如果你也在 怎样代写数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing EE4015这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing是指使用数字处理,如通过计算机或更专业的数字信号处理器,来执行各种信号处理操作。以这种方式处理的数字信号是一连串的数字,代表时间、空间或频率等领域中连续变量的样本。在数字电子学中,数字信号被表示为脉冲序列,它通常由晶体管的开关产生。
数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing模拟信号处理是信号处理的子领域。DSP的应用包括音频和语音处理、声纳、雷达和其他传感器阵列处理、频谱密度估计、统计信号处理、数字图像处理、数据压缩、视频编码、音频编码、图像压缩、电信的信号处理、控制系统、生物医学工程和地震学等。数字信号处理器(DSP)将现实世界的信号,如语音、音频、视频、温度、压力或位置,经过数字化处理,然后以数学方式处理它们。数字信号处理器被设计用于快速执行数学功能,如 “加”、”减”、”乘 “和 “除”。
数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。最高质量的数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此数字信号处理Digital Signal Processing作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在电子代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的电子代写服务。我们的专家在电路基础Circuit Fundamentals代写方面经验极为丰富,各种电路基础Circuit Fundamentals相关的作业也就用不着说。
电子代写|数字信号处理代写Digital Signal Processing代考|Codes and Sequences Used in Communication Systems
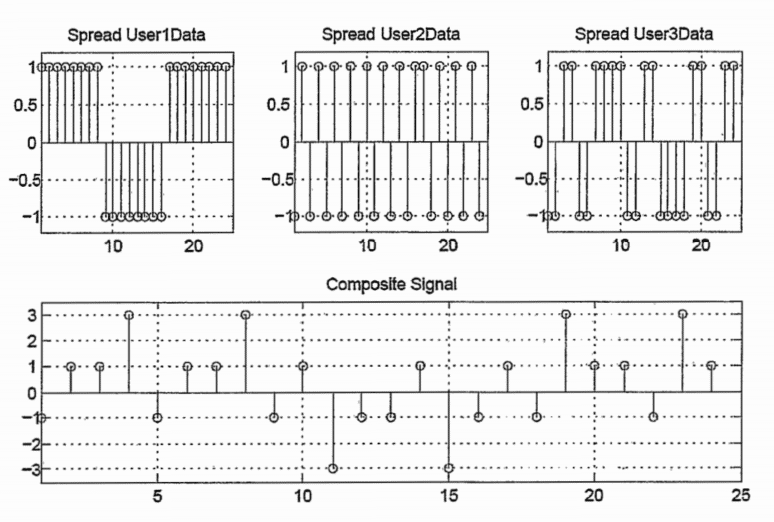
Correlators are heavily used in direct sequence spread spectrum, or DSSS, communication systems, which have found great utility in military applications and later in communication standards such as CDMA, WCDMA and WLAN $802.11 \mathrm{~b}$.
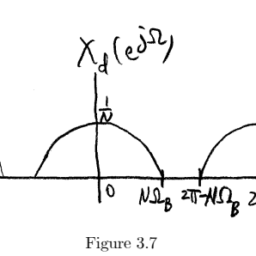
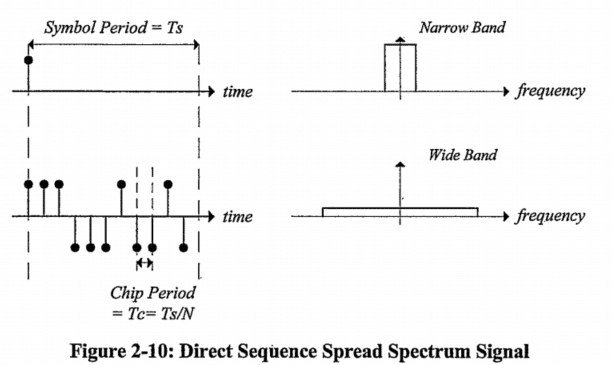
The basic premise is to replace a data symbol, which extends over a period $T_{\mathrm{s}}$, with a specific code sequence of $N$ other symbols. These other symbols, also called chips, feature a chip period of $T_{\mathrm{s}} / N$, which naturally leads to a spreading effect on the signal bandwidth, as seen in the figure above. The process of replacing a data symbol by such a sequence is called spreading, while the recovery of the original data symbol by the correlator is called despreading. What appears to be a waste of bandwidth to the casual observer was advantageous in the battlefield. The despreading process mitigated the effect of enemy jamming signals that had previously wiped out the narrow band version of the communication link.
Eventually, the technology made it into commercial cell phone systems that needed to share the same frequency band with older narrow band cell phone infrastructures. These older narrow band cell phone signals looked just like jammers to the spread DSSS waveforms. The commercial implementation, called code division multiple access, or CDMA, also allowed several users to communicate over the same spread bandwidth via orthogonal spreading codes.
