长的1902.
图 10a 中所示的 Bridgman 方法采用了包含熔融材料的坩埚,该坩埚相对于立式熔炉的轴向温度梯度移动。可以在炉子的高温区和低温区之间插入一个额外的绝热损失区,以获得陡峭和更好调节的温度梯度。定向结晶的速度由温度场的速度控制;向上移动熔炉比降低坩埚更有利,以尽量减少可能干扰结晶的搅拌。坩埚的最冷点是下端;在这里,熔体开始结晶,坩埚的狭窄部分支持单晶的选择在一世吨H一种pr这p和r,F一种s吨Gr这在一世nGd一世r和C吨一世这n由最初的多晶材料制成。或者,可以将晶种放置在坩埚的下端以诱导沿特定方向生长。Bridgman 方法也适用于水平配置。
物理代写|半导体物理代写SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS代考|GROWTH FROM THE VAPOR PHASE
在气相生长中,源材料在高温下通过升华或化学反应转移到气相吨>,通过扩散或对流输送到生长区,然后在较低温度下结晶吨<. 升华-冷凝过程也称为物理气相沉积磷在D,而化学辅助过程通常称为化学气相沉积C在D当在封闭配置和化学蒸气传输中执行时C在吨在开放式配置中。10再结晶可通过自晶生长或晶种发生在安瓿壁上。基本设置如图 11 所示。
物理代写|半导体物理代写SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS代考|GROWTH OF ORGANIC CRYSTALS
有机晶体的生长单元是大分子而不是图 8 中示意性示出的原子,并且它们在表面的扭结点处的结合需要一些能量才能正确定向。晶体具有非常弱的分子间键,因此熔化温度低,参见“晶体键合”一章中的表 6。尽管如此,上述生长方法基本上也适用于有机半导体的制造,但它们的蒸汽压、生长单元的低热稳定性和有限的溶剂溶解度通常需要对常规生长技术进行特定修改;有关评论,请参阅 Kloc 等人。2010.
气相生长是制造有机单晶最常用的方法,特别是对于更小、更易挥发的分子。11通常,使用如图 11a、b 所示的开口管或密封安瓿来应用物理蒸汽传输。有机源材料在石英管的一端被加热到升华温度,蒸发,然后通过惰性载气(如氮气)或通过在真空中扩散输送到保持在降低温度下的沉积区。有机半导体的纯度通常较差,但与传统半导体相比,其对缺陷的敏感性相当。这有利于气相生长:重杂质可能保留在汽化区或在结晶区之前的较高温度下已经沉积,而该区后面的较轻杂质则保持在更低的温度下。从气相生长的晶体通常具有最好的纯度和结构质量。

物理代写|半导体物理代写Semiconductor Physics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。