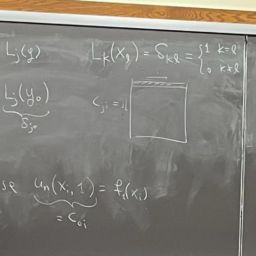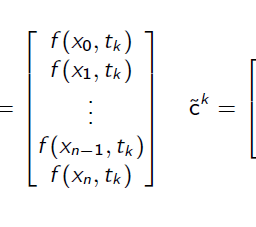数学代写| Chebyshev polynomials 数值分析代考
数值分析代写
Polynomial interpolants
- Suppose we are given $n+1$ distinct points $\left{x_{i}\right}_{i=0}^{n} \subset[a, b]$ and corresponding values $\left{f_{i}\right}_{i=0}^{n} \subset \mathbb{R}$.
- We wish to find a polynomial $p_{n} \in \mathcal{P}{n}$ such that $$ p{n}\left(x_{i}\right)=f_{i}
$$ - If $f_{i}$ are in fact values of some function $f$ at $x_{i}$, that is, $f_{i}=f\left(x_{i}\right)$, such a polynomial $p_{n}$ is called a polynomial interpolant of $f$.
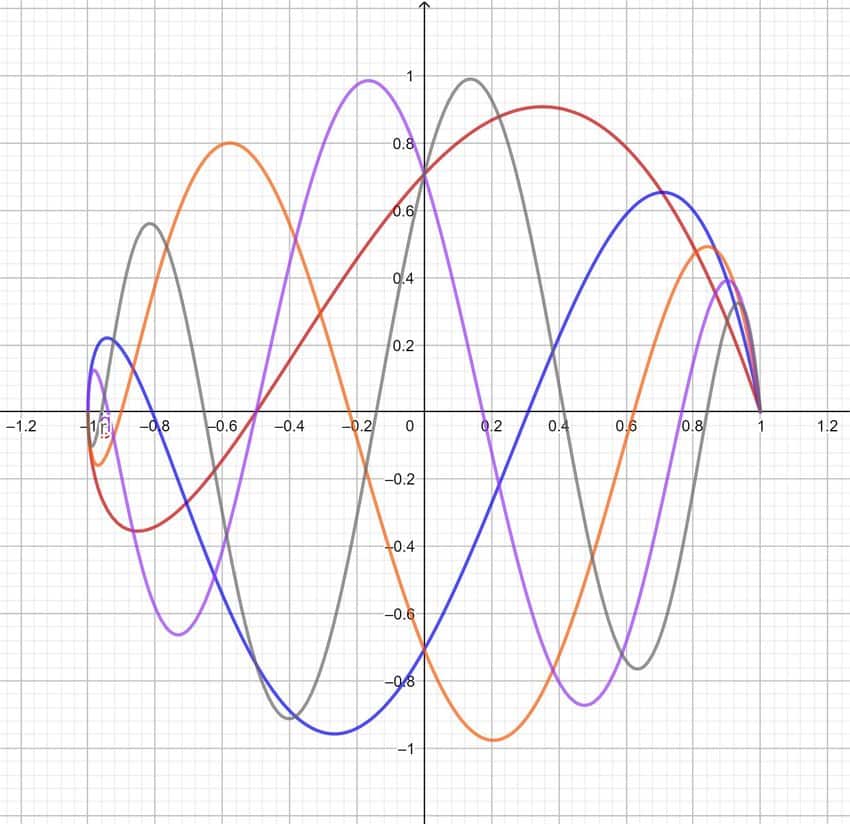
Lagrange polynomials
- To construct the interpolant, we make use of Lagrange polynomials $L_{j} \in \mathcal{P}{n}, j=0, \ldots, n$, that satisfies $$ L{j}\left(x_{i}\right)=\delta_{i j}, \quad \delta_{i j}= \begin{cases}1 & \text { if } i=j \ 0 & \text { otherwise. }\end{cases}
$$ - The interpolant $p_{n} \in \mathcal{P}{n}$ is then given by $$ p{n}(x)=\sum_{j=0}^{n} f_{j} L_{j}(x)
$$
Construction of Lagrange polynomials $L_{j}$
- Define the polynomial $\pi_{n+1} \in \mathcal{P}{n+1}$, $$ \pi{n+1}(x)=\left(x-x_{0}\right)\left(x-x_{1}\right) \cdots\left(x-x_{n}\right)=\prod_{i=0}^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right)
$$ - We define $\ell_{j}(x)$ as $\pi_{n+1}(x)$ divided by the factor $\left(x-x_{j}\right)$,
$$
\begin{aligned}
\ell_{j}(x) &=\frac{\pi_{n+1}(x)}{\left(x-x_{j}\right)} \
&=\prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j}^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right) \
&=\left(x-x_{0}\right) \cdots\left(x-x_{j-1}\right)\left(x-x_{j+1}\right) \cdots\left(x-x_{n}\right)
\end{aligned}
$$ - Dividing by $\ell_{j}\left(x_{j}\right)$, we have $L_{j}(x)$, that is,
$$
L_{j}(x)=\frac{\ell_{j}(x)}{\ell_{j}\left(x_{j}\right)}=\prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j}^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right) / \prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j}^{n}\left(x_{j}-x_{i}\right)
$$
数值分析代考
义公式$\pi_{n+1} \in \macal{P}{n+1}$, $$ \pi{n+1}(x)=\left(x-x_{0}\right) \左(x-x_{1}\right) \cdots\left(x-x_{n}\right)=\prod_{i=0}^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right) $$ 我们将$\ell_{j}(x)$定义为$\pi_{n+1}(x)$除以因子$\left(x-x_{j}\right)$, $$ \开始{关注} \ell_{j}(x) &=\frac{\pi_{n+1}(x)}{\left(x-x_{j}\right)} \ &=\prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j}^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right) \ &=\left(x-x_{0}\right) \cdots\left(x-x_{j-1}\right)\left(x-x_{j+1}\right) \cdots\left(x -x_{n}\右) \end{关注} $$ 除以$\ell_{j}\left(x_{j}\right)$,我们有$L_{j}(x)$,即 $$ L_{j}(x)=\frac{\ell_{j}(x)}{\ell_{j}\left(x_{j}\right)}=\prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j }^{n}\left(x-x_{i}\right) / \prod_{i=0 \atop i \neq j}^{n}\left(x_{j}-x_{i}\right) $$

数学代写| Chebyshev polynomials 数值分析代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
时间序列分析代写
统计作业代写
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程