如果你也在 怎样代写自然语言处理Natural Language Processing学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。自然语言处理Natural Language Processing是一个用于机器学习和人工智能的免费和开源的软件库。它可以用于一系列的任务,但特别专注于深度神经网络的训练和推理。
自然语言处理Natural Language Processing是语言学、计算机科学和人工智能的一个子领域,涉及计算机和人类语言之间的互动,特别是如何为计算机编程以处理和分析大量的自然语言数据。其目标是使计算机能够 “理解 “文件的内容,包括文件中语言的上下文细微差别。然后,该技术可以准确地提取文件中的信息和见解,并对文件本身进行分类和组织。
my-assignmentexpert™自然语言处理Natural Language Processing代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的自然语言处理Natural Language Processing作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此自然语言处理Natural Language Processing作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在机器学习Machine Learning代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的机器学习Machine Learning代写服务。我们的专家在自然语言处理NLP代写方面经验极为丰富,各种自然语言处理NLP相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的自然语言处理NLP及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|GATES
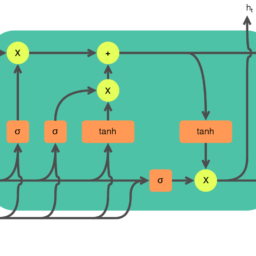
Quantifying changes in hidden state dynamics is one technique for providing explanations in recurrent networks (Strobelt et al., 2017). Such explanations are at the level of continuous output and are discussed in Chapter 7. In this chapter, I discuss explanations based on gate activations. Gates, however, are in some sense not easily interpretable. They add parameters to neural networks, and introduce nonlinear computations that are hard to comprehend holistically. For this reason, researchers have suggested using uptraining methods to interpret gated recurrent networks, e.g., Hou and Zhou (2020). On the other hand, gate activations have been widely used to visualize the inner working of recurrent networks, especially in the context of synthetic (formal) languages (Suzgun et al., 2019; Weiss et al., 2018). Lakretz et al. (2019) visualize gate dynamics to show how language models encode linguistic properties Ghaeini et al. (2018) compare visualizations of input, forget, and output gate activations with attention in natural language inference models. Wang and Jiang (2016) used visualizations of forget gates to arrive at the conclusion that recurrent architectures for natural language inference worked by remembering important mismatches, useful for predicting contradictions, while forgetting matching phrases.
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|ATTENTION
While there have been several papers that try to use gate values as a vehicle to understand recurrent networks, attention (Bahdanau et al., 2015; Vaswani et al., 2017) has attracted the mostwell, attention. Even in the seminal paper of Bahdanau et al. (2015), attention was used to shed light on the inner workings of a machine translation architecture. Subsequently, dozens of researchers have used attention weights to analyze the inner workings of recurrent and transformer architectures; see, for example, Rei and Søgaard (2018) for a comparison of gradient-based and attention-based analyses across sentiment analysis and grammatical error correction. While the extent to which attention faithfully represents input token importance has been subject of debate (Serrano and Smith, 2019), attention is still widely used to provide explanations (Bastings and Fillippova, 2020).
Jain and Wallace (2019) show that attention is often uncorrelated with gradient-based saliency scores, and completely different set of attention weights often result in the same predictions. This was also shown in Serrano and Smith (2019), and Moradi et al. (2019) showed similar results for machine translation. Pruthi et al. (2020a) explicitly showed how to manipulate attention weights to provide deceitful explanations without hurting performance.
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|ATTENTION ROLL-OUT AND ATTENTION FLOW
In multi-layer transformer architectures, information about input tokens is quickly mixed, and attention weights at different layers can therefore be unreliable if not interpreted properly. Attention flow and layer-wise attention training $(\S 5.4)$ are methods for computing more reliable attention weights. Abnar and Zuidema (2020) propose two different algorithms for this: attention roll-out and attention flow.
In attention roll-out, Abnar and Zuidema (2020) compute the attention associated with a particular position, i.e., a particular time step $t$ at some layer $l$ by an attention head $h, \mathbf{A}{h(t)}^{l}$, by summing over all multiplications of edge weights along a path connecting the current position with higher (connected) positions in the network. In attention flow, in contrast, maximum flow values are used to represent attention. This means that to compute $\mathbf{A}{h(t)}^{l}$, we rely on the maximum path, i.e., the largest multiplication of edge weights, rather than the sum of all possible path weights.