The spread waveforms have a further advantage over their narrow band counterparts regarding multipath distortion. In mobile communication systems, transmitted RF signals tend to take different paths by bouncing off different objects to reach the receiver antenna. This multipath effect introduces linear distortion into the older narrow band signals and can only be counteracted by the use of sophisticated equalization schemes. Whereas such equalizers can at best attempt to mitigate multipath distortion, a device called a Rake receiver (used specifically for spread signals) can actually take advantage of the multiple incoming spread signals by cleverly combining them. Because of these and other advantages, wide band communication systems like CDMA and WCMDA all but took over the cell phone industry. Today, the new $4 \mathrm{G}$ cell phone architecture called LTE uses a different scheme called OFDM, or orthogonal frequency division multiplexing.
电子代写|数字信号处理代写Digital Signal Processing代考|The Fourier Transform
The Fourier transform [3], or $F T$, is one of the most powerful numerical techniques used in the field of digital signal processing and analysis. In the realm of communication engineering, its purpose is to find the frequency representation of a time domain test signal $x(t)$, which may be either real or complex. The Fourier transform accomplishes this task by detecting the presence of complex sinusoids, $e^{j 2 \pi f t}$, inside this time domain signal. The detection happens via the correlation process that was the focus of the last section.
$$
X(f)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \cdot\left(e^{j 2 \pi f t}\right)^* d t
$$
The FT output, $X(f)$, indicates the magnitude and orientation (phase) of the detected complex sinusoid. The Fourier transform calculation may be repeated at many different frequencies, $f$, to produce the spectrum of the signal under test $x(t)$. In the following sections, we will examine several variants of the Fourier transform.
$\text { CTFT } \rightarrow$ The continuous time Fourier transform is primarily an academic tool used to familiarize ourselves with the behavior and properties of the transform. Given that we generally find the transform result via closed form integration, it does not allow us to easily compute the spectrum of just any arbitrary test signal $x(t)$.
$\text { DTFT } \rightarrow$ The discrete time Fourier transform is the discretized counterpart to the CTFT. It requires a sampled input sequence, $x[n]$, which invariably changes the computational problem from one of integration to one of summation. Whereas the input sequence, $x[n]$, must be sampled at discrete time instances, the frequency $f$ at which $X(f)$ is evaluated is continuous between the Nyquist frequency bounds. In plain English: Feel free to evaluate the DTFT at any frequency between $\pm F_{\text {sampling }} / 2$. The DTFT is easily computed for any arbitrary test sequences, $x[n]$, given the fact that we use summation rather than the more cumbersome integration of the CTFT.
数字信号处理代写
电子代写|数字信号处理代写数字信号处理代写|通信系统中使用的代码和序列
直接序列扩频或DSSS通信系统中大量使用了相关器,这些系统在军事应用中发现了巨大的效用,后来在CDMA、WCDMA和WLAN 802.11美元\mathrm{~b}$等通信标准中也有应用。
其基本前提是用N$其他符号的特定编码序列来代替一个在$T_{mathrm{s}}$期间延伸的数据符号。这些其他符号也被称为芯片,其芯片周期为$T_{mathrm{s}}/N$,这自然导致了数据符号和芯片之间的关系。/ N$,这自然导致了对信号带宽的扩散效应,如上图所示。用这样的通信链路替换一个数据符号的过程。
最终,该技术进入了商业手机系统,需要与老式窄带手机基础设施共享同一频段。这些旧的窄带手机信号对于传播的DSSS波形来说就像干扰器。被称为码分多址或CDMA的商业实现,也允许几个用户通过正交扩频码在同一扩频带宽上通信。
在多径失真方面,传播波形比它们的窄带同行有进一步的优势。在移动通信系统中,传输的射频信号往往采取不同的路径,从不同的物体上反弹到达接收天线。这种多径效应将线性失真引入旧的窄带信号,只能通过使用复杂的均衡方案来抵消。虽然这种均衡器充其量只能试图缓解多径效应,但像CDMA和WCMDA这样的宽频通信系统却完全接管了手机行业。今天,被称为LTE的新的4美元/mathrm{G}$手机架构使用一种不同的方案,称为OFDM,即正交频分复用。
电子代写|数字信号处理代写数字信号处理代写傅里叶变换
傅里叶变换
3
或$F T$,是数字信号处理和分析领域中最强大的数字技术之一。在通信工程领域,其目的是为了
找到时域测试信号$x(t)$的频率表示,它可能是实数或复数。傅里叶比变换完成了这一任务,它检测了
$$
X(f)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \cdot\left(e^{j 2 \pi f t}\right) ^* d t
$$
频率,$f$,以产生被测信号$x(t)$的频谱。在下面的章节中,我们将研究傅里叶变换的几个变种。
\傅里叶变换的几个变种:$$$${underline{\text { CTFT }}}。\backslash$ rightarrow xt.ذtext ${$ DTFT $}$ RightarrowThediscretetimeFouriertrans form ishediscretizedcounterparttheCT FT. 它需要一个采样的输入序列,$x$
$n$
的输入序列,这在很大程度上改变了从积分到求和的计算问题。在输入序列中,x
$n$
必须在极短的时间内进行采样,那么$mathrm{xf}$的频率是多少?
\2.DTFT的计算方法是:1. /2.对于任何一个任意的测试序列,$x$,DTFT都可以轻松计算出来。
$n$
\币,鉴于我们使用的是求和法,而不是CTFT的更繁琐的积分法。

电子代写|数字信号处理代写Digital Signal Processing代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。