如果你也在 怎样代写优化和运筹学Operations Research MATH4202这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。优化和运筹学Operations Research在两次世界大战后的几十年里,运筹学的工具被更广泛地应用于商业、工业和社会中的问题。从那时起,运筹学已经扩展为一个广泛用于从石油化工到航空、金融、物流和政府等行业的领域,转而专注于开发可用于分析和优化复杂系统的数学模型,并成为一个活跃的学术和工业研究领域。
优化和运筹学Operations Research采用了其他数学科学的技术,如建模、统计和优化,为复杂的决策问题找到最佳或接近最佳的解决方案。由于强调实际应用,运筹学与许多其他学科有重叠之处,特别是工业工程。运筹学通常关注的是确定一些现实世界目标的极端值:最大(利润、绩效或收益)或最小(损失、风险或成本)。运筹学起源于二战前的军事工作,它的技术已经发展到涉及各种行业的问题。
my-assignmentexpert™优化和运筹学Operations Research代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的优化和运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此优化和运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在网课代修方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的网课代修服务。我们的专家在优化和运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种优化和运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的优化和运筹学Operations Research MATH4202 及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
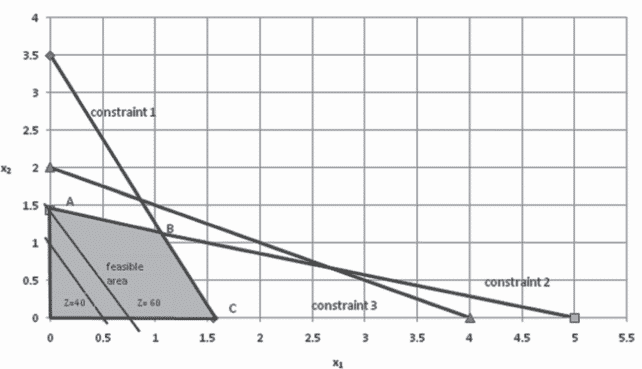
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写|Illustration of Maximization: AdIDAS AG Retall Stores
Case of Adidas AG illustrated in first chapter would be used to explain graphical process for achieving a solution. Model has been reproduced here again:
Maximize Profit $\mathrm{Z}=80 \mathrm{x}{1}+40 \mathrm{x}{2}$
Constraint 1: $9 \mathrm{x}{1}+4 \mathrm{x}{2} \leq 14$
Constraint 2: $2 \mathrm{x}{1}+7 \mathrm{x}{2} \leq 10$
Constraint 3: $5 \mathrm{x}{1}+10 \mathrm{x}{2} \leq 20$
$$
\mathrm{x}{1}, \mathrm{x}{2}, \mathrm{x}_{3} \geq 0
$$
Solution involves following steps:
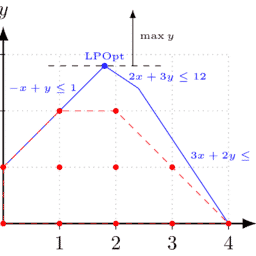
Step 1: As it is observed from the above equations that power of decision variables is one making model a linear one. Also as explained earlier, it fulfils other assumptions as well. Thus, when constraint equations are drawn on a graph, they would be represented by a straight line. Every straight line equation requires two extreme points. They are calculated by putting one decision variable at a time equal to zero and finding value for other. For instance, in the case of constraint 1 , putting $x_{1}=0$ would give $x_{2}=3$ and putting $x_{2}=0$ would give $x_{1}=2$. Conceptually, it implies that when no units are being sold from location A then all sales would come from location B and vice versa. Line graph of constraint 1 is shown in Figure 2.1.
Two important understandings are derived from graphical representations.
- First, linear equation provides a straight line which in turn indicates that slope of line is constant at all points on the line. This further infers that solution of objective function $\mathrm{Z}$ for different points on the line would be the same. For example, at $x_{1}=0.2 ; x_{2}$ is approximately equal to 3 which would give $Z$ as 136 . At $x_{1}=0.4 ; x_{2}$ is equal to $2.6$ which again gives $Z$ as 136 . Value of $Z$ is the same in both cases. Similarly, at any other point on the line, results would be the same, implying almost infinite optimal solutions.
- Second, as constraint has inequality of less than equal to $(\leq)$, all values below this line would provide feasible solutions. For example, putting $\mathrm{x}{1}=0.4$ and $\mathrm{x}{2}=1$ left-hand side of constraint 1 would be $7.6$, which is less than right-hand side thus not violating the constraint making solution feasible. However, at $x_{1}=1.4, x_{2}$ is approximately equal to $0.4$ which would make left-hand side of constraint $14.2$, which is greater than right-hand side violating the constraint making solution infeasible. However, this point does give an optimal value of $\mathrm{Z}$. Thus, very importantly, every optimal solution is not feasible.
