数学代写| Determinants 代考
离散数学在计算领域有广泛的应用,例如密码学、编码理论、 形式方法, 语言理论, 可计算性, 人工智能, 理论 数据库和软件的可靠性。 离散数学的重点是理论和应用,而不是为了数学本身而研究数学。 一切算法的基础都是离散数学一切加密的理论基础都是离散数学
编程时候很多奇怪的小技巧(特别是所有和位计算相关的东西)核心也是离散数学
其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
离散数学代写
The determinant is a function defined on square matrices and its value is a scalar. A key property of determinants is that a matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is non-zero. The determinant of a $2 \times 2$ matrix is given by
$$
\left|\begin{array}{ll}
a & b \
c & d
\end{array}\right|=a d-b c
$$
The determinant of a $3 \times 3$ matrix is given by
$$
\left|\begin{array}{llc}
a & b & c \
d & e & f \
g & h & i
\end{array}\right|=a e i+b f g+c d h-a f h-b d i-c e g
$$
Cofactors
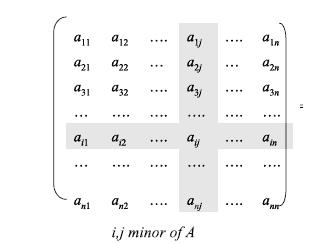
Let $A$ be an $n \times n$ matrix. For $1 \leq i, j \leq n$, the $(i, j)$ minor of $A$ is defined to be the $(n-1) \times(n-1)$ matrix obtained by deleting the $i$-th row and $j$-th column of $A$ (Fig. 8.5).
140
8 Matrix Theory
Fig. $8.5$ Determining the $(i, j)$ minor of $\mathrm{A}$
$$
\left(\begin{array}{cccccc}
a_{11} & a_{12} & \ldots . & a_{1 j} & \ldots & a_{1 n} \
a_{21} & a_{22} & \ldots & a_{2 j} & \ldots & a_{2 n} \
a_{31} & a_{32} & \ldots . & a_{3 j} & \ldots . & a_{3 n} \
\ldots & \ldots . & \ldots & \ldots . & \ldots . & \ldots . \
a_{i 1} & a_{i 2} & \ldots . & a_{i j} & \ldots . & a_{i n} \
\ldots & \ldots . & \ldots . & \ldots . & \ldots . & \ldots . \
a_{n 1} & a_{n 2} & \ldots . & a_{n j} & \ldots . & a_{n n}
\end{array}\right)
$$
$i, j$ minor of $A$
The shaded row is the $i$ th row, and the shaded column is the $j$ th column. These both are deleted from A to form the $(i, j)$ minor of A, and this is a $(n-1) \times(n-1)$ matrix.
The $(i, j)$ cofactor of $A$ is defined to be $(-1)^{i+j}$ times the determinant of the $(i, j)$ minor. The $(i, j)$ cofactor of $A$ is denoted by $K_{i},(A)$.
The cofactor matrix Cof A is formed in this way where the $(i, j)$ th element in the cofactor matrix is the $(i, j)$ cofactor of A.
Definition of Determinant
The determinant of a matrix is defined as
$$
\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A}=\sum_{j=1}^{n} A_{i j} K_{i j} .
$$
Another words the determinant of $\mathrm{A}$ is determined by taking any row of $A$ and multiplying each element by the corresponding cofactor and adding the results. The determinant of the product of two matrices is the product of their determinants.
$$
\operatorname{det}(A B)=\operatorname{det} A \times \operatorname{det} B
$$
Definition
The adjugate of $A$ is the $n \times n$ matrix $A d j(A)$ whose $(i, j)$ entry is the $(j, i)$ cofactor $K_{j i}(A)$ of $A$. That is, the adjugate of $\mathrm{A}$ is the transpose of the cofactor matrix of $\mathrm{A}$. Inverse of $\mathbf{A}$
The inverse of $\mathrm{A}$ is determined from the determinant of $\mathrm{A}$ and the adjugate of $\mathrm{A}$. That is,
$$
\mathrm{A}^{-1}=\frac{1}{\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A}} \operatorname{Adj} A=\frac{1}{\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A}}(\operatorname{Cof} \mathrm{A})^{\mathrm{T}}
$$
