经济代写| Dominance and best responses 微观经济学代写
经济代写
Dominance means that a strategy is better than the others. We distinguish between (weak) dominance and strict dominance:
DEFINITION II. 11 (DOMINANCE). Let $\Delta=(S, W, u$ ) be a decision situation in strategic form. Strategy $s \in S$ (weakly) dominates strategy $s^{\prime} \in S$ if and only if $u(s, w) \geq u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ holds for all $w \in W$ and $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ is true for at least one $w \in W$. Strategy $s \in S$ strictly dominates strategy $s^{\prime} \in S$ if and only if $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ holds for all $w \in W$. Then, strategy $s^{\prime}$ is called (weakly) dominated or strictly dominated, respectively. A strategy
16
II. DECISIONS IN STRATEGIC FORM
that dominates every other strategy is called dominant (weakly or strictly, respectively).
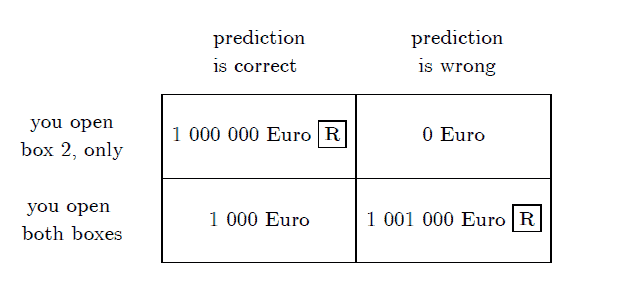
The decision matrix II.2 depicted in figure II.2 (p. 11) is clearly solvable by strict dominance. Opening both boxes yields an extra amount of Euro $1000 .$
There is a simple procedure to find out whether we have dominant strategies. For every state of the world, we find the best strategy and put a ” $R$ ” into the corresponding field. The letter ” $R$ ” is reminiscent of response the decision maker responds to a state of the world by choosing the payoff maximizing strategy for that state. Take, for example, the second Newcomb matrix:
\begin{tabular}{c|c|c|}
\multicolumn{1}{c}{ prediction is correct pou open box 2 , only you open both boxes } & 1000000 Euro $\mathrm{R}$ & \multicolumn{1}{c|}{0 Euro } \
\cline { 2 – 3 } & 1000 Euro & 1001000 Euro \
\hline
\end{tabular}
Since the best strategy (best response) depends on the state of the world, no strategy is dominant. The $R$-procedure needs to be formalized. Before doing so, we familiarize the reader with the notion of a power set and with arg max.
DEFINITION II.12 (POWER SET). Let $M$ be any set. The set of all subsets of $M$ is called the power set of $M$ and is denoted by $2^{M}$.
For example, $M:={1,2,3}$ has the power set
$$
2^{M}={\emptyset,{1},{2},{3},{1,2},{1,3},{2,3},{1,2,3}} .
$$
Note that the empty set $\emptyset$ also belongs to the power set of $M$, indeed to the power set of any set. $M:={1,2,3}$ has eight elements which is equal to $2^{3}=2^{|{1,2,3}|}$. This is a general rule: For any set $M$, we have $\left|2^{M}\right|=2^{|M|}$.
2 plays a special role in the definition of a power set. The reason is simple – every element $m$ belongs to or does not belong to a given subset.
In order to introduce arg max, consider a firm that tries to maximize its profit $\Pi$ by choosing the output $x$ optimally. The output $x$ is taken from
优势意味着一种策略比其他策略更好。我们区分(弱)支配和严格支配:
定义二。 11(统治)。令 $\Delta=(S, W, u$ ) 为战略形式的决策情境。策略 $s \in S$ (弱) 支配策略 $s^{\prime} \in S$ 当且仅当 $u(s, w) \geq u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right )$ 对所有 $w \in W$ 成立,并且 $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ 对至少一个 $w \in W$ 成立。策略 $s \in S$ 严格支配策略 $s^{\prime} \in S$ 当且仅当 $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ 成立对于所有 $w \in W$。然后,策略 $s^{\prime}$ 分别被称为(弱)支配或严格支配。一种策略
