如果你也在 怎样代写金融机构管理Financial Institution Management FIN150这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融机构管理Financial Institution Management是金融的一个领域,涉及资金来源、公司的资本结构、管理者为增加公司对股东的价值而采取的行动,以及用于分配金融资源的工具和分析。公司金融的主要目标是最大化或增加股东价值。
金融机构管理Financial Institution Management最常见的金融机构类型是商业银行、投资银行、保险公司和经纪公司。这些实体为个人和商业客户提供广泛的产品和服务,如存款、贷款、投资和货币兑换。
金融机构管理Financial Institution Management代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。最高质量的金融机构管理Financial Institution Management作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融机构管理Financial Institution Management作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在金融 Finaunce代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的金融 Finaunce代写服务。我们的专家在金融机构管理Financial Institution Management代写方面经验极为丰富,各种金融机构管理Financial Institution Management相关的作业也就用不着说。
金融代写|企业融资代写Corporate Finance代考|OVERVIEW
Managing the complex and evolving suite of hardware and software that a financial institution needs to operate effectively is a somewhat daunting task. It is usually made more difficult because the overlapping vintages of legacy systems and critical process dependencies make major design changes extremely difficult. The phrase “changing the wheels on a bus while it’s still driving” is often used to describe large IT system changes, and with good reason. But to the extent that financial institutions are simply unwilling to take on major system redesign projects because they are too difficult, too risky, or both, they are creating great economic opportunity for those who are willing and able. Certainly, the best motivator and greatest risk mitigant is a clear vision for what a modernized system ought to look like, and what capabilities would be created or greatly enhanced by implementing such a system. Armed with this vision, an institution can plan to advance toward that vision using a combination of opportunistic and incremental changes and larger, more deliberate transformation projects. And, equally importantly, incremental or large steps that are inconsistent with the vision can be avoided.
One of the biggest questions and challenges when it comes to overall system design is the level of centralization and integration that an institution should target. By centralization we mean that data is all ultimately, officially stored in one originating data model, although it may be passed down to more local and more specialized data structures to facilitate use. By integration, we mean the existence of common identifying information for like data elements across data structures. Two data structures that contain overlapping data, for which common identifiers exist in each, can be said to be integrated. If all of the overlapping data in both systems is identical and has identical identifiers, the two systems can be said to be fully integrated. One of the principle suggestions of this book is that an institution should consider this goal-the targeting of a desired level of centralization and integration of data storage-as a key strategic decision. Local (so-called) data marts whose contents include locally loaded data that did not originate from the core system, or cannot be directly tied back to the core model, lack both centralization and integration. One of the main problems with a lack of integration is that it creates the need for reconciliation, and data reconciliations are costly and create operational risk. Data emanating from an integrated data repository do not need reconciliation.
金融代写|企业融资代写Corporate Finance代考|Storage and Retrieval
As explained above, there are three things an institution needs to do with data: store and retrieve, process, and analyze and report on it. Storage and retrieval software, hardware, and architectural design are fundamental to the efficient use of large volumes of data. Industrial strength databases are huge, complex, expensive, and costly to change. And yet overall information efficiency begins with the underlying storage and retrieval systems, so physical capabilities should drive the system design and product selection processes. In many cases, the storage and retrieval software comes bundled under the same brand as the physical database hardware. In stark contrast to the software tools devoted to data analytics and reporting, which are subject to a frothy churn of specialized tools, rapidly evolving techniques, and boom-and-bust vendors, the landscape of storage and retrieval software has been remarkably stable. It is based on scientific principles of database architecture and a theory of database design, with SQL as the basic codeveloped data moving and processing software. These have been the features of commercial data storage and retrieval virtually since the beginning, and can be traced back to Edgar F. Codd’s influential 1970 paper written at IBM, “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks.” This paper helped to establish the principles of database design that are still current today, supported now by four decades of experience. Also, since 1986 the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has maintained standards of the SQL language that vendors are strongly incented to conform to. Importantly, because of the relative stability of core architecture design principles and operating software, institutions bear little obsolescence risk in committing to long-run core data system design strategies. It is worth noting that this pioneering research in data system design was targeted directly toward the financial services industry, as it was perceived to be the obvious commercial leader in this field-a position they can no longer claim to hold.