行列式是在方阵上定义的函数,其值为标量。行列式的一个关键特性是,当且仅当其行列式非零时,矩阵才是可逆的。 $2 \times 2$ 矩阵的行列式由下式给出
$$
\left|\begin{数组}{ll}
a & b \
开发
\end{数组}\right|=a d-b c
$$
$3 \times 3$ 矩阵的行列式由下式给出
$$
\left|\begin{数组}{llc}
a & b & c \
d & e & f \
g&h&我
\end{数组}\right|=a e i+b f g+c d h-a f h-b d i-c e g
$$
辅因子
令$A$ 为$n\times n$ 矩阵。对于$1 \leq i, j \leq n$,$A$ 的$(i, j)$ 次要定义为删除$ 得到的$(n-1) \times(n-1)$ 矩阵$A$ 的第 i$-th 行和 $j$-th 列(图 8.5)。
140
8 矩阵理论
图 $8.5$ 确定 $\mathrm{A}$ 的 $(i, j)$ 小调
$$
\left(\begin{数组}{cccccc}
a_{11} & a_{12} & \ldots 。 & a_{1 j} & \ldots & a_{1 n} \
a_{21} & a_{22} & \ldots & a_{2 j} & \ldots & a_{2 n} \
a_{31} & a_{32} & \ldots 。 & a_{3 j} & \ldots 。 & a_{3 n} \
\ldots & \ldots 。 & \ldots & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 \
a_{i 1} & a_{i 2} & \ldots 。 & a_{i j} & \ldots 。 & a_{i n} \
\ldots & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 & \ldots 。 \
a_{n 1} & a_{n 2} & \ldots 。 & a_{n j} & \ldots 。 & a_{n n}
\end{数组}\右)
$$
$a$ 的 $i, j$ 小调
阴影行是第 $i$ 行,阴影列是第 $j$ 列。这两个都从 A 中删除以形成 A 的 $(i, j)$ 小调,这是一个 $(n-1) \times(n-1)$ 矩阵。
$A$ 的 $(i, j)$ 辅因子定义为 $(-1)^{i+j}$ 乘以 $(i, j)$ 小调的行列式。 $A$ 的 $(i, j)$ 辅因子用 $K_{i},(A)$ 表示。
辅因子矩阵 Cof A 以这种方式形成,其中辅因子矩阵中的第 $(i, j)$ 元素是 A 的 $(i, j)$ 辅因子。
行列式的定义
矩阵的行列式定义为
$$
\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A}=\sum_{j=1}^{n} A_{i j} K_{i j} 。
$$
换句话说,$\mathrm{A}$ 的行列式是通过取 $A$ 的任何一行并将每个元素乘以相应的辅因子并添加结果来确定的。两个矩阵的乘积的行列式是它们的行列式的乘积。
$$
\operatorname{det}(A B)=\operatorname{det} A \times \operatorname{det} B
$$
定义
$A$ 的对数是 $n \times n$ 矩阵 $A dj(A)$,它的 $(i, j)$ 条目是 $(j, i)$ 辅因子 $K_{ji}(A)$澳元。也就是说,$\mathrm{A}$ 的对数是 $\mathrm{A}$ 的辅因子矩阵的转置。 $\mathbf{A}$ 的逆
$\mathrm{A}$ 的逆由 $\mathrm{A}$ 的行列式和 $\mathrm{A}$ 的并量决定。那是,
$$
\mathrm{A}^{-1}=\frac{1}{\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A}} \operatorname{Adj} A=\frac{1}{\operatorname{det} \mathrm{A }}(\operatorname{Cof} \mathrm{A})^{\mathrm{T}}
$$
图论代考
自然数 $\mathbb{N}$ 由数字 $\{1,2,3, \ldots\}$ 组成。整数 $\mathbb{Z}$ 由 $\{\ldots-2,-1,0,1,2, \ldots\}$ 组成。有理数 $\mathbb{Q}$ 由 $\left\{{ }^{p} /_{q}\right.$ 形式的所有数字组成,其中 $p$ 和 $q$ 是整数,$ \left.q \neq 0\right\}$。实数 $\mathbb{R}$ 被定义为有理数收敛序列的集合,它们是有理数的超集。它们包含有理数和无理数。复数 $\mathbb{C}$ 由 $\{a+bi$ 形式的所有数字组成,其中 $a, b \in \mathbb{R}$ 和 $i=\sqrt{-} 1\}美元。 毕达哥拉斯三元组(图 3.2)是满足毕达哥拉斯方程 $x^{2}+y^{2}=z^{2}$ 的三个整数的组合。有无数个这样的三元组,这种三元组的一个例子是 $3,4,5$,因为 $3^{2}+4^{2}=5^{2}$。 毕达哥拉斯学派发现了音乐和数字之间的数学关系,他们的哲学是数字隐藏在从音乐到科学和自然的一切事物中。这导致了他们的哲学,即“一切都是数字”。

数学代写| DISCRETE MATHEMATICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
抽象代数代考
抽象代数就是一门概念繁杂的学科,我们最重要的一点我想并不是掌握多少例子。即便是数学工作者也不会刻意记住Jacobson环、正则环这类东西,重要的是你要知道这门学科的基本工具和基本手法,对概念理解了没有,而这一点不需要用例子来验证,只需要看看你的理解和后续概念是否相容即可。
矩阵论代考matrix theory
数学,矩阵理论是一门研究矩阵在数学上的应用的科目。矩阵理论本来是线性代数的一个小分支,但其后由于陆续在图论、代数、组合数学和统计上得到应用,渐渐发展成为一门独立的学科。
密码学代考
密码学是研究编制密码和破译密码的技术科学。 研究密码变化的客观规律,应用于编制密码以保守通信秘密的,称为编码学;应用于破译密码以获取通信情报的,称为破译学,总称密码学。 电报最早是由美国的摩尔斯在1844年发明的,故也被叫做摩尔斯电码。
- Cryptosystem
- A system that describes how to encrypt or decrypt messages
- Plaintext
- Message in its original form
- Ciphertext
- Message in its encrypted form
- Cryptographer
- Invents encryption algorithms
- Cryptanalyst
- Breaks encryption algorithms or implementations
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。