如果你也在 怎样代写优化和运筹学Operations Research MATH487 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。优化和运筹学Operations Research在两次世界大战后的几十年里,运筹学的工具被更广泛地应用于商业、工业和社会中的问题。从那时起,运筹学已经扩展为一个广泛用于从石油化工到航空、金融、物流和政府等行业的领域,转而专注于开发可用于分析和优化复杂系统的数学模型,并成为一个活跃的学术和工业研究领域。
优化和运筹学Operations Research采用了其他数学科学的技术,如建模、统计和优化,为复杂的决策问题找到最佳或接近最佳的解决方案。由于强调实际应用,运筹学与许多其他学科有重叠之处,特别是工业工程。运筹学通常关注的是确定一些现实世界目标的极端值:最大(利润、绩效或收益)或最小(损失、风险或成本)。运筹学起源于二战前的军事工作,它的技术已经发展到涉及各种行业的问题。
my-assignmentexpert™优化和运筹学Operations Research代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的优化和运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此优化和运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在网课代修方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的网课代修服务。我们的专家在优化和运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种优化和运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的优化和运筹学Operations Research MATH487 及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
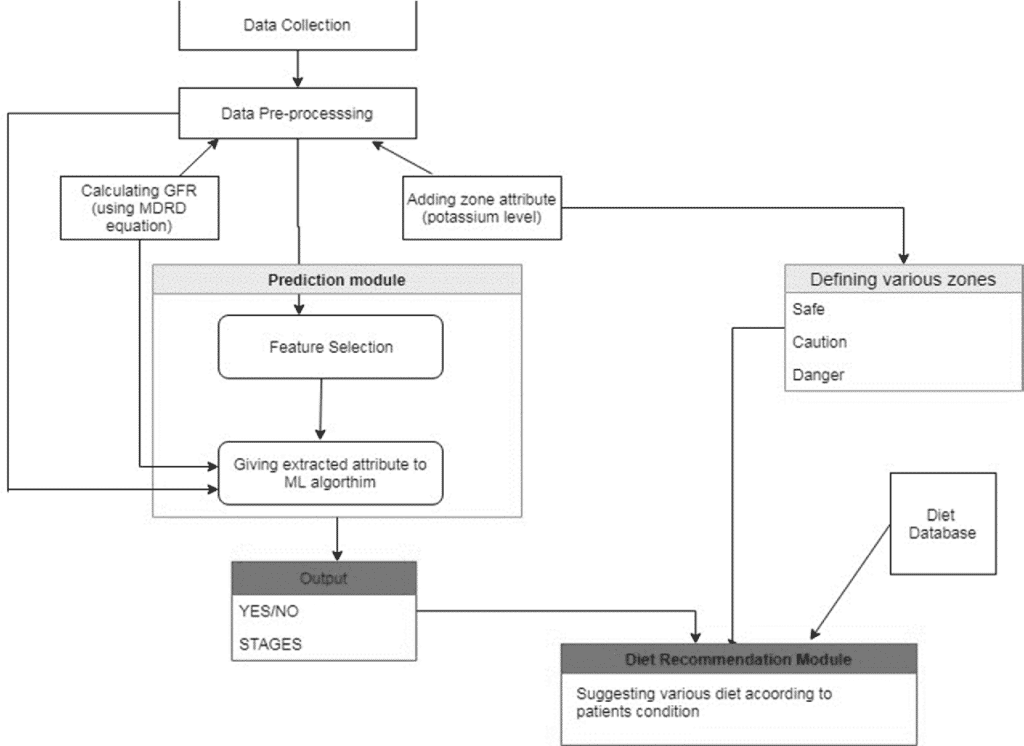
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写|Diet Problem
The LP method of model formulation to solve multi criteria problems can also be used to find number of units of each diet an individual should take which would fulfil calorie intake at lowest possible cost. Or, from producers’ perspective how many units of combination of various diets or foods should be offered which would maximize the profits. Thus, the purpose of maximization or minimization depends on the number of units of alternative diets. The application of LPP in solving such questions is illustrated in the following case.
