如果你也在 怎样代写missing data这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。missing data在统计学中,当观察中的变量没有存储数据值时,就会出现缺失数据,或缺失值。缺失数据是一种常见的现象,对从数据中得出的结论会有很大的影响。
missing data缺失数据的发生可能是由于无应答:没有为一个或多个项目或整个单位(”主体”)提供信息。有些项目比其他项目更有可能产生无应答现象:例如关于收入等私人主题的项目。损耗是一种可能发生在纵向研究中的缺失–例如研究发展,在一定时期后重复测量。当参与者在测试结束前退出,并且有一个或多个测量项目缺失时,就会出现缺失现象。
my-assignmentexpert™missing data作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的missing data作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此missing data作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在missing data代写方面经验极为丰富,各种missing data相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的missing data及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|missing data代考|Motivation
The idea behind weighting is simple: to make the respondents as similar as possible to the original sample in terms of the distribution of some variables. Suppose that in a sample of size 100 , there were 60 women and 40 men. Among the 60 women, suppose 40 provided information on income, while only 10 among the 40 men provided income. Clearly, the respondents providing income have lost their original representation on gender. If the analysis is restricted to respondents, then bias may be introduced, especially if the income is correlated with gender. To compensate or correct for the loss of representation, a weight of $60 / 40=3 / 2=1.5$ is attached to each responding woman and a weight of $40 / 10=4$ is attached to each responding man. With these weights, the respondents are now weighted back to the original sample representation of 60 women and 40 men. The numbers $1.5$ and 4 are called nonresponse adjustment weights and the two cells formed based on gender are the adjustment cells.
In a probabilistic framework, 40 women respondents can be viewed as a subsample of 60 women with the selection probability $2 / 3$, and 10 men as a subsample 40 men with the selection probability $1 / 4$. That is, 50 respondents have been subsampled from 100 subjects in the original sample with varying probabilities of selection, and the weights are proportional to the inverse of these probabilities. These probabilities are called response probabilities or propensities. Women have a response propensity of $2 / 3$ and men, $1 / 4$.
A study design yielding the observed data may be viewed as an approximate two-phase sample design, where in the first phase 100 subjects were selected and asked gender. In the second phase, a subsample of women and men were selected with the stated probabilities and income was ascertained. The two-phase or multiphase design is a very common in many large scale surveys. These designs have appeared in econometric literature and in biostatistics in more recent times. The two-phase approximation is useful for creating appropriate inferences.
数学代写|missing data代考|Adjustment Cell Method
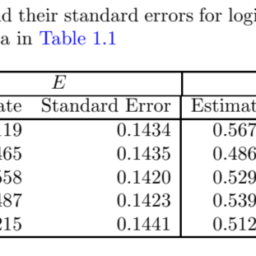
Consider the data presented in Table 1.1. There are four adjustment cells defined by $D$ and $E$. The number of respondents is 212 and nonrespondents is 87 in the cell $D=0, E=0$. The weights for each of the 212 respondents will be $w_{1}=(212+87) / 212=1.4104$. The weight for 170 respondents in the $D=0, E=1$ is $w_{2}=(170+99) / 170=1.5198$. Similarly the weights for the 97 respondents in the cell $D=1, E=0$ is $w_{3}=1.4949$ and for $D=1, E=1$ is $w_{4}=1.0669$.
A weighted logistic regression (for example, PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC in SAS) can be fit to the complete cases to compensate for differential response rates across these 4 cells. The weighted estimates and their standard errors are $\widehat{\beta}{o}=-0.5306(0.1281), \widehat{\beta{1}}=0.4287(0.1693)$ and $\widehat{\beta}_{2}=0.5477(0.0903)$. The weighted estimates are close to the before-deletion data set estimates. The standard errors are obviously larger than the complete-data standard errors.
The adjustment cells, generally, are formed by creating a cross-classification of variables measured on both respondents and nonrespondents. Continuous variables are categorized. With many variables, the cross classification may create a sparse table and, hence, highly variable weights. The cells have to be collapsed to make the estimated response rate stable enough to construct the weights. A random effect model could be used to estimate the cell-specific response rates by smoothing or shrinking the cell-specific estimates towards the overall estimate. Thus, the development of nonresponse adjustment weights is problem specific. A general purpose approach for developing weights is based on the propensity score methods.
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|Response Propensity Model
Consider an observational study to evaluate the effect of a binary treatment or exposure variable on the outcome. In the absence of randomization, the propensity scores are often used to create balanced groups of treated and untreated subjects, and then the distribution of the outcome variable is compared across these homogeneous groups.The situation is similar here where the response indicator $R$ is the “treatment” or “exposure” (with $R=1$ denoting respondents and $R=0$ for nonrespondents) and $X$ is set of covariates available for respondents and nonrespondents. A response propensity is the probability of $R=1$ expressed as a function of $X$.
Considerable literature in survey methodology is devoted to understand the nature of the relationship between $R$ and $X$. If one were interested in trying to increase the response rates, variables $X$ that can be subjected to experimentation (intervened) is of considerable interest. Thus, the study of relationship between $R$ and $X$ is of considerable interest on its own merit for developing design modifications to improve the response rates.
