如果你也在 怎样代写Network CITS3002这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。Network网络由两台或更多的计算机组成,它们被连接起来,以共享资源(如打印机和光盘),交换文件,或允许电子通信。网络上的计算机可以通过电缆、电话线、无线电波、卫星或红外线光束连接。
Network网络,一种具有网络理论研究属性的图无尺度网络,一个学位分布遵循幂律的网络小世界网络,一种数学图形,其中大多数节点不是邻居,但有共同的邻居流量网络,一个有向图,每条边都有一个容量,每条边都接受一个流量。
Network代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的Network作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此Network作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在计算机Quantum computer代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的计算机Quantum computer代写服务。我们的专家在Network代写方面经验极为丰富,各种Network相关的作业也就用不着 说。
计算机代考|Network作业代写|MULTIACCESS NETWORKS
Developed in the mid-1970s by researchers at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC), the Ethernet eventually became the dominant local area networking technology, emerging from a pack of competing technologies. Today, it competes mainly with $802.11$ wireless networks but remains extremely popular in campus networks and datacenters. The more general name for the technology behind the Ethernet is Carrier Sense, Multiple Access with Collision Detect (CSMA/CD).
As indicated by the CSMA name, the Ethernet is a multiple-access network, meaning that a set of nodes sends and receives frames over a shared link. You can, therefore, think of an Ethernet as being like a bus that has multiple stations plugged into it. The “carrier sense” in CSMA/CD means that all the nodes can distinguish between an idle and a busy link, and “collision detect” means that a node listens as it transmits and can therefore detect when a frame it is transmitting has interfered (collided) with a frame transmitted by another node.
The Ethernet has its roots in an early packet radio network, called Aloha, developed at the University of Hawaii to support computer communication across the Hawaiian Islands. Like the Aloha network, the fundamental problem faced by the Ethernet is how to mediate access to a shared medium fairly and efficiently (in Aloha, the medium was the atmosphere, while in the Ethernet, the medium was originally a coax cable). The core idea in both Aloha and the Ethernet is an algorithm that controls when each node can transmit.
Modern Ethernet links are now largely point-to-point; that is, they connect one host to an Ethernet switch, or they interconnect switches. As a consequence, the “multiple-access” algorithm is not used much in today’s wired Ethernets, but a variant is now used in wireless networks, such as $802.11$ networks (also known as Wi-Fi). Due to the enormous influence of Ethernet, we chose to describe its classic algorithm here and then explain how it has been adapted to Wi-Fi in the next section. We will also discuss Ethernet switches elsewhere. For now, we will focus on how a single Ethernet link works.
计算机代考|Network作业代写|Physical Properties
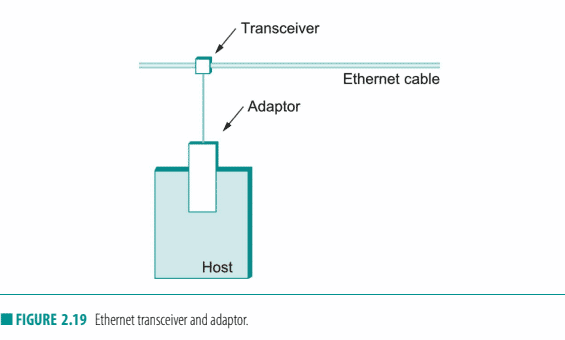
Ethernet segments were originally implemented using coaxial cable of length up to $500 \mathrm{~m}$. (Modern Ethernets use twisted copper pairs, usually a particular type known as “Category 5,” or optical fibers, and in some cases can be quite a lot longer than $500 \mathrm{~m}$.) This cable was similar to the type used for cable TV. Hosts connected to an Ethernet segment by tapping into it. A transceiver, a small device directly attached to the tap, detected when the line was idle and drove the signal when the host was transmitting. It also received incoming signals. The transceiver, in turn, connected to an Ethernet adaptor, which was plugged into the host. This configuration is shown in Figure 2.19.
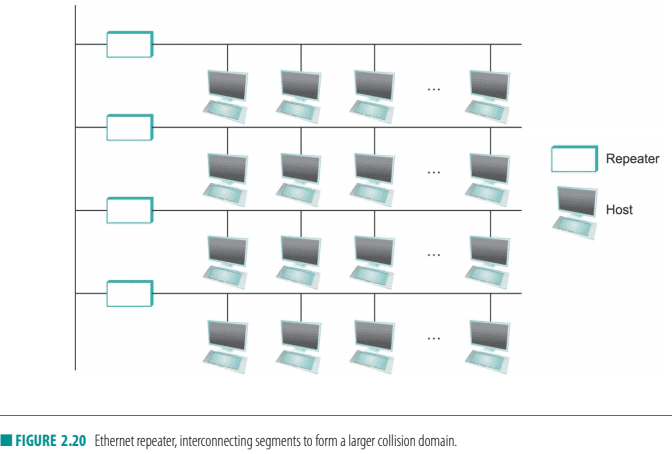
Multiple Ethernet segments can be joined together by repeaters (or a multiport variant of a repeater, called a $h u b$ ). A repeater is a device that forwards digital signals, much like an amplifier forwards analog signals; repeaters do not understand bits or frames. No more than four repeaters could be positioned between any pair of hosts, meaning that a classical Ethernet had a total reach of only $2500 \mathrm{~m}$. For example, using just two repeaters between any pair of hosts supports a configuration similar to the one illustrated in Figure 2.20; that is, a segment running down the spine of a building with a segment on each floor.