16
二、战略形式的决定
支配所有其他策略的称为支配(分别为弱或严格)。
图 II.2(第 11 页)中描述的决策矩阵 II.2 显然可以通过严格支配来解决。打开两个盒子会产生额外的 1000 欧元。$
有一个简单的程序可以找出我们是否有优势策略。对于世界的每一个状态,我们找到最好的策略,并在相应的字段中输入一个“$R$”。字母“$R$”让人想起决策者通过选择该状态的收益最大化策略来响应世界状态的响应。以第二个 Newcomb 矩阵为例:
\begin{表格}{c|c|c|}
\multicolumn{1}{c}{ 预测正确 pou open box 2 , only you open both box } & 1000000 Euro $\mathrm{R}$ & \multicolumn{1}{c|}{0 Euro } \
\cline { 2 – 3 } & 1000 欧元 & 1001000 欧元 \
\hline
\end{表格}
由于最佳策略(最佳响应)取决于世界的状态,因此没有策略占主导地位。 $R$ 程序需要正式化。在此之前,我们让读者熟悉幂集的概念和 arg max。
定义 II.12(电源组)。令 $M$ 为任意集合。 $M$ 的所有子集的集合称为$M$ 的幂集,记为$2^{M}$。
例如,$M:={1,2,3}$ 具有幂集
$$
2^{M}={\emptyset,{1},{2},{3},{1,2},{1,3},{2,3 },{1,2,3}} 。
$$
注意空集$\emptyset$ 也属于$M$ 的幂集,实际上属于任何集合的幂集。 $M:={1,2,3}$ 有八个元素,等于 $2^{3}=2^{|{1,2,3}|}$。这是一般规则:对于任何集合 $M$,我们有 $\left|2^{M}\right|=2^{|M|}$。
2 在幂集的定义中起着特殊的作用。原因很简单 – 每个元素 $m$ 属于或不属于给定子集。
为了引入 arg max,考虑一家试图通过最优选择输出 $x$ 来最大化其利润 $\Pi$ 的公司。输出$x$ 取自Dominance 意味着一个策略比其他策略更好。我们区分(弱)支配和严格支配:
定义二。 11(统治)。令 $\Delta=(S, W, u$ ) 为战略形式的决策情境。策略 $s \in S$ (弱) 支配策略 $s^{\prime} \in S$ 当且仅当 $u(s, w) \geq u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right )$ 对所有 $w \in W$ 成立,并且 $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ 对至少一个 $w \in W$ 成立。策略 $s \in S$ 严格支配策略 $s^{\prime} \in S$ 当且仅当 $u(s, w)>u\left(s^{\prime}, w\right)$ 成立对于所有 $w \in W$。然后,策略 $s^{\prime}$ 分别被称为(弱)支配或严格支配。一种策略
16
二、战略形式的决定
支配所有其他策略的称为支配(分别为弱或严格)。
图 II.2(第 11 页)中描述的决策矩阵 II.2 显然可以通过严格支配来解决。打开两个盒子会产生额外的 1000 欧元。$
有一个简单的程序可以找出我们是否有优势策略。对于世界的每一个状态,我们找到最好的策略,并在相应的字段中输入一个“$R$”。字母“$R$”让人想起决策者通过选择该状态的收益最大化策略来响应世界状态的响应。以第二个 Newcomb 矩阵为例:
\begin{表格}{c|c|c|}
\multicolumn{1}{c}{ 预测正确 pou open box 2 , only you open both box } & 1000000 Euro $\mathrm{R}$ & \multicolumn{1}{c|}{0 Euro } \
\cline { 2 – 3 } & 1000 欧元 & 1001000 欧元 \
\hline
\end{表格}
由于最佳策略(最佳响应)取决于世界的状态,因此没有策略占主导地位。 $R$ 程序需要正式化。在此之前,我们让读者熟悉幂集的概念和 arg max。
定义 II.12(电源组)。令 $M$ 为任意集合。 $M$ 的所有子集的集合称为$M$ 的幂集,记为$2^{M}$。
例如,$M:={1,2,3}$ 具有幂集
$$
2^{M}={\emptyset,{1},{2},{3},{1,2},{1,3},{2,3 },{1,2,3}} 。
$$
注意空集$\emptyset$ 也属于$M$ 的幂集,实际上属于任何集合的幂集。 $M:={1,2,3}$ 有八个元素,等于 $2^{3}=2^{|{1,2,3}|}$。这是一般规则:对于任何集合 $M$,
经济代考
微观经济学又称个体经济学,小经济学,是宏观经济学的对称。 微观经济学主要以单个经济单位( 单个的生产者、单个的消费者、单个市场的经济活动)作为研究对象,分析单个生产者如何将有限的资源分配在各种商品的生产上以取得最大的利润;单个消费者如何将有限的收入分配在各种商品的消费上以获得最大的满足。

其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
微观经济学 是研究人们和企业在资源分配、商品和服务交易价格等方面做出的决策。它考虑税收、法规和政府立法。
计量经济学代考
计量经济学是以一定的经济理论和统计资料为基础,运用数学、统计学方法与电脑技术,以建立经济计量模型为主要手段,定量分析研究具有随机性特性的经济变量关系的一门经济学学科。 主要内容包括理论计量经济学和应用经济计量学。 理论经济计量学主要研究如何运用、改造和发展数理统计的方法,使之成为经济关系测定的特殊方法。
相对论代考
相对论(英語:Theory of relativity)是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由愛因斯坦创立,依其研究对象的不同可分为狭义相对论和广义相对论。 相对论和量子力学的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,它们共同奠定了现代物理学的基础。
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。
复分析代考
学习易分析也已经很冬年了,七七八人的也续了圧少的书籍和论文。略作总结工作,方便后来人学 Đ参考。
复分析是一门历史悠久的学科,主要是研究解析函数,亚纯函数在复球面的性质。下面一昭这 些基本内容。
(1) 提到复变函数 ,首先需要了解复数的基本性左和四则运算规则。怎么样计算复数的平方根, 极坐标与 $x y$ 坐标的转换,复数的模之类的。这些在高中的时候囸本上都会学过。
(2) 复变函数自然是在复平面上来研究问题,此时数学分析里面的求导数之尖的运算就会很自然的 引入到复平面里面,从而引出解析函数的定义。那/研究解析函数的性贡就是关楗所在。最关键的 地方就是所谓的Cauchy一Riemann公式,这个是判断一个函数是否是解析函数的关键所在。
(3) 明白解析函数的定义以及性质之后,就会把数学分析里面的曲线积分 $a$ 的概念引入复分析中, 定义几乎是一致的。在引入了闭曲线和曲线积分之后,就会有出现复分析中的重要的定理: Cauchy 积分公式。 这个是易分析的第一个重要定理。