Both methods lead to less mixed attention weights at higher layers, i.e., more distinct attention patterns. The authors show that roll-out and maximum flow values correlate much better than raw attention weights – with both gradient-based methods and the effect of leaving out input tokens on output. Attention roll-out is faster than attention flow, and the evaluations in Abnar and Zuidema (2020) suggest that there is little reason to choose attention flow over attention roll-out. DeRose et al. (2020) present a similar method for backward computation of attention flow, as well as per-instance visualizations thereof.
自然语言处理代写
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|GATES
量化隐藏状态动态的变化是在循环网络中提供解释的一种技术小号吨r○b和l吨和吨一个l.,2017. 这种解释处于连续输出的水平,在第 7 章中进行了讨论。在本章中,我将讨论基于门激活的解释。然而,盖茨在某种意义上是不容易解释的。他们向神经网络添加参数,并引入难以整体理解的非线性计算。出于这个原因,研究人员建议使用提升训练方法来解释门控循环网络,例如,Hou 和 Zhou2020. 另一方面,门激活已被广泛用于可视化循环网络的内部工作,特别是在合成的上下文中F○r米一个l语言小号在和G在n和吨一个l.,2019;在和一世ss和吨一个l.,2018. 拉克雷茨等人。2019可视化门动力学以显示语言模型如何编码语言属性 Ghaeini 等人。2018将输入、遗忘和输出门激活的可视化与自然语言推理模型中的注意力进行比较。王和江2016使用遗忘门的可视化得出的结论是,自然语言推理的循环架构通过记住重要的不匹配来工作,这对于预测矛盾很有用,同时忘记了匹配的短语。
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|ATTENTION
虽然有几篇论文试图使用门值作为理解循环网络的工具,但注意乙一个Hd一个n一个在和吨一个l.,2015;在一个s在一个n一世和吨一个l.,2017已经吸引了最多的关注。即使在 Bahdanau 等人的开创性论文中。2015,注意力被用来阐明机器翻译架构的内部工作原理。随后,数十名研究人员使用注意力权重来分析循环和变压器架构的内部工作原理;例如,参见 Rei 和 Søgaard2018用于在情感分析和语法错误校正中比较基于梯度和基于注意力的分析。虽然注意力在多大程度上忠实地代表了输入令牌的重要性,但一直存在争议小号和rr一个n○一个nd小号米一世吨H,2019,注意力仍然被广泛用于提供解释乙一个s吨一世nGs一个ndF一世ll一世pp○在一个,2020.
耆那教和华莱士2019表明注意力通常与基于梯度的显着性分数不相关,并且完全不同的注意力权重集通常会导致相同的预测。这也显示在塞拉诺和史密斯2019,和莫拉迪等人。2019显示了机器翻译的类似结果。普鲁蒂等人。2020一个明确展示了如何操纵注意力权重以提供欺骗性的解释而不损害性能。
机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考|ATTENTION ROLL-OUT AND ATTENTION FLOW
在多层转换器架构中,有关输入标记的信息会迅速混合,因此如果解释不当,不同层的注意力权重可能会不可靠。注意力流和分层注意力训练§(§5.4)是计算更可靠的注意力权重的方法。阿布纳尔和祖德玛2020为此提出了两种不同的算法:注意力推出和注意力流。
在注意力推广中,Abnar 和 Zuidema2020计算与特定位置相关的注意力,即特定时间步长吨在某一层l通过注意力头 $l$ by an attention head $h, \mathbf{A}{h(t)}^{l}$, by summing over all multiplications of edge weights along a path connecting the current position with higher (connected) positions in the network. In attention flow, in contrast, maximum flow values are used to represent attention. This means that to compute $\mathbf{A}{h(t)}^{l}$,我们依赖于最大路径,即边权重的最大乘法,而不是所有可能路径权重的总和。
这两种方法都导致较高层的注意力权重混合较少,即注意力模式更加明显。作者表明,与原始注意力权重相比,roll-out 和最大流量值的相关性要好得多——同时具有基于梯度的方法和省略输入标记对输出的影响。Attention roll-out 比 attention flow 快,在 Abnar 和 Zuidema 中的评估2020表明几乎没有理由选择注意力流而不是注意力推出。德罗斯等人。2020提出了一种用于注意力流反向计算的类似方法,以及每个实例的可视化。

机器学习代写|自然语言处理代写NLP代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。