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写|ILlUSTRATION OF MINIMIZATION: ROSE’S LUXURY RESTAURANT
The US hotel industry experienced strong growth from a period of $2009-2018$ as indicated by increase in gross bookings from $\$ 116$ billion to $\$ 185$ billion (https://www2. deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/consumer-business/us-consumer2019-us-travel-and-hospitality-outlook.pdf). This had a positive spillover effect on associated sectors such as transportation and restaurants. Such unprecedented growth driven by vigorous economy and high consumer spending encouraged many restaurants to expand their operations. Rose’s luxury in Washington DC intended to tap into favourable market conditions and decided for expansion of its restaurant. The restaurant provides eclectic menu to its clients. The restaurant serves predominantly two types of customers. Two member couples and four member families were its prime customers who enjoyed their services especially during dinner time. To cater to both types of customers, restaurant manager set two types of seating arrangements. One type of arrangement (i) catering to couples constituted two chairs and a round table. Such arrangement occupied maximum of $16 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ of space. Other arrangement (ii) catering to four member families constituted four chairs and a rectangular table. It occupied maximum of $30 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ of space. Various numbers of both types of seating arrangements had to be arranged in maximum of $1,000 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ of space. It was estimated by the manager from past data that combined minimum demand of A type of seating arrangement in one cycle was 20 and that of B was 15 . The kitchen of restaurant can prepare maximum of 40 meals to cater to demand of both types of customers if all the seating arrangements are taken. It was estimated that during peak evening hours to serve one arrangement of A type incurs a cost of $\$ 10$, whereas for B type, the cost is $\$ 15$. Manager wants to find the optimal number of seating arrangements, which would minimize cost. A higher number of seats arranged would cause congestion, which would increase the cost, while a lower number of seats would result in extra vacant spaces, implying improper utilization of space, which would increase the cost again.
优化和运筹学代写
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代 与冖|ILLUSTRATION OF MAXIMIZATION: ADIDAS AG RETALL STORES
第一章中的 Adidas AG 案例将用于解释实现解决方案的图形过程。模型在这里再次被复制:
最大化利润 $\mathrm{Z}=80 \mathrm{x} 1+40 \mathrm{x} 2$
约束 $1: 9 \mathrm{x} 1+4 \mathrm{x} 2 \leq 14$
约束 $2: 2 \mathrm{x} 1+7 \mathrm{x} 2 \leq 10$
约束 $3: 5 \times 1+10 \times 2 \leq 20$
$$
\mathrm{x} 1, \mathrm{x} 2, \mathrm{x}{3} \geq 0 $$ 解决方法包括以下步洜: 步漈 1: 从上述方程可以看出,决策变量的草是使模型成为线性模型的龺。同样如前所述,它也满足其他假设。因此,当在图上绘制约束方程时,它们将由一条直线表 示。每个直线方程都需要两个极值点。它们是通过将一个決策变量置于等于 0 的时问并为其他变量找到值来计算的。例如,在约束 1 的情况下,将 $x{1}=0$ 会哈 $x_{2}=3$ 并把 $x_{2}=0$ 会哈 $x_{1}=2$.从概念上讲,这意味着当 $\mathrm{A} \mathrm{~ 位 置 没 有 出 售 任 何 单 位 时 , 所 有 销 龶 都 栘 来 自 ~ B 位 置 , 反 之 亦}$ 从图形表示中得出两个重要的理解。
首先,线性方程提供了一条直线,这反过来表明直线的斜率在直线上的所有点上都是恒定的。这进一步推断出目标函数的解Z对于线上的不同点将是相同的。例 如,在 $x_{1}=0.2 ; x_{2}$ 大约等于 3 这将给出 $Z$ 作为 136 。在 $x_{1}=0.4 ; x_{2}$ 等于 $2.6$ 这又给了 $Z$ 作为 136 。的价值 $Z$ 在这两种情况下都是一样的。类似地,在线上的任何 其他点,结果都是相同的,这意味着几乎无限的最优解。
其次,由于约束的不等式小于等于 $(\leq)$ ,这条线以下的所有值都将提供可行的解决方安。例如,把 $x=0.4$ 和 $1 \times 2=1$ 约束 1 的左侧将是 $7.6$ ,它小于右手边,因此 不违反使解决方宴可行的约束。然而,在 $x_{1}=1.4, x_{2}$ 大约等于 $0.4$ 这将使紖束的左侧 $14.2$, 大于右手边,违反了使解决方案不可行的约束。然而,这一点确实给 出了一个最优值Z. 因此,非常重要的是,每个最优解都不可行。
数学代写|优化和运筹学代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代 写|ILLUSTRATION OF MINIMIZATION: ROSE’S LUXURY RESTAURANT
美国酒占业经历了一段时期以来的强呩增长 $2009-2018$ 正如总预订量的増加所表明的那样 $\$ 116$ 亿到 $\$ 185$ 十亿
https://www2.deloitte. com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/consumer – business/us – consumer 2019 – us – travel – and – hospitality – outlook. $\mathrm{~ . ~ 䢒 对 交 通 和 粲 饮 等 相 关 行 业 产 生 了 积 极 的 溢 出 效 应 。 强 㔚 的 经 济 和 高 消 费 支 出 推 动 了 这 种 前 所 末 有 的 增 长 , 鼓 励 了 许 多 歿}$ $\mathrm{~ 算 利 用 有 利 的 市 场 条 件 , 并 决 定 扩 大 其 㢭 厅 俢 于 㛑}$ $\mathrm{~ 其 是 在 晩 濋 时 间 享 受 他 们 的 服 梦}$ 排占据了最大 $16 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ 的空间。其他安排 $i i$ 四把椅子和一张长方形桌子为四个成员家庭提供㢭饮服务。它占据了最大 $30 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ 的空间。两种猋型的座位安排的不同数量必须安 排在最多 $1,000 \mathrm{ft}^{2}$ 的空间。经理根据过去的数据估计, $\mathrm{A}$ 关座位安排在一个周期内的最低需求为 20 个, $\mathrm{B}$ 类为 15 个。㛑厅的厨房最多可淮备 $40 \mathrm{~ 份 尓}$ 型顾客的需求。据估计,在晩高峰时段,为一种 $\mathrm{A}$ 类安排服务会产生 $\$ 10$ ,而对于 $B$ 类型,成本为 $\$ 15$. 经理想要找到最佳的座位安排数量,这将使成本最小化。座位数 多会造成拥堵,增加成本,而座位数少会造成额外空置空间,意味着空间利用不当,又会增加成本。

数学代写|优化和运筹学代写Operations Research代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。