A fast food restaurant intended to change consumers’ perception from selling unhealthy foods to healthy foods. The manager from previous data estimated that most liked and sold items/diets were chicken burger along with regular fries and a regular shake. Most of customers tend to buy these items to one combined meal. The manager created a promotion campaign wherein calorie intake of these three diets was shown, and it was emphasized that such intake was within healthy limits. This emphasis was highlighted by displaying calorie in grams of each nutrient in each of the diet. Each diet or food item, namely burger, fries and shake, was indicated to have certain common nutrients, which were sodium, sugar, trans-fat, protein and fibre. Furthermore, as most of customers combine these three food items to form one combined meal so calorie intake is sum of calories from these food items i.e. maximum calorie intake of $2,000 \mathrm{~g}$ of sodium meant that by having one unit of chicken burger along with fries and shake would result in calorie intake of less than or equal to $2,000 \mathrm{~g}$. Similarly, data regarding calorie of all nutrients for each food item was displayed. Maximum calorie intake data implies that combination of one unit of each type of diet would be within healthy limits.
The major purpose of showing such detailed data to customers was primarily to increase profits from enhanced sales of new items. Restaurant manager wanted to estimate number of units of each food item/diet that should be sold to earn maximum profit if per unit of burger, fries and shake give a profit of $\$ 1.5, \$ 0.6$ and $\$ 0.8$ respectively. The formulation of LPP for such problem is illustrated next. The following data indicates nutrient intake of these food items in grams per serving.
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写|Blending Problem
The LPP model can be formulated for problems when the same items are combined in different proportion to produce different products. For instance, an alloy is created by adding different metals in different quantities, and if these quantities are varied, then a different metal would be formed. Thus, a problem of identifying amount of each metal to be added in such a proportion so that final demand of different products is met is resolved by using the LPP model. Blending problems mostly occur in oil industry where petrol and diesel are primary products, which are produced by adding similar chemicals in different proportions to crude oil. The constraint of limited supply of ingredients that go into production of final product limits the quantity produced. Thus, the formulation of LPP in such cases also indicates the maximum number of final products that could be manufactured with this limited availability of ingredients so that the optimum profit can be achieved. The following illustration explains the process of formulating LPP model with regard to an oil production company.
Petrol India Ltd. uses three types of chemicals (C1, C2 and C3) in different proportions to produce three different types of oil (A, B and C). Each oil takes a maximum limit of each type of chemical. For instance, a maximum of $60 \%, 20 \%$ and $15 \%$ of $\mathrm{C1}$, C2 and C3 are required to produce a barrel of oil A. Similarly, a barrel of B requires a maximum of $55 \%, 20 \%$ and $30 \%$ of $\mathrm{C} 1, \mathrm{C} 2$ and $\mathrm{C} 3$. Finally, a maximum of $70 \%$, $10 \%$ and $15 \%$ of $\mathrm{C} 1, \mathrm{C} 2$ and $\mathrm{C} 3$ are required to produce a barrel of $\mathrm{C}$. The production of each type of oil is constrained by the availability of each type of ingredient. For a particular production schedule, a maximum of $4,000,3,200$ and 1,400 tonnes of C1, C2 and C3 are available. The purpose is to estimate number of barrels of each type of oil that can be produced by blending different chemicals so as to generate maximum profit if one barrel of $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}$ and $\mathrm{C}$ gives a profit of $\$ 15, \$ 14$ and $\$ 13.5$, respectively.
Solution:
The formulation of LPP requires defining decision variables. As in the case of blending problem, each ingredient, in this case, a chemical, is utilized in limited quantities to produce three different final products, so a decision variable would indicate the amount of a particular ingredient used in the production of a particular final product. Thus:
