如果你也在 怎样代写断裂力学Fracture mechanics MAE543这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。断裂力学Fracture mechanics是研究材料中裂纹扩展的力学领域。它使用分析性固体力学的方法来计算裂纹的驱动力,使用实验性固体力学的方法来描述材料的抗断裂性。
断裂力学Fracture mechanics从理论上讲,尖锐裂纹尖端前方的应力变得无限大,不能用来描述裂纹周围的状态。断裂力学用于表征裂纹上的载荷,通常使用一个参数来描述裂纹尖端的完整载荷状态。许多不同的参数已经被开发出来。当裂纹尖端的塑性区相对于裂纹长度较小时,裂纹尖端的应力状态是材料内部弹性力的结果,被称为线性弹性断裂力学(LEFM),可以用应力强度因子{displaystyle K}K来描述。尽管裂纹上的载荷可以是任意的,但在1957年,G. Irwin发现任何状态都可以简化为三个独立的应力强度因子的组合。
断裂力学Fracture mechanics代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。最高质量的断裂力学Fracture mechanics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此断裂力学Fracture mechanics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在物理Physical代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的物理Physical代写服务。我们的专家在断裂力学Fracture mechanics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种断裂力学Fracture mechanics相关的作业也就用不着说。
物理代写|断裂力学代写Fracture mechanics代考|Fracture mechanics field of application
Fracture is a phenomenon that has received constant attention, practically since machines and structures found use in both wartime and peace time. Particularly, the use of mechanical and structural components such as beams, columns, shafts, pressure vessels, cables, gears, and so forth have always come along with the risk of fracture. Frequently, the fracture of a structural component is accompanied with great material, economic and human losses. It is also common that, although failures may occur once in a lifetime, a single failure can mean a great catastrophe, which is the case for airplane crashes, explosions of gas pipelines, or nuclear reactor failures. The losses are not only limited to human and economic ones, but also there are additional losses, such as delays in production, environmental damage, and the detriment of the company’s public perception and image. Premature fracture of small components, such as screws and bolts, is also an insidious problem, since consumers associate it with poor quality, which results in sales reduction. In summary, it would be impossible to quantify the magnitude of losses caused by fracture-related failures, but what is certain is that fracture may be the limiting factor for the success of industries and entire economies.
Fracture mechanics is the discipline that provides the basis and methodology for the design and assessment of cracked components in order to determine the effect of the presence of a crack. It is also applied to develop structures and materials more resistant to fracture. Through time, it has been demonstrated that the traditional criteria of structure design under the assumption of absence of flaws, and further compensating its effect by means of safety factors are risky and often lack any technical foundation. The fact is that flaws, especially cracks, inevitably appear in both mechanical and structural components due to poor manufacturing, inadequate construction, or introduced during service, so the engineers have to deal with them, and the best way is by analyzing their effect on the mechanical behavior.
The problem of fracture has kept scientists and engineers busy since the eras of the great Leonardo DaVinci and Galileo. However, it was until the beginning of the twentieth century that Griffith was able to calculate the fracture strength of brittle materials, but even so, theoretical and experimental difficulties hindered the development of fracture mechanics until 1956, when George R. Irwin introduced the concept of stress intensity factor and fracture toughness, giving birth to modern fracture mechanics. Nowadays, the study of fracture mechanics is a fundamental part of mechanical, materials and metallurgical engineering. A significant fact is that over $40 \%$ of the articles published in engineering and materials science journals are related, directly or indirectly to mechanical behavior and fracture. Within the industry, fracture mechanics is extensively used in the aeronautic, aerospace, chemical processing, oil refining, and nuclear industries, and it has begun to be used more frequently in the automobile industry, pipeline hydrocarbon transport, and construction industries.
物理代写|断裂力学代写Fracture mechanics代考|Definition of stress and strain
The French mathematician and scientist Augustin Louis Cauchŷ introduced the concept of stress in 1833 . He used the movement laws by Euler, and Newton’s mechanics, to determine the displacements produced on a static solid body subject to surface loads. Based on Newton’s second law, which states, “to every action, there is a corresponding reaction,” Cauchy figured out that when an external force is applied on a static body, an internal reaction force balancing the external force is instantaneously produced. The magnitude of such reaction is directly proportional to the magnitude of the applied force and inversely proportional to the size of the cross-section area, this reaction being stress.
Under Cauchŷ’s principle, the mechanical behavior of solid materials may be summarized as follows: Loads produce stresses, the stresses cause strain, and strain leads to fracture; therefore the aim is to determine the stresses and strains produced in a loaded solid body and determine the material’s strength to withstand such stresses without neither excessively straining nor fracturing.
To facilitate the analysis of the mechanical behavior of solids, it is necessary to simplify the system, because materials are complex arrays of atoms, crystalline defects, second phases, and microstructural heterogeneities.
The basic assumptions for the initial approach of mechanical behavior include the following:
The material is a continuum: This means that matter fills in the total volume and there are no voids nor interruptions. Under this assumption, it can be established that there will be an infinitesimal volume (a volume that tends to zero, but it never is zero), where the forces and areas be defined, so the stress exists in a point. This assumption is also the reason why the study of mechanics of materials is called continuum mechanics.
The material is homogeneous: The whole volume is filled in with the same type of matter.
