运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
作为专业的留学生服务机构,Assignmentexpert™多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于论文代写,A作业代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,网课代修等等。为涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学生提供辅导服务,辅导学科包括数学,物理,统计,化学,金融,经济学,会计学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
运筹学代写
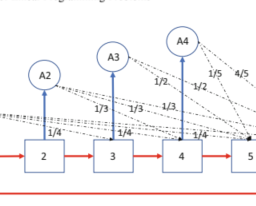
The transportation problem was stated briefly in Chap. 2. We restate it here. There are $m$ origins that contain various amounts of a commodity that must be shipped to $n$ destinations to meet demand requirements. Specifically, origin $i$ contains an amount $a_{i}$, and destination $j$ has a requirement of amount $b_{j}$. It is assumed that the system is balanced in the sense that total supply equals total demand. That is,
$$
\sum_{i=1}^{m} a_{i}=\sum_{j=1}^{n} b_{j} .
$$
The numbers $a_{i}$ and $b_{j}, i=1,2, \ldots, m ; j=1,2, \ldots, n$, are assumed to be nonnegative, and in many applications they are in fact nonnegative integers. There is a unit cost $c_{i j}$ associated with the shipping of the commodity from origin
102
4 The Simplex Method $i$ to destination $j$. The problem is to find the shipping pattern between origins and destinations that satisfies all the requirements and minimizes the total shipping cost. In mathematical terms the above problem can be expressed as finding a set of $x_{i j}$ ‘ $\mathrm{s}, i=1,2, \ldots, m ; j=1,2, \ldots, n$, to
$$
\begin{gathered}
\text { minimize } \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} c_{i j} x_{i j} \
\text { subject to } \sum_{j=1}^{n} x_{i j}=a_{i} \quad \text { for } i=1,2, \ldots, m \
\sum_{i=1}^{m} x_{i j}=b_{j} \quad \text { for } \quad j=1,2, \ldots, n \
x_{i j} \geqslant 0 \quad \text { for all } \quad i \text { and } j
\end{gathered}
$$
This mathematical problem, together with the assumption (4.28), is the general transportation problem. In the shipping context, the variables $x_{i j}$ represent the amounts of the commodity shipped from origin $i$ to destination $j$.
The structure of the problem can be seen more clearly by writing the constraint equations in standard form:
(4.30)
$x_{1 n}+x_{2 n} \quad+x_{m n}=b_{n}$
The structure is perhaps even more evident when the coefficient matrix $\mathbf{A}$ of the system of equations above is expressed in vector-matrix notation as
$$
\mathbf{A}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc}
\mathbf{1}^{T} & & & \
& \mathbf{1}^{T} & & \
& & \ddots & \
& & & \mathbf{1}^{T} \
\mathbf{I} & \mathbf{I} & \cdots & \mathbf{I}
\end{array}\right]
$$
4.5 The Simplex Method for Transportation Problems
103
where $\mathbf{1}=(1,1, \ldots, 1)$ is $n$-dimensional, and where each $\mathbf{I}$ is an $n \times n$ identity matrix.