$\mathrm{x}{11}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 1$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{A}$, $\mathrm{x}{12}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{Cl}$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{B}$,
$\mathrm{x}{13}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 1$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{C}$, $\mathrm{x}{21}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 2$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{A}$,
$\mathrm{x}{22}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 2$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{B}$, $\mathrm{x}{23}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 2$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{C}$,
$\mathrm{x}{31}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 3$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{A}$, $\mathrm{x}{32}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 3$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{B}$, and
$\mathrm{x}_{33}$ : amount of chemical $\mathrm{C} 3$ required to produce one unit of oil $\mathrm{C}$
优化和运筹学代写
数学代写优化和运筹学代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代写|DIET PROBLEM
用于解决多标准问题的模型制定的 LP 方法也可用于找出个人应该悉取的每种饮食的单位数,这些饮食将以䟡可能低的成本完成卡路里摄入。或者,从生产者的角度来 看,应该提供多少单位的各种饮食或食物的组合才能使利润最大化。因此,最大化或最小化的目的取大于萫代饮食的单位数量。LPP在解诀此关问题中的应用在以下宴 例中进行了说明。
$\mathrm{~ 一 家 快 粲 店 , 旨 在 改 变 消 费 者 的 观 念 , 从 销 售 不 健 康 食 品 转 向 健 康 食 品 。 经 理 根 据 之 前 的 数 据 估 计 , 最 喜 欢 和 销 售 的 商 品 / 饮 食 是 鸡 肉 汉 保 以 及 普 通 蓍}$ $\mathrm{~ 大 多 数 顾 客 倾 向 于 将 这 些 物 品 购 买 到 一 顿 组 合 餐 中 。 经 理 发 起 了 一 项 促 销 活 动 , 其 中 显 示 了 这 三 种 饮 食 的 卡 路 里 攝 入 量 , 并 强 调 这 种 撮 入 量 在 健 㡷}$ 种饮食中每种营养素的卡路里克数来强调这一重点。每种饮食或食物,即汉堡、暑条和奶昔,都被指出含有某些常见的营养素,即钠、糖、反式脂肪、蛋白质和纤维。 此外, $2,000 \mathrm{~g}$ 钠意味着一个单位的鸡肉汉保和薯条和奶昔会导致卡路里摄入量小于或等于 $2,000 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~ . ~ 同 样 , 显 示 了 每 种 食 品 的 所 有 营}$ 入量数据意味羊每种饮食的一个单位的组合将在健康范围内。
向㝘户展示交些详细数据的主要目的主要是增加新产品销售的利润。踶厅经理相要估计每单位汉堡、蓍条和奶昔的利润为,应出售的每种食品/饮食的单位数量以获得 最大利润 $\$ 1.5, \$ 0.6$ 和 $\$ 0.8$ 分别。接下来说明针对此㫧问题的 LPP 公式。以下数据表明这些食品的营养摄入量 (以每份克数为单位)。
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代 写|BLENDING PROBLEM
LPP模型可以针对相同项目按不同比例组合生产不同产品时的问题制定。例如,通过添加不同数量的不同金属来创建合金,如果这些数量不同,则会形成不同的金属。 因㰣,使用LPP模型解快了㛣别每种金属以这样的比例添加的量以满足不同产品的最终需求的问题。混合问题主要发生在石油工业中,石油和柴由是主要产品,通过在 原油中添加不同比例的关似化学品来生产。进入最终产品生产的原料供应有限,限制了生产的数量。因此,在这种情况下,LPP的配方也表明了在这种有限的成分可用 性的情况下可以生产的最终产品的最大数量,从而可以实现最佳利润。下图说明了某石油生产公司制定LPP模型的过程。
Petrol India Ltd. 使用三种化学品 $C 1, C 2 a n d C 3$ 以不同的比例生产三种不同类型的油 $A, B a n d C$. 每种油对每种化学物质都有最大限制。例如,最多 $60 \%, 20 \%$ 和 $15 \%$ 的 $\mathrm{C} 1, \mathrm{C} 2$ 和 $\mathrm{C} 3$ 是生产一桶油 $\mathrm{A}$ 所必需的。同样,一桶 $\mathrm{B}$ 最多需要 $55 \%, 20 \%$ 和 $30 \%$ 的 C1, C2和C3. 最后,最多 $70 \%, 10 \%$ 和 $15 \%$ 的 C1, $\mathrm{C} 2$ 和 33 需要生产一桶 $\mathrm{C}$. 每种油的 生产都受到每种成分的可用性的限制。对于特定的生产计划,最多 $4,000,3,200$ 以及 1,400 吨 $C 1 、 C 2$ 和 $C 3$ 可供选择。目的是估计通过混合不同的化学品可以生产的每 种石油的桶数,以便在每桶石油的情况下产生最大利清。A, B和 C利润为 $\$ 15, \$ 14$ 和 $\$ 13.5$ ,分别。
解决方莞:
LPP 的制定需要定义决策变量。与混合问题的情兄一样,每种成分(在这种情况下是一种化学品) 都以有限的数量使用以生产三种不同的最终产品,因此块策变量将指 示用于生产特定最终产品的特定成分的数量产品。因此:
$\mathrm{x} 11$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 1$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{x} 12$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{Cl}$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{B}$,
$\mathrm{x} 13$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 1$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{x} 21$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 2$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{A}$,
$\mathrm{x} 22:$ 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 2$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{B}, \mathrm{x} 23$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 2$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{C}$,
$\mathrm{x} 31:$ 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 3$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{x} 32:$ 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 3$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{B}$, 和
$\mathrm{x}_{33}$ : 化学量 $\mathrm{C} 3$ 需要生产一单位石油 $\mathrm{C}$

数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

