如果你也在 怎样代写金融衍生品Financial Derivatives 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融衍生品Financial Derivatives是金融工具的三大类之一,另外两类是股权(即股票或股份)和债权(即债券和抵押贷款)。历史上最古老的衍生品例子,由亚里士多德证明,被认为是古希腊哲学家泰勒斯签订的橄榄合同交易,他在交换中获利。1936年被取缔的桶装水商店是一个较近的历史例子。
金融衍生品Financial Derivatives在金融领域,衍生品是一种合同,其价值来自于一个基础实体的表现。衍生品可用于多种目的,包括对价格变动进行保险(套期保值),为投机增加价格变动的风险,或进入其他难以交易的资产或市场。一些更常见的衍生品包括远期、期货、期权、掉期,以及这些的变体,如合成抵押债务和信用违约掉期。大多数衍生品在场外(场外)或芝加哥商品交易所等交易所进行交易,而大多数保险合同已经发展成为一个独立的行业。在美国,在2007-2009年的金融危机之后,将衍生品转移到交易所进行交易的压力越来越大。
金融衍生品Financial Derivatives代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。最高质量的金融衍生品Financial Derivatives作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融衍生品Financial Derivatives作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial Derivatives代考|A GENERALIST’S APPROACH TO DERIVATIVE CONTRACTS
What are derivative contracts? A derivative contract is a delayed delivery agreement whose value depends on or is derived from the value of another, underlying transaction. The underlying transaction may be from a market for immediate delivery (spot or cash market) or from another derivative market. A key point of the definition is that delivery of the underlying is delayed until sometime in the future. Economic conditions will not remain static over time; changing economic conditions can make the delayed delivery contract more or less valuable to the initial contract counterparties. Because the contract obligations do not become real until a future date, derivative contract positions are unfunded today, are carried off the balance sheet, and the financial requirements for initiating a derivative contract are just sufficient for a future performance guarantee of counterparty obligations.
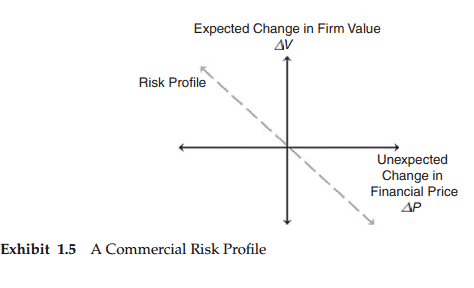
Before beginning a discussion of contract types, it is helpful to depict the profiles of the commercial risks being managed with derivative contracts. The first step in any risk management plan is to accurately assess the exposure facing the decision maker. Consider Exhibit 1.5, which plots the expected change in the value of a firm, $\Delta V$, as a function of the unexpected change in a financial price, $\Delta P$. The price could be for a firm output or for a firm input. The dashed line indicates that as the price increases $(\Delta P>0)$ unexpectedly, the value of the firm falls. The specific relationship is consistent with many conditions, such as an unexpected rise in input cost, a loss of significant market share as output prices unexpectedly rise, or even a rise in the price of a fixed income asset due to an unexpected decline in yields. The key is simply that the unexpected price rise causes the expected value of the enterprise to fall.
It is also instructive to ask whether there are alternatives to derivative contracts in managing commercial risks. Significant, low-frequency commercial risks are transferred through insurance contracts, for example. While virtually any risk can be insured, negotiation costs and hefty premiums may prevent insurance from being a cost effective mechanism for risk transfer. On-balance sheet transactions such as the restructuring of asset and/or liability accounts to correct an unwanted exposure are another alternative to derivative contracts. Customer resistance to restructuring may affect profitability as, say, a squeeze on net interest income results when a bank offers discounts on loans or premium deposit rates to accomplish the restructuring. Finally, firms can exercise their ability to set rates and prices to transfer risk to customers and stakeholders. Such exercise of market power as an alternative to derivative contracting depends on the degree of competition in output and input markets. Firms facing different competitive pressures may have different preferences for derivatives relative to other risk transfer methods.