The goal of adjustment, however, is different. Attempt is being made to reduce nonresponse bias in the inference “after-the-fact.” This is similar to the analysis of observational study where $R$ is a treatment or exposure indicator and has not been randomized except that in the missing data problem the “null hypothesis” of no difference between the respondents (treated or exposed) and nonrespondents (untreated or unexposed) is assumed to be true (MAR conditional on the response propensity). It is important therefore to include in $X$, not only the variables that explain differences between $R=1$ and $R=0$, but also make the null hypothesis of no differences in $f(Y \mid R=0, X)$ and $f(Y \mid R=1, X)$ plausible. Thus, the focus of the selection of $X$ should be on those that are related to both $R$ and $Y$. In other words, the goal is to achieve independence between $R$ and $Y$ conditional on $X$.
missing data代写
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|MOTIVATION
加权背后的想法很简单:使受访者在某些变量的分布方面尽可能与原始样本相似。假设在大小为 100 的样本中,有 60 名女性和 40 名男性。在这 60 名女性中,假设 40 人提供了收入信息,而 40 名男性中只有 10 人提供了收入信息。显然,提供收入的受访者已经失去了原来的性别代表性。如果分析仅限于受访者,则可能会引入偏见,尤其是在收入与性别相关的情况下。为了补偿或纠正代表权的损失,权重为60/40=3/2=1.5附在每个响应的女人身上,重量为40/10=4附在每个响应的人身上。有了这些权重,受访者现在被加权到 60 名女性和 40 名男性的原始样本表示。号码1.5和 4 称为无响应调整权重,根据性别形成的两个单元格是调整单元格。
在概率框架中,40 位女性受访者可以被视为具有选择概率的 60 位女性的子样本2/3, 10 个人作为子样本 40 个人具有选择概率1/4. 也就是说,从原始样本中的 100 名受试者中以不同的选择概率对 50 名受访者进行了二次抽样,并且权重与这些概率的倒数成正比。这些概率称为响应概率或倾向。女性有反应倾向2/3和男人,1/4.
产生观察数据的研究设计可以被视为近似的两阶段样本设计,其中在第一阶段选择了 100 名受试者并询问性别。在第二阶段,按照规定的概率选择女性和男性的子样本,并确定收入。两阶段或多阶段设计在许多大规模调查中非常常见。这些设计最近出现在计量经济学文献和生物统计学中。两阶段近似对于创建适当的推论很有用。
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|ADJUSTMENT CELL METHOD
考虑表 1.1 中的数据。有四个调整单元格定义为D和和. 单元格中的受访者人数为 212 人,非受访者人数为 87D=0,和=0. 212 名受访者的权重分别为在1=(212+87)/212=1.4104. 170名受访者的权重D=0,和=1是在2=(170+99)/170=1.5198. 同样,单元格中 97 名受访者的权重D=1,和=0是在3=1.4949并且对于D=1,和=1是在4=1.0669.
加权逻辑回归F这r和X一种米pl和,磷R这C小号在R在和是大号这G一世小号吨一世C一世n小号一种小号可以适合完整的案例,以补偿这 4 个单元格的不同响应率。加权估计值及其标准误为 $\widehat{\beta} {o}=-0.53060.1281, \widehat{\beta {1}}=0.42870.1693一种nd\widehat{\beta}_{2}=0.54770.0903美元。加权估计接近于删除前的数据集估计。标准误明显大于完整数据标准误。
通常,调整单元是通过对受访者和非受访者测量的变量进行交叉分类而形成的。连续变量被分类。对于许多变量,交叉分类可能会创建一个稀疏表,因此会产生高度可变的权重。必须折叠单元以使估计的响应率足够稳定以构建权重。随机效应模型可用于通过将特定于细胞的估计值平滑或缩小到总体估计值来估计特定于细胞的响应率。因此,不答复调整权重的制定是针对特定问题的。开发权重的通用方法是基于倾向得分方法。
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|RESPONSE PROPENSITY MODEL
考虑一项观察性研究来评估二元治疗或暴露变量对结果的影响。在没有随机化的情况下,倾向得分通常用于创建治疗和未治疗受试者的平衡组,然后在这些同质组之间比较结果变量的分布。这里的情况与反应指标相似R是“治疗”还是“暴露”在一世吨H$R=1$d和n这吨一世nGr和sp这nd和n吨s一种nd$R=0$F这rn这nr和sp这nd和n吨s和X是一组可供受访者和非受访者使用的协变量。反应倾向是R=1表示为X.
调查方法中的大量文献致力于了解两者之间关系的性质R和X. 如果有人有兴趣尝试提高响应率,变量X可以进行实验的一世n吨和r在和n和d具有相当大的兴趣。因此,研究两者之间的关系R和X在开发设计修改以提高响应率方面,它本身具有相当大的优势。
然而,调整的目标是不同的。正在尝试减少“事后”推断中的不响应偏差。这类似于观察性研究的分析,其中R是一个治疗或暴露指标,除了在缺失数据问题中,受访者之间没有差异的“零假设”之外没有被随机化吨r和一种吨和d这r和Xp这s和d和未答复者在n吨r和一种吨和d这r在n和Xp这s和d假定为真米一种RC这nd一世吨一世这n一种l这n吨H和r和sp这ns和pr这p和ns一世吨是. 因此,重要的是包含在X,不仅是解释两者之间差异的变量R=1和R=0,但也做出无差异的零假设F(是∣R=0,X)和F(是∣R=1,X)似是而非。因此,选择的重点X应该在与两者相关的那些上R和是. 换句话说,目标是实现彼此之间的独立性R和是有条件的X.

数学代写|missing data代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。