The material is isotropic: The properties are the same in any direction. Based on these assumptions, a static solid under the action of an applied external force $F_A$ remains static, if and only if this force is balanced by an internal force $F i$, of the same magnitude and opposite direction to $F_A$. The force causes an internal reaction in the solid that is directly proportional to the magnitude of the applied force and the number of particles resisting the action of such force, being proportional to the cross-section area $A$. The magnitude of the internal reaction is the stress, represented by the symbol $\sigma$, and can be defined as:
$$
\sigma=F / A
$$
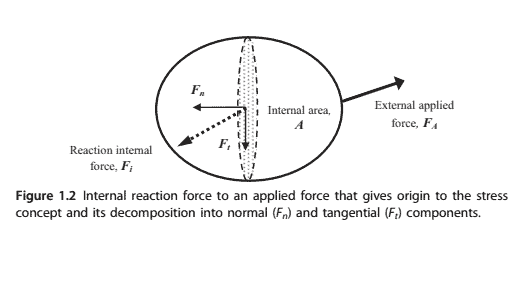
The internal force is a vector, since it has magnitude and direction, therefore it can be split into two components: One perpendicular to the cross-section area $\left(F_n\right)$ and the other parallel (or tangential) to the crosssection area $\left(F_t\right)$, as shown in Fig. 1.2.
断裂力学代写
物理代写|断裂力学代写断裂力学代考|断裂力学应用领域
.
实际上,自从机器和结构在战时和和平时期得到使用以来,断裂是一个一直受到关注的现象。特别是使用机械和结构部件,如梁、柱、轴、压力容器、电缆、齿轮等,总是伴随着断裂的风险。结构构件的断裂往往伴随着巨大的物质、经济和人员损失。同样常见的是,尽管一生中可能会发生一次故障,但一次故障就可能意味着一场巨大的灾难,飞机坠毁、天然气管道爆炸或核反应堆故障就是这种情况。这些损失不仅限于人员和经济上的损失,还包括生产延误、环境破坏、公司公众认知和形象的损害等附加损失。小部件的过早断裂,如螺钉和螺栓,也是一个潜在的问题,因为消费者把它与质量低劣联系在一起,从而导致销量下降。总而言之,无法量化压裂相关故障造成的损失,但可以肯定的是,压裂可能是行业和整个经济成功的限制因素
断裂力学是一门为设计和评估裂缝构件提供基础和方法的学科,目的是确定裂缝存在的影响。它也被应用于开发更抗断裂的结构和材料。实践证明,传统的结构设计标准在假定缺陷不存在的前提下,以安全因素进一步补偿其影响,是有风险的,往往缺乏技术基础。事实是,由于制造质量差、施工不到位或在使用过程中引入的缺陷,特别是裂缝,不可避免地出现在机械和结构部件中,因此工程师必须处理它们,而最好的方法是分析它们对机械性能的影响
自伟大的列奥纳多·达芬奇和伽利略时代以来,骨折问题就一直使科学家和工程师们忙个不停。然而,直到20世纪初,Griffith才能够计算出脆性材料的断裂强度,但即便如此,理论和实验上的困难阻碍了断裂力学的发展,直到1956年,George R. Irwin引入了应力强度因子和断裂韧性的概念,现代断裂力学诞生了。目前,断裂力学研究已成为机械、材料和冶金工程的基础。一个重要的事实是,在工程和材料科学期刊上发表的文章中,有超过$40 \%$的文章直接或间接地与力学行为和断裂有关。在工业领域,断裂力学广泛应用于航空、航天、化工加工、炼油和核工业,并开始在汽车工业、管道油气运输和建筑工业中更频繁地使用
物理代写|断裂力学代写骨折力学代考|应力和应变的定义
1833年,法国数学家和科学家奥古斯丁·路易斯·考西拉姆提出了应力的概念。他利用欧拉和牛顿力学的运动定律,来确定受表面载荷作用的静态固体产生的位移。根据牛顿第二定律,“每一个作用力都有相应的反作用力”,柯西计算出当一个外力作用在一个静止的物体上时,会立即产生一个与外力平衡的内反作用力。这种反作用力的大小与施加的力的大小成正比,与横截面面积的大小成反比,这个反作用力就是应力
在cauchlum原理下,固体材料的力学行为可以概括为:载荷产生应力,应力引起应变,应变导致断裂;因此,其目的是确定在受载固体中产生的应力和应变,并确定材料在不过度拉伸或破裂的情况下承受这些应力的强度
为了便于分析固体的力学行为,有必要简化系统,因为材料是原子、晶体缺陷、第二相和微观结构非均质的复杂阵列。
力学行为初始方法的基本假设包括以下几点
物质是一个连续体:这意味着物质填满了整个体积,没有空隙,也没有中断。在这个假设下,可以确定有一个无穷小的体积(一个趋向于零的体积,但它永远不会是零),在这个体积中力和面积都是确定的,因此应力存在于一个点。这一假设也是为什么材料力学的研究被称为连续介质力学的原因
物质均质:整个体积被同一种物质填满 材料是各向同性的:在任何方向上性能都是相同的。基于这些假设,当且仅当这个力被一个与$F_A$大小相同方向相反的内力$F i$所平衡时,在外加外力$F_A$作用下的静态固体将保持静止。该力在固体中引起内部反作用力,该反作用力与施加的力的大小和抵抗这种力作用的粒子的数量成正比,与横截面面积$A$成正比。内反力的大小就是应力,用符号$\sigma$表示,可以定义为:
$$
\sigma=F / A
$$
内力是一个矢量,因为它有大小和方向,所以它可以分为两个分量:一个垂直于横截面面积$\left(F_n\right)$,另一个平行(或切向)于横截面面积$\left(F_t\right)$,如图1.2所示。

物理代写|断裂力学代写Fracture mechanics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。