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial Derivatives代考|Forward Contracts
The most straightforward type of derivative contract is a contract that transfers ownership obligations on the spot but delivery obligations at some future date, called a forward contract. One party agrees to purchase the underlying instrument in the future from a second party at a price negotiated and set today. Forward contracts are settled once-at contract maturity – at the forward price agreed on initially. Industry practice is that no money changes hands between the buyer and seller when the contract is first negotiated. That is, the initial value of a forward contract is zero. As the price of the deliverable instrument changes in the underlying spot market, the value of a forward contract initiated in the past can change.
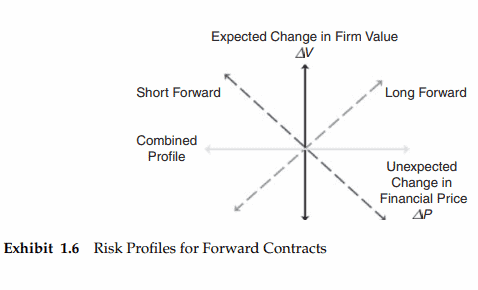
To illustrate the value change in a forward contract, consider Exhibit 1.6. All other things equal and for every unexpected dollar increase in the financial price, $\Delta P$, an agreement to purchase (long forward) the underlying instrument at the lower forward price increases expected firm value, $\Delta V$. Alternatively, Exhibit 1.6 shows that an agreement to sell (short forward) the underlying instrument at the lower forward price decreases expected firm value. The forward contract long (short) benefits from the contract if the underlying instrument price rises (falls) before the contract matures. The exhibit also shows that both buying and selling exactly the same forward contract create a combined position that makes the firm value insensitive to unexpected changes in the underlying price (the horizontal axis). Comparing Exhibits 1.5 and 1.6, the commercial risk profile in Exhibit 1.5 is the same as the risk profile for a short forward contract. To hedge away the risk or make the firm insensitive to unexpected changes in the underlying price, the firm should enter into a long forward contract (Exhibit 1.6).
A feature of a forward contract is that the credit or default risk implicit in delayed delivery performance is two-sided. The default risk is real because most forward contracts are settled by physical delivery. Recall the forward contract buyer can either make a gain or take a loss depending on the forward price set initially and the price of the underlying at contract maturity. If the underlying instrument price rises (falls), the contract buyer gains (loses) on the forward contract. Because the value of the contract is settled only at contract maturity and no payments are made at origination or during the term of the contract, a forward contract buyer is exposed to the credit risk that the seller will default on forward contract delivery obligations when the underlying asset can be sold for more in the spot market. Likewise, a forward contract seller is exposed to the credit risk that the buyer will default on forward contract payment obligations when the underlying asset can be purchased for less in the spot market.
Consider a forward rate agreement as an example of a forward contract on interest rates. A forward rate agreement is an agreement to pay a fixed interest rate on a pre-determined, notional principal amount and receive a floating rate cash flow on the same notional principal amount at contract maturity. Note that only the interest cash flows are intended to change hands at contract maturity. If the floating rate return is higher than the fixed rate cost agreed to at contact initiation, the forward rate long gains the difference in cash. If the floating rate return is lower than the fixed rate cost agreed to at contact initiation, the forward rate short gains the difference in cash. The forward rate long gains if interest rates rise or fixed income prices fall over the life of the contract. A map of the forward rate agreement cash flows is illustrated in Exhibit 1.7, where $\bar{R}$ is the fixed rate set at contract origination, time 0 , and $\tilde{R}$ is the actual rate realized at time $t$, the maturity of the contract.