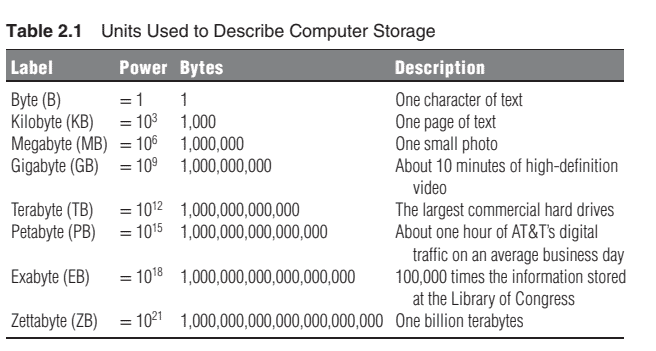
One of the key revelations of these pioneering researchers was that storage and retrieval performance was highly insensitive to data volume as long as the data was normalized. Normalization can be thought of simply as structuring the data to speed up the process of storage and retrieval, although as it turned out, other forms of data processing (besides storage and retrieval) can also be performed at very high efficiency if the data is sufficiently normalized. A fully normalized data structure might look like Table 2.2. In this case, all of a wide variety of data elements are stored in a single table. Each record has a record ID, which helps the computer locate specific data elements. Each record also has a date, which in this case is the as of date for the specific data point. The data itself, whatever it may be, is stored in the value field. Anything can be stored in this single table: corn prices, telephone numbers, baseball scores, air temperatures, and so on. Heterogeneity is not a problem and is not relevant. The code field is what is used to identify the data. The code itself links to a separate look-up table or sequence of look-up tables that identify the contents of the value field of corn prices, telephone numbers, baseball scores, air temperatures, or whatever. When the data is stored this way, the computer can retrieve a data element or a function of the data-for example, the maximum corn price-equally fast, whether there are 10,000 or 100,000,000 corn prices in the table. Thus, to efficiently store and retrieve very large amounts of data, normalization is the key. This remarkable result does have limits and limitations. Data volumes can get large enough to impair performance. As data volumes rise, the questions that institutions must answer include these: How much and what types of data should be stored in this structured way (as opposed to not being stored or not being structured)? ${ }^1$ Where should consolidated normalization be applied versus distributed normalization? And, are there alternative storage and retrieval modes that could replace or augment these traditional design principles?
金融机构管理代写
金融代写|企业融资代写CORPORATE FINANCE代考|OVERVIEW
管理金融机构有效运营所需的复杂且不断发展的硬件和软件套件是一项有些艰巨的任务。它通常变得更加困难,因为遗留系统的重叠年份和关键流程依赖性使得重大设计更改变得极其困难。“在公交车还在行驶的时候更换车轮”这句话经常被用来描述 IT 系统的重大变化,这是有充分理由的。但就金融机构只是因为太困难、太冒险或两者兼而有之而不愿意承担重大系统重新设计项目而言,它们正在为那些愿意和有能力的人创造巨大的经济机会。当然,最好的激励因素和最大的风险缓解剂是对现代化系统应该是什么样子的清晰愿景,以及通过实施这样一个系统将创造或大大增强什么能力。有了这个愿景,一个机构可以计划通过结合机会主义和渐进的变化以及更大、更深思熟虑的转型项目来实现这个愿景。而且,同样重要的是,可以避免与愿景不一致的增量或大步骤。
