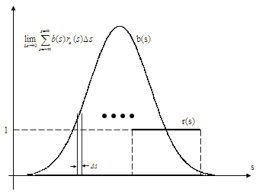
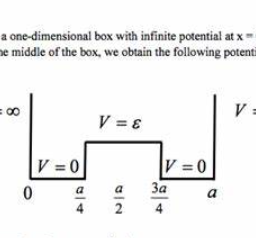
运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
作为专业的留学生服务机构,Assignmentexpert™多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于论文代写,A作业代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,网课代修等等。为涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学生提供辅导服务,辅导学科包括数学,物理,统计,化学,金融,经济学,会计学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
运筹学代写
Conic Linear Programming, hereafter CLP, is a natural extension of Linear programming (LP). In LP, the variables form a vector which is required to be component-wise nonnegative, while in CLP they are points in a pointed convex cone (see Appendix B.1) of an Euclidean space, such as vectors as well as matrices of finite dimensions. For example, Semidefinite programming (SDP) is a kind of CLP, where the variable points are symmetric matrices constrained to be positive semidefinite. Both types of problems may have linear equality constraints as well. Although CLPs have long been known to be convex optimization problems, no efficient solution algorithm was known until about two decades ago, when it was discovered that interior-point algorithms for LP discussed in Chap. 5 , can be adapted to solve certain CLPs with both theoretical and practical efficiency. During the same to solve certain CLPs with both theoretical and practical efficiency. During the same period, it was discovered that CLP, especially SDP, is representative of a wide assortment of applications, including combinatorial optimization, statistical comoptimal control, etc. CLP is now widely recognized as a powerful mathematical computation model of general importance.
First, we illustrate several convex cones popularly used in conic linear optimization.
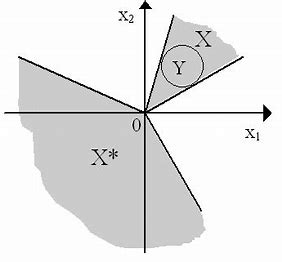
Example 1 The followings are all (closed) convex cones.
- The $n$-dimensional nonnegative orthant, $E_{+}^{n}=\left{\mathbf{x} \in E^{n}: \mathbf{x} \geq 0\right}$, is a convex cone.
( Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021 D. G. Luenberger, Y. Ye, Linear and Nonlinear Programming, International Series in Operations Research \& Management Science 228, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85450-8_6 – The set $\left{(u ; \mathbf{x}) \in E^{n+1}: u \geq|\mathbf{x}|_{p}\right}$ is a convex cone in $E^{n+1}$, called the $p$-order - The set of all $n$-dimensional symmetric positive semidefinite matrices, denoted by $\mathcal{S}_{+}^{n}$, is a convex cone, called the positive semidefinite matrix cone. When $\mathrm{X}$ is positive semidefinite (positive definite), we often write the property as $\mathbf{X} \succeq(\succ) 0$. cone where $1 \leq p<\infty$. When $p=2$, the cone is called second-order cone or “Ice-cream” cone.
Sometimes, we use the notion of conic inequalities $\mathbf{P} \succeq_{K} \mathbf{Q}$ or $\mathbf{Q} \preceq_{K} \mathbf{P}$, in which cases we simply mean $\mathbf{P}-\mathbf{Q} \in K$.
Suppose $\mathbf{A}$ and $\mathbf{B}$ are $k \times n$ matrices. We define the inner product
$$
\mathbf{A} \bullet \mathbf{B}=\operatorname{trace}\left(\mathbf{A}^{T} \mathbf{B}\right)=\sum_{i, j} a_{i j} b_{i j}
$$
When $k=1$, they become $n$-dimensional vectors and the inner product is the standard dot product of two vectors. In SDP, this definition is almost always used for the case where the matrices are both square and symmetric. The matrix norm associated with the inner product is called Frobenius norm:
$$
|\mathbf{X}|_{f}=\sqrt{\mathbf{X} \bullet \mathbf{X}}
$$
For a cone $K$, the dual of $K$ is the cone
$$
K^{*}:={\mathbf{Y}: \mathbf{X} \bullet \mathbf{Y} \geq 0 \text { for all } \mathbf{X} \in K}
$$
It is not difficult to see that the dual cones of the first two cones in Example 1 are all them self, respectively; while the dual cone of the $p$-order cone is the $q$-order cone where
$$
\frac{1}{p}+\frac{1}{q}=1
$$
One can see that when $p=2, q=2$ as well; that is, they are both 2 -order cones. For a closed convex cone $K$, the dual of the dual cone is itself.
