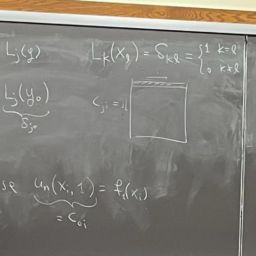数学代写| Boundary conditions 数值分析代考
数值分析代写
- Evaluating the system at $\left{x_{i}\right}_{i=0}^{n}$ at the interior points
$$
u_{x x, n}\left(x_{i}\right)=f\left(x_{i}\right), \quad i=1, \ldots, n-1 .
$$ - The boundary conditions lead to the relations
$$
u_{n}\left(x_{0}\right)=0, \quad u_{n}\left(x_{n}\right)=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad c_{n}=c_{0}=0
$$ - These relations lead to the system of equations
$$
\tilde{L}{n} \mathrm{c}=\mathrm{d}, \quad \mathrm{c}=\left[\begin{array}{c} c{1} \
\vdots \
c_{n-1}
\end{array}\right], \quad \mathrm{d}=\left[\begin{array}{c}
\left.f\left(x_{1}\right)\right) \
\vdots \
f\left(x_{n-1}\right)
\end{array}\right]
$$
where $\tilde{L}{n}$ is the $(1: n, 1: n)$ sub-block of $\left(\mathrm{D}{n}\right)^{2}$ - What if the given boundary condition is not zero, $u(-1)=u_{\ell} \quad u(1)=u_{r} \quad$ for some given $u_{\ell}, u_{r} \in \mathbb{R}$
- Then, we revisit the system
$\left(D_{n}\right)^{2} c$ - Consider the relation
$$
u_{x x, n}\left(x_{i}\right)=f\left(x_{i}\right)
$$
without the boundary conditions.
This leads to the system
$$
L_{n} \mathrm{c}=\mathrm{d} \quad \text { where } L_{n}:=\left(\mathrm{D}_{n}\right)^{2}
$$ - On the other hand, the boundary condition requires
$$
c_{0}=u_{r}, \quad c_{n}=u_{\ell}
$$ - Let us force the boundary conditions
$$
c_{0}=u_{r}, \quad c_{n}=u_{\ell} .
$$
This guarantees that our approximation $u_{n}$ satisfies the boundary conditions. - Then, in terms of the linear system $L_{n} \mathrm{c}=\mathrm{d}$
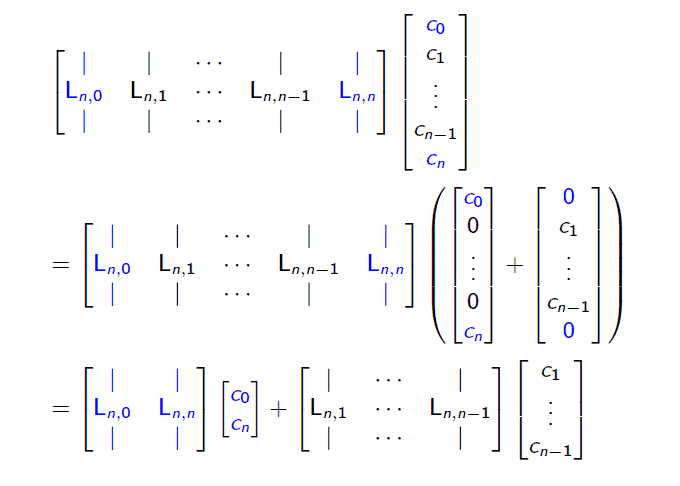
$$
\left[\begin{array}{ccccc}
\mid & \mid & \cdots & \mid & \mid \
L_{n, 0} & L_{n, 1} & \cdots & L_{n, n-1} & L_{n, n} \
\mid & \mid & \cdots & \mid & \mid
\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c}
c_{0} \
c_{1} \
\vdots \
c_{n-1} \
c_{n}
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c}
d_{0} \
d_{1} \
\vdots \
d_{n-1} \
d_{n}
\end{array}\right]
$$ - If you enforce the boundary conditions, the system for $c_{1}, \ldots, c_{n-1}$ corresponding to the interpolation points in the interior is also affected.