Any signal placed on the Ethernet by a host is broadcast over the entire network; that is, the signal is propagated in both directions, and repeaters and hubs forward the signal on all outgoing segments. Terminators attached to the end of each segment absorb the signal and keep it from bouncing back and interfering with trailing signals. The original Ethernet specifications used the Manchester encoding scheme described in an earlier section, while 4B/5B encoding (or the similar $8 \mathrm{~B} / 10 \mathrm{~B}$ scheme) is used today on higher-speed Ethernets.
It is important to understand that whether a given Ethernet spans a single segment, a linear sequence of segments connected by repeaters, or multiple segments connected in a star configuration, data transmitted by any one host on that Ethernet reach all the other hosts. This is the good news. The bad news is that all these hosts are competing for access to the same link, and, as a consequence, they are said to be in the same collision domain. The multiaccess part of the Ethernet is all about dealing with the competition for the link that arises in a collision domain.
Network作业代写
计算机代考|NETWORK作业代写|MULTIACCESS NETWORKS
由施乐帕洛阿尔托研究中心的研究人员于 1970 年代中期开发 $P A R C$ ,以太网最終成为主导的局域网技术,从一系列竞争技术中脱颖而出。今天,它主要与 $802.11$ 无线网络,但在校园网络和数据中心中仍然非常流行。以太网背后技术的更通用名称是载波侦听、多路访问和冲突检测 $C S M A / C D$.
正如 CSMA名称所示,以太网是一个多路访问网络,这意味着一组节点通过共享链路发送和接收帧。因此,您可以将以太网视为揷入了多个站点的总线。CSMA/CD 中的“载波侦听”意味着所有节点都可以区分空闲和㸼忙的链路,而“冲突检测”意味着节点在传输时进行侦听,因此可以检测到它正在传输的帧何时受到干扰 collided与另一个节点发送的帧。
以太网起源于早期的分组无线电网络,称为 Aloha,由夏威夷大学开发,用于支持夏威夷群岛的计算机通信。与Aloha 网络一样,以太网面临的根本问题是如何公 平有效地调解对共字介质的访问 inAloha, themediumwastheatmosphere, whileintheEthernet, themediumwasoriginallyacoaxcable. Aloha 和以太网的 核心思想是控制每个节点何时可以传输的算法。
现代以太网链路现在主要是点对点的。也就是说,它们将一台主机连接到以太网交换机,或者它们互连交换机。因此, “多路访问”算法在当今的有线以太网中使用 不多,但现在在无线网络中使用了一种变体,例如802.11网络alsoknownasWi-Fi. 由于以太网的巨大影响,我戈 节解释它是如何适应Wi-Fi的。我们还将在别处讨论以太网交换机。现在,我们将关注单个以太网链路的工作原理。
计算机代考|NETWORK作业代写|PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
以太网段最初是使用长度可达的同轴电跕实现的 $500 \mathrm{~m}$.
ModernEthernetsusetwistedcopperpairs, usuallyaparticulartypeknownas “Category5, “oropticalfibers, andinsomecasescanbequitealotlongerthan 这种电跕类似于用于有线电视的类型。主机通过接入以太网段连接到它。收发器,一种直接连接到分接头的小型设备,在线路空闲时检测并在主机传输时驱动信 号。它还接收传入信号。收发器依次连接到揷入主机的以太网适配器。此配置如图 $2.19$ 所示。
多个以太网段可以通过中继器连接在一起oramultiportvariantofarepeater, calleda\$hub\$. 中继器是一种转发数字信号的设备,就像放大器转发模拟信号一
样;中继器不理解位或帧。任何一对主机之间最多只能放置四个中继器,这意味着传统以太网的总覆盖范围仅为 $2500 \mathrm{~m}$. 例如,在任何一对主机之间仅使用两个中
继器支持类似于图 $2.20$ 中所示的配置;也就是说,沿着建筑物的娄椎延伸的一段,每层都有一段。
主机放置在以太网上的任何信号都会在整个网络上广播;也就是说,信号在两个方向上传播,中继器和集线器在所有传出段上转发信号。连接到每个段末端的终结 J间速以太网。
重要的是要了解给定的以太网是否跨越单个分段、由中继器连接的线性分段序列,或以星形配置连接的多个分段,以太网上任何一个主机传输的数据都会到达所有 其他主机。的链路竞争。

计算机代考|Network作业代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