圆锥线性规划(以下简称 CLP)是线性规划 (LP) 的自然扩展。在 LP 中,变量形成一个向量,该向量需要按分量非负,而在 CLP 中,它们是欧几里得空间的一个尖凸锥(见附录 B.1)中的点,例如向量以及有限矩阵方面。例如,半定规划 (SDP) 是一种 CLP,其中变量点是对称矩阵,被约束为半正定。这两种类型的问题也可能具有线性等式约束。尽管 CLP 长期以来一直被认为是凸优化问题,但直到大约 20 年前才知道有效的求解算法,当时人们发现了第 1 章中讨论的 LP 的内点算法。 5,可以适应解决某些CLP的理论和实际效率。同时以理论和实际效率解决某些 CLP。在同一时期,人们发现 CLP,尤其是 SDP,代表了各种应用,包括组合优化、统计最优控制等。CLP 现在被广泛认为是一种具有普遍重要性的强大数学计算模型。
首先,我们说明了在圆锥线性优化中常用的几个凸锥。
例1 下面都是(闭)凸锥。
- $n$ 维非负正数,$E_{+}^{n}=\left{\mathbf{x} \in E^{n}: \mathbf{x} \geq 0\right}$ , 是一个凸锥。
(Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021 DG Luenberger, Y. Ye,线性和非线性规划,国际运筹学与管理科学系列 228,https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85450-8_6 – The设置 $\left{(u ; \mathbf{x}) \in E^{n+1}: u \geq|\mathbf{x}|_{p}\right}$ 是 $ 中的凸锥E^{n+1}$,称为$p$-order - 所有 $n$ 维对称正半定矩阵的集合,记为 $\mathcal{S}_{+}^{n}$,是一个凸锥,称为正半定矩阵锥。当 $\mathrm{X}$ 为半正定(正定)时,我们常将性质写为 $\mathbf{X} \succeq(\succ) 0$。锥,其中 $1 \leq p<\infty$。当 $p=2$ 时,圆锥称为二阶圆锥或“冰淇淋”圆锥。
有时,我们使用圆锥不等式 $\mathbf{P} \succeq_{K} \mathbf{Q}$ 或 $\mathbf{Q} \preceq_{K} \mathbf{P}$ 的概念,在这种情况下,我们只需均值 $\mathbf{P}-\mathbf{Q} \in K$。
假设 $\mathbf{A}$ 和 $\mathbf{B}$ 是 $k \times n$ 矩阵。我们定义内积
$$
\mathbf{A} \bullet \mathbf{B}=\operatorname{trace}\left(\mathbf{A}^{T} \mathbf{B}\right)=\sum_{i, j} a_{ij} b_{ij}
$$
当 $k=1$ 时,它们成为 $n$ 维向量,内积是两个向量的标准点积。在 SDP 中,这个定义几乎总是用于矩阵既是正方形又是对称的情况。与内积相关的矩阵范数称为 Frobenius 范数:
$$
|\mathbf{X}|_{f}=\sqrt{\mathbf{X} \bullet \mathbf{X}}
$$
对于圆锥 $K$,$K$ 的对偶是圆锥
$$
K^{*}:={\mathbf{Y}: \mathbf{X} \bullet \mathbf{Y} \geq 0 \text { for all } \mathbf{X} \in K}
$$
不难看出,例1中前两个锥体的对偶锥体都是自身;而 $p$-order 锥的双锥是 $q$-order 锥,其中
$$
\frac{1}{p}+\frac{1}{q}=1
$$
可见当$p=2时,q=2$也是如此;也就是说,它们都是 2 阶锥。对于闭凸锥$K$,对偶锥的对偶就是它本身。
运筹学代考
什么是运筹学代写
运筹学(OR)是一种解决问题和决策的分析方法,在组织管理中很有用。在运筹学中,问题被分解为基本组成部分,然后通过数学分析按定义的步骤解决。
运筹学的过程大致可以分为以下几个步骤:
- 确定需要解决的问题。
- 围绕问题构建一个类似于现实世界和变量的模型。
- 使用模型得出问题的解决方案。
- 在模型上测试每个解决方案并分析其成功。
- 实施解决实际问题的方法。
与运筹学交叉的学科包括统计分析、管理科学、博弈论、优化理论、人工智能和复杂网络分析。所有这些学科的目标都是解决某一个现实中出现的复杂问题或者用数学的方法为决策提供指导。 运筹学的概念是在二战期间由参与战争的数学家们提出的。二战后,他们意识到在运筹学中使用的技术也可以被应用于解决商业、政府和社会中的问题。
运筹学代写的三个特点
所有运筹学解决实际问题的过程中都具有三个主要特征:
- 优化——运筹学的目的是在给定的条件下达到某一机器或者模型的最佳性能。优化还涉及比较不同选项和缩小潜在最佳选项的范围。
- 模拟—— 这涉及构建模型,以便在应用解决方案刀具体的复杂大规模问题之前之前尝试和测试简单模型的解决方案。
- 概率和统计——这包括使用数学算法和数据挖掘来发现有用的信息和潜在的风险,做出有效的预测并测试可能的解决方法。
运筹学领域提供了比普通软件和数据分析工具更强大的决策方法。此外,运筹学可以根据特定的业务流程或用例进行定制,以确定哪些技术最适合解决问题。
运筹学可以应用于各种活动,比如:计划和时间管理(Planning and Time Management),城乡规划(Urban and Rural Planning),企业资源计划(ERP)与供应链管理(Supply Chain Management)等等。 如有代写代考需求,欢迎同学们联系Assignmentexpert™,我们期待为你服务!