数值分析代考
一个简单的边值问题
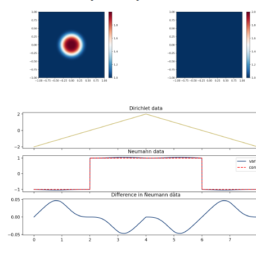
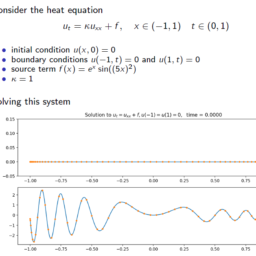
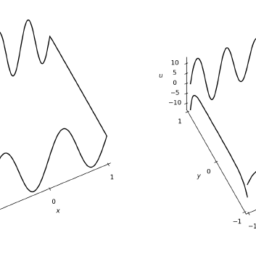
- 考虑泊松问题
$$
u_{x x}(x)=f(x) \quad \text { for } x \in(-1,1), \quad u(-1)=0, \quad u(1)=0 。
$$
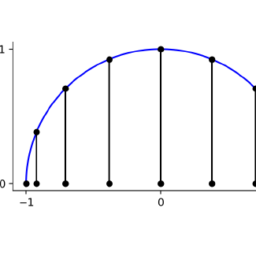
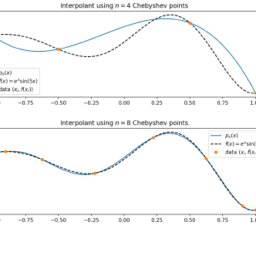
(这里 $\left.u_{xx}=u^{\prime \prime} .\right)$ 源项给出为 $f(x)=e^{-x} \sin \left((5 x )^{2}\右)$ - 该计划是通过其插值 $u_{n}$ 来近似 $u$,
$$
u_{n}(x):=\sum_{i=0}^{n} c_{i} L_{i}(x)
$$ - $u_{n}$ 的导数近似为
$$
u_{x, n}(x):=\sum_{i=0}^{n} u_{n}^{\prime}\left(x_{i}\right) L_{i}(x)
$$ - 相似地,
$$
u_{x x, n}(x):=\sum_{i=0}^{n} u_{n}^{\prime \prime}\left(x_{i}\right) L_{i}(x)
$$ - 我们可以运行以下代码
1 将 numpy 导入为 np
$\begin{对齐}&2 \&3\end{对齐} \quad x=n p \cdot \cos (n p \cdot$ linspace $(0, n p \cdot p i, N))$
$\begin{array}{ll}4 & \text { DN }=\text { df_mat }(x)\end{array}$
$\begin{数组}{ll}5 & \mathrm{DN}=\mathrm{df}_{-} \text {mat }(\mathrm{x}) \ 6 & \mathrm{D} 2=\ mathrm{DN} \cdot \operatorname{dot}(\mathrm{DN})\end{array}$
$\begin{array}{ll}7 & \mathrm{c}=\mathrm{np} \cdot \mathrm{zeros}((\mathrm{N}))\end{array}$
$f=f \operatorname{unc}(x)$
tD2 $=$ D2 $[1:(N-1), 1:(N-1)]$
$t f=f[1:(N-1)]$
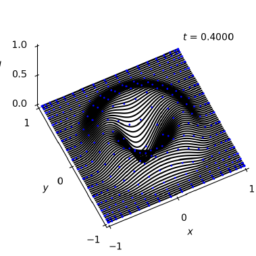
$c[1:(N-1)]=n p \cdot l i n a l g \cdot s o l v e(t D 2, t f)$ - 使用更精细的网格绘制得到的解决方案

数学代写| Chebyshev polynomials 数值分析代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
时间序列分析代写
统计作业代写
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程