金融衍生品代写
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial Derivatives代考|A GENERALIST’S APPROACH TO DERIVATIVE CONTRACTS
衍生品合约是什么?衍生合约是一种延期交割的合约,其价值取决于或衍生自另一项基础交易的价值。标的交易可能来自即期交割市场(现货或现金市场),也可能来自另一个衍生品市场。该定义的一个关键点是底层的交付被延迟到未来的某个时候。经济状况不会长期保持不变;经济条件的变化会使延期交货合同对初始合同对手方的价值增加或减少。由于合约义务直到未来的某一天才变为现实,衍生品合约头寸今天没有资金,被从资产负债表中扣除,而启动衍生品合约的财务要求仅足以保证交易对手义务的未来履行。在开始讨论合同类型之前,描述衍生合同管理的商业风险概况是有帮助的。任何风险管理计划的第一步都是准确评估决策者面临的风险。考虑图表1.5,它绘制了公司价值$\Delta V$的预期变化,作为金融价格$\Delta P$的意外变化的函数。价格可以是固定的产出,也可以是固定的投入。虚线表示,当价格意外上涨(P>0)时,公司价值下降。这种具体关系与许多条件是一致的,例如投入成本意外上升,由于产出价格意外上升而失去大量市场份额,甚至由于收益率意外下降而导致固定收益资产价格上涨。关键很简单,价格的意外上涨导致企业的预期价值下降。
在管理商业风险时,是否存在衍生品合约的替代品,这一问题也具有指导意义。例如,重大的、低频率的商业风险通过保险合同转移。虽然几乎任何风险都可以投保,但谈判费用和高昂的保费可能使保险无法成为转移风险的成本效益机制。资产负债表上的交易,如重组资产和/或负债账户以纠正不必要的风险敞口,是衍生品合约的另一种选择。客户对重组的抵制可能会影响盈利能力,例如,当银行提供贷款折扣或存款溢价利率以完成重组时,净利息收入会受到挤压。最后,公司可以行使他们设定利率和价格的能力,将风险转移给客户和利益相关者。这种行使市场力量作为衍生品合约的替代方案取决于产出和投入市场的竞争程度。相对于其他风险转移方法,面临不同竞争压力的公司可能对衍生品有不同的偏好。
金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial Derivatives代考|Forward Contracts
最直接的衍生合约类型是一种在现货上转移所有权义务,但在未来某个日期转移交割义务的合约,称为远期合约。一方同意在未来以今天商定的价格从另一方购买标的金融工具。远期合约在合约到期时按最初商定的远期价格一次性结算。行业惯例是,在合同第一次谈判时,买方和卖方之间没有金钱易手。也就是说,远期合约的初始值为零。随着可交割工具的价格在标的现货市场上的变化,过去启动的远期合约的价值也会发生变化。
为了说明远期合约的价值变化,请参考表1.6。在其他条件相同的情况下,对于金融价格$\Delta P$的每一次意外美元上涨,以较低的远期价格购买(远期)标的金融工具的协议会增加预期公司价值$\Delta V$。另外,表1.6显示,以较低的远期价格出售(远期卖空)标的金融工具的协议会降低预期的公司价值。如果标的金融工具的价格在合约到期前上涨(下跌),远期合约多头(空头)就会从合约中获利。图表还显示,购买和出售完全相同的远期合约会产生一个组合头寸,使公司价值对基础价格(横轴)的意外变化不敏感。比较表1.5和表1.6,表1.5中的商业风险概况与短期远期合约的风险概况相同。为了对冲风险或使公司对基础价格的意外变化不敏感,公司应该签订长期远期合约(见表1.6)。
远期合约的一个特点是,信用风险或违约风险隐含在延迟交割的履行是双向的。违约风险是真实存在的,因为大多数远期合约都是通过实物交割结算的。回想一下,远期合约的买方可以根据最初设定的远期价格和合约到期时标的价格获利或亏损。如果标的金融工具价格上涨(下跌),合约买方在远期合约上获利(亏损)。由于合约的价值只在合约到期时结算,而在合约开始时或在合约期间不付款,因此远期合约买方面临的信用风险是,当标的资产在现货市场上可以卖出更高的价格时,卖方将违约履行远期合约交割义务。同样,远期合约的卖方也面临着这样的信用风险:当标的资产可以在现货市场上以更低的价格购买时,买方将违约履行远期合约的支付义务。
将远期利率协议作为远期利率合约的一个例子。远期利率协议是一种协议,以预先确定的名义本金支付固定利率,并在合同到期时以相同的名义本金获得浮动利率现金流量。请注意,只有利息现金流量打算在合同到期时转手。如果浮动利率的收益高于合约开始时约定的固定利率成本,远期利率就会以现金形式获得差额。如果浮动利率收益低于签约时约定的固定利率成本,远期利率空头将以现金形式获得差额。如果在合约有效期内利率上升或固定收益价格下跌,远期利率就会上涨。远期利率协议的现金流图如图1.7所示,其中$\bar{R}$是合同开始时0时刻设定的固定利率,$\tilde{R}$是合同到期日$t$时刻实现的实际利率。

金融代写|金融衍生品代写Financial Derivatives代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。