数学代写| Conservation of energy 数值分析代考
数值分析代写
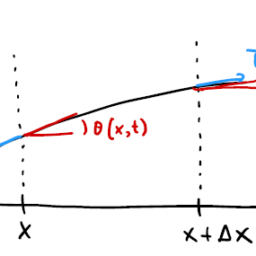
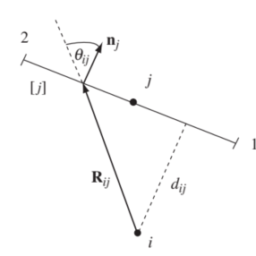
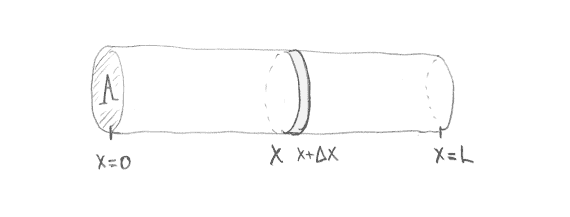
- The heat energy between $x$ and $x+\Delta x$ changes in time due only to:
- heat energy flowing across edges (at $x$ and $x+\Delta x$ )
- heat energy generated inside
This describes conservation of energy.
$\left[\begin{array}{c}\text { change in } \ \text { heat energy } \ \text { per unit time }\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c}\text { heat energy flowing } \ \text { across the boundaries } \ \text { per unit time }\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c}\text { heat energy generated } \ \text { in the interior } \ \text { per unit time \& volume }\end{array}\right]$
- The heat flux is a function $\phi(x, t)$ : the amount of thermal energy per unit time flowing to the right per unit surface area.
e.g. if $\phi(x, t)<0$ then heat flows to the left.
- The net heat flow per unit time for our thin slice is
$$
\phi(x, t) A-\phi(x+\Delta x, t) A .
$$ - Denote by $Q(x, t)$ internal sources of thermal energy,
- Then the conservation of energy becomes
$$
\frac{\partial}{\partial t}[e(x, t) A \Delta x] \approx \phi(x, t) A-\phi(x+\Delta x, t) A+Q(x, t) A \Delta x .
$$ - Divide by $A, \Delta x$, then take the limit $\Delta x \rightarrow 0$,
$$
\frac{\partial e}{\partial t}=-\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}+Q \text {. }
$$ - Heat energy e and the temperature $u$ are related by,
$$
e(x, t)=c(x) \rho(x) u(x, t)
$$ - $c(x)$ : specific heat
the amount of heat energy that must be applied to a unit mass of a substance to raise its tempurature one unit. - $c$ depends on the material, so let $c=c(x)$ as above. $c$ also depends on the temperature $u$ (i.e., $c=c(u, x)$ ) but it is approximately independent of temperature.
- $\rho(x)$ is the mass density indicating that the rod can be made of non-uniform material.
数值分析代考
- $x$ 和 $x+\Delta x$ 之间的热能随时间变化,仅由于:
- 流过边缘的热能(在 $x$ 和 $x+\Delta x$ 处)
2.内部产生的热能
这描述了能量守恒。
$\left[\begin{array}{c}\text { 变化 } \ \text { 热能 } \ \text { 每单位时间 }\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{ array}{c}\text { 热能流动} \ \text { 跨越边界} \ \text { 每单位时间}\end{array}\right]+\left[\begin{array}{c} \text { 产生的热能 } \ \text { 在内部 } \ \text { 每单位时间 \& 体积 }\end{array}\right]$
- 热通量是一个函数 $\phi(x, t)$ :每单位时间每单位表面积向右流动的热能量。
例如如果 $\phi(x, t)<0$ 则热量流向左侧。
- 我们的薄片单位时间的净热流是
$$
\phi(x, t) A-\phi(x+\Delta x, t) A 。
$$ - 用 $Q(x, t)$ 表示内部热能源,
- 那么能量守恒就变成了
$$
\frac{\partial}{\partial t}[e(x, t) A \Delta x] \approx \phi(x, t) A-\phi(x+\Delta x, t) A+Q(x, t) A \Delta x 。
$$ - 除以$A,\Delta x$,然后取极限$\Delta x \rightarrow 0$,
$$
\frac{\partial e}{\partial t}=-\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}+Q \text {. }
$$ - 热能 e 和温度 $u$ 相关,
$$
e(x, t)=c(x) \rho(x) u(x, t)
$$ - $c(x)$ : 比热
必须施加在单位质量的物质上以将其温度升高一个单位的热量。 - $c$ 取决于材料,因此如上令 $c=c(x)$。 $c$ 还取决于温度 $u$(即 $c=c(u, x)$ ),但它与温度大致无关。
- $\rho(x)$ 是质量密度,表明杆可以由非均匀材料制成。

数学代写| Chebyshev polynomials 数值分析代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
时间序列分析代写
统计作业代写
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程