当涉及到整体系统设计时,最大的问题和挑战之一是机构应该瞄准的集中化和集成水平。通过集中化,我们的意思是数据最终全部正式存储在一个原始数据模型中,尽管它可能会被传递到更本地和更专业的数据结构以方便使用。通过集成,我们的意思是跨数据结构存在相似数据元素的公共标识信息。两个包含重叠数据的数据结构,每个数据结构中都存在共同的标识符,可以说是集成的。如果两个系统中的所有重叠数据都相同并且具有相同的标识符,则可以说这两个系统是完全集成的。本书的一个主要建议是,机构应该将这一目标——实现数据存储所需的集中化和集成水平——作为一项关键的战略决策。当地的so-called内容包括并非源自核心系统或无法直接绑定回核心模型的本地加载数据的数据集市缺乏集中化和集成。缺乏集成的主要问题之一是它会产生对账的需求,而数据对账成本高昂并会带来运营风险。来自集成数据存储库的数据不需要核对。
金融代写|企业融资代写CORPORATE FINANCE代考|STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL
如上所述,机构需要对数据做三件事:存储和检索、处理以及分析和报告数据。存储和检索软件、硬件和架构设计是有效使用大量数据的基础。工业实力数据库庞大、复杂、昂贵且更改成本高昂。然而,整体信息效率始于底层存储和检索系统,因此物理能力应该驱动系统设计和产品选择过程。在许多情况下,存储和检索软件与物理数据库硬件捆绑在同一品牌下。与专门用于数据分析和报告的软件工具形成鲜明对比的是,这些软件工具受到专业工具、快速发展的技术和繁荣与萧条供应商的泡沫搅动的影响,存储和检索软件的格局一直非常稳定。它以数据库体系结构的科学原理和数据库设计理论为基础,以SQL为基础共同开发的数据移动和处理软件。这些实际上从一开始就是商业数据存储和检索的特征,并且可以追溯到 Edgar F. Codd 于 1970 年在 IBM 撰写的有影响力的论文“大型共享数据库的数据关系模型”。这篇论文帮助建立了今天仍然流行的数据库设计原则,现在得到了四年经验的支持。此外,自 1986 年以来,美国国家标准协会 以SQL为基础共同开发的数据移动和处理软件。这些实际上从一开始就是商业数据存储和检索的特征,并且可以追溯到 Edgar F. Codd 于 1970 年在 IBM 撰写的有影响力的论文“大型共享数据库的数据关系模型”。这篇论文帮助建立了今天仍然流行的数据库设计原则,现在得到了四年经验的支持。此外,自 1986 年以来,美国国家标准协会 以SQL为基础共同开发的数据移动和处理软件。这些实际上从一开始就是商业数据存储和检索的特征,并且可以追溯到 Edgar F. Codd 于 1970 年在 IBM 撰写的有影响力的论文“大型共享数据库的数据关系模型”。这篇论文帮助建立了今天仍然流行的数据库设计原则,现在得到了四年经验的支持。此外,自 1986 年以来,美国国家标准协会 ” 这篇论文帮助建立了当今仍然流行的数据库设计原则,这些原则现在得到了四十年经验的支持。此外,自 1986 年以来,美国国家标准协会 ” 这篇论文帮助建立了当今仍然流行的数据库设计原则,这些原则现在得到了四十年经验的支持。此外,自 1986 年以来,美国国家标准协会ANSI一直维护供应商强烈希望遵守的 SQL 语言标准。重要的是,由于核心架构设计原则和操作软件的相对稳定性,机构在致力于长期核心数据系统设计策略时几乎没有过时的风险。值得注意的是,这项数据系统设计方面的开创性研究直接针对金融服务行业,因为它被认为是该领域明显的商业领导者——他们不能再声称拥有这一地位。
这些先驱研究人员的一项重要发现是,只要数据被规范化,存储和检索性能就对数据量高度不敏感。规范化可以简单地认为是结构化数据以加速 存储和检索过程,尽管事实证明,其他形式的数据处理besidesstorageandretrieval如果数据足够标准化,也可以以非常高的效率执行。完全规 范化的数据结构可能如表 2.2 所示。在这种情况下,所有各种各样的数据元素都存储在一个表中。每条记录都有一个记录 ID,它可以帮助计算机定 位特定的数据元素。每条记录还有一个日期,在本例中是特定数据点的截止日期。数据本身,无论它是什么,都存储在值字段中。任何东西都可 以存储在这张表中: 玉米价格、电话号码、棒球比分、气温等等。异质性不是问题,也不相关。代码字段用于标识数据。代码本身链接到一个单 独的查找表或查找表序列,这些查找表标识玉米价格值字段的内容,电话号码、棒球比分、气温或其他任何信息。当数据以这种方式存储时,无 论表中有 10,000 还是 $100,000,000$ 玉米价格,计算机都可以同样快速地检索数据元素或数据的函数一-例如,最高玉米价格。因此,要有效地存储 和检索大量数据,规范化是关键。这个显着的结果确实有局限性和局限性。数据量可能会大到足以影响性能。随看数据量的增加,机构必须回答 的问题包括:应该以这种结构化方式存储多少数据和什么类型的数据表格中的玉米价格是一万还是一亿。因此,要有效地存储和检索大量数据, 规范化是关键。这个显着的结果确实有局限性和局限性。数据量可能会大到足以影响性能。随着数据量的增加,机构必须回答的问题包括:应该 以这种结构化方式存储多少数据和什么类型的数据表格中的玉米价格是一万还是一亿。因此,要有效地存储和检索大量数据,规范化是关键。这 个显着的结果确实有局限性和局限性。数据量可能会大到足以影响性能。随着数据量的增加,机构必须回答的问题包括:应该以这种结构化方式 存储多少数据和什么类型的数据asopposedtonotbeingstoredornotbeingstructured? ${ }^1$ 与分布式规范化相比,应该在哪里应用统一规范化? 而 且,是否有替代的存储和检索模式可以替代或增强这些传统设计原则?

金融代写|金融机构管理代写Financial Institution Management代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

