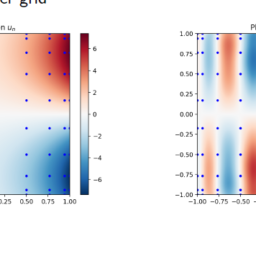
数学代写|The heat equation 偏微分方程代写
数值分析代写
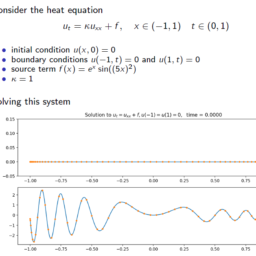
- Derived the heat equation
$$
u_{t}=\kappa u_{x x}+f \quad \text { for } x \in(-1,1), \quad t \in(0,1),
$$
where $u=u(x, t)$ and $f=f(x, t)$. - The initial condition is $u(x, 0)=u_{0}(x)$
- Possible boundary conditions
- Dirichlet condition: $u(-1)=u_{\ell}, u(1)=u_{r}$.
- Neumann condition: $u_{x}(-1)=u_{\ell}, u_{x}(1)=u_{r}$.
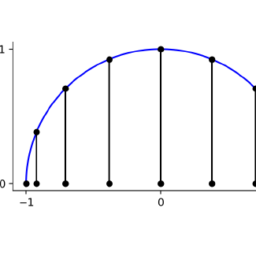
- Mixed coundition: $u(-1)=u_{\ell}, u_{x}(1)=u_{r}$ (or vice versa).- Recall our polynomial approximation
$$
u_{n}(x)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i} L_{i}(x)
$$ - Suppose the coefficients now depend on time
$$
u_{n}(x, t)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}(t) L_{i}(x)
$$
(separation of variables) - Now, taking the derivative with respect to time and space
$$
u_{t, n}(x, t)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}^{\prime}(t) L_{i}(x), \quad u_{x x, n}\left(x_{i}, t\right)=\left(u_{n}\right){x x}\left(x{i}, t\right)
$$ - Then, the solution should satisfy
$$
u_{t, n}\left(x_{i}, t\right)=\kappa u_{x x, n}\left(x_{i}, t\right)+f\left(x_{i}, t\right), \quad \text { for } i=1, \ldots, n-1 .
$$- Let us discretize the temporal variable $t$. Define a time grid
$$
t_{k}=\frac{k}{n}, \quad \mathrm{k}=0, \ldots, \mathrm{n}
$$ - Now we approximate the term $c_{i}(t)$ at these times $t_{k}$,
$$
u_{n}^{k}(x)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}^{k} L_{i}(x), \quad u_{x x, n}^{k}\left(x_{i}\right)=\left(u_{n}^{k}\right)^{\prime \prime}(x) .
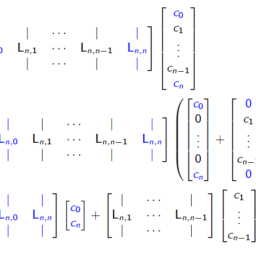
$$ - Further, we approximate $u_{t, n}(x, t)$ by a discrete derivative,
$$
\frac{u_{n}^{k+1}\left(x_{i}, t\right)-u_{n}^{k}\left(x_{i}, t\right)}{1 / n}=\kappa u_{x x, n}^{k+1}\left(x_{i}\right)+f\left(x_{i}, t_{k+1}\right) \quad \text { for } i=1, \ldots, n-1 .
$$
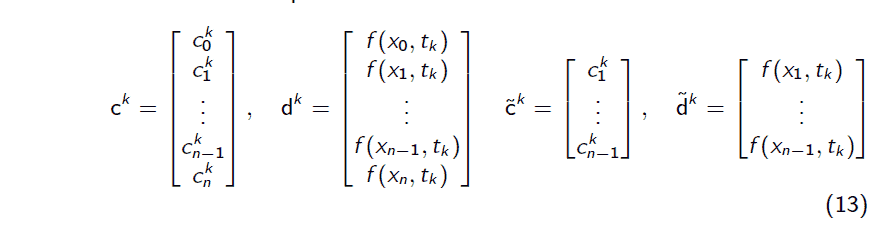
数值分析代考
推导出热方程
$$
u_{t}=\kappa u_{x x}+f \quad \text { for } x \in(-1,1), \quad t \in(0,1),
$$
其中 $u=u(x, t)$ 和 $f=f(x, t)$。
- 初始条件是$u(x, 0)=u_{0}(x)$
- 可能的边界条件
- 狄利克雷条件:$u(-1)=u_{\ell}, u(1)=u_{r}$。
- 诺伊曼条件:$u_{x}(-1)=u_{\ell}, u_{x}(1)=u_{r}$。
- 混合条件:$u(-1)=u_{\ell}, u_{x}(1)=u_{r}$(反之亦然)。- 回想一下我们的多项式逼近
$$
u_{n}(x)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i} L_{i}(x)
$$ - 假设系数现在取决于时间
$$
u_{n}(x, t)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}(t) L_{i}(x)
$$
(变量分离) - 现在,取时间和空间的导数
$$
u_{t, n}(x, t)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}^{\prime}(t) L_{i}(x), \quad u_{xx, n }\left(x_{i}, t\right)=\left(u_{n}\right){xx}\left(x{i}, t\right)
$$ - 那么,解决方案应该满足
$$
u_{t, n}\left(x_{i}, t\right)=\kappa u_{xx, n}\left(x_{i}, t\right)+f\left(x_{i}, t \right), \quad \text { for } i=1, \ldots, n-1 。
$$- 让我们离散化时间变量 $t$。定义时间网格
$$
t_{k}=\frac{k}{n}, \quad \mathrm{k}=0, \ldots, \mathrm{n}
$$ - 现在我们在这些时间 $t_{k}$ 近似术语 $c_{i}(t)$,
$$
u_{n}^{k}(x)=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i}^{k} L_{i}(x), \quad u_{xx, n}^{k }\left(x_{i}\right)=\left(u_{n}^{k}\right)^{\prime \prime}(x) 。
$$ - 此外,我们通过离散导数逼近 $u_{t, n}(x, t)$,
$$
\frac{u_{n}^{k+1}\left(x_{i}, t\right)-u_{n}^{k}\left(x_{i}, t\right)}{1 / n}=\kappa u_{xx, n}^{k+1}\left(x_{i}\right)+f\left(x_{i}, t_{k+1}\right) \quad \text { 对于 } i=1, \ldots, n-1 。
$$

数学代写|The heat equation 偏微分方程代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
时间序列分析代写
统计作业代写
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程