In practice it is usually unnecessary to write out the constraint equations of the transportation problem in the explicit form (4.30). A specific transportation problem is generally defined by simply presenting the data in compact form, such as:
$$
\mathbf{a}=\left(a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{m}\right)
$$
运输问题在第 1 章中简要说明。 2. 我们在这里重述。有 $m$ 来源包含不同数量的商品,必须将其运送到 $n$ 目的地以满足需求要求。具体来说,起点$i$ 包含金额$a_{i}$,目的地$j$ 要求金额$b_{j}$。假设系统在总供给等于总需求的意义上是平衡的。那是,
$$
\sum_{i=1}^{m} a_{i}=\sum_{j=1}^{n} b_{j} 。
$$
数字 $a_{i}$ 和 $b_{j}, i=1,2, \ldots, m ; j=1,2, \ldots, n$, 被假定为非负数,在许多应用中它们实际上是非负整数。有一个单位成本 $c_{i j}$ 与商品从原产地的运输相关联
102
4 单纯形法$i$ 到目的地$j$。问题是找到满足所有要求并最小化总运输成本的起点和目的地之间的运输模式。用数学术语,上述问题可以表示为找到一组 $x_{i j}$ ‘ $\mathrm{s}, i=1,2, \ldots, m ; j=1,2, \ldots, n$, 到
$$
\开始{聚集}
\text { 最小化 } \sum_{i=1}^{m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} c_{i j} x_{i j} \
\text { 服从 } \sum_{j=1}^{n} x_{i j}=a_{i} \quad \text { for } i=1,2, \ldots, m \
\sum_{i=1}^{m} x_{i j}=b_{j} \quad \text { for } \quad j=1,2, \ldots, n \
x_{i j} \geqslant 0 \quad \text { 对于所有 } \quad i \text { 和 } j
\结束{聚集}
$$
这个数学问题,连同假设(4.28),是一般的运输问题。在运输上下文中,变量 $x_{i j}$ 表示商品从起点 $i$ 运输到目的地 $j$ 的数量。
通过将约束方程写成标准形式,可以更清楚地看出问题的结构:
(4.30)
$x_{1 n}+x_{2 n} \quad+x_{m n}=b_{n}$
当上述方程组的系数矩阵 $\mathbf{A}$ 以向量矩阵表示法表示时,该结构可能更加明显
$$
\mathbf{A}=\left[\begin{数组}{cccc}
\mathbf{1}^{T} & & & \
& \mathbf{1}^{T} & & \
& & \ddots & \
& & & \mathbf{1}^{T} \
\mathbf{I} & \mathbf{I} & \cdots & \mathbf{I}
\end{数组}\right]
$$
4.5 交通问题的单纯形法
103
其中 $\mathbf{1}=(1,1, \ldots, 1)$ 是 $n$ 维,其中每个 $\mathbf{I}$ 是一个 $n \times n$ 单位矩阵。
在实践中,通常不需要以显式形式(4.30)写出运输问题的约束方程。一个特定的运输问题通常通过简单地以紧凑的形式呈现数据来定义,例如:
$$
\mathbf{a}=\left(a_{1}, a_{2}, \ldots, a_{m}\right)
$$
运筹学代考
什么是运筹学代考
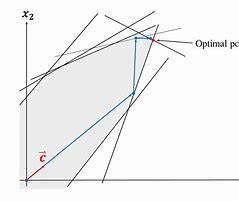
运筹学(OR)是一种解决问题和决策的分析方法,在组织管理中很有用。在运筹学中,问题被分解为基本组成部分,然后通过数学分析按定义的步骤解决。
运筹学的过程大致可以分为以下几个步骤:
- 确定需要解决的问题。
- 围绕问题构建一个类似于现实世界和变量的模型。
- 使用模型得出问题的解决方案。
- 在模型上测试每个解决方案并分析其成功。
- 实施解决实际问题的方法。
与运筹学交叉的学科包括统计分析、管理科学、博弈论、优化理论、人工智能和复杂网络分析。所有这些学科的目标都是解决某一个现实中出现的复杂问题或者用数学的方法为决策提供指导。 运筹学的概念是在二战期间由参与战争的数学家们提出的。二战后,他们意识到在运筹学中使用的技术也可以被应用于解决商业、政府和社会中的问题。
运筹学代考的三个特点
所有运筹学解决实际问题的过程中都具有三个主要特征:
- 优化——运筹学的目的是在给定的条件下达到某一机器或者模型的最佳性能。优化还涉及比较不同选项和缩小潜在最佳选项的范围。
- 模拟—— 这涉及构建模型,以便在应用解决方案刀具体的复杂大规模问题之前之前尝试和测试简单模型的解决方案。
- 概率和统计——这包括使用数学算法和数据挖掘来发现有用的信息和潜在的风险,做出有效的预测并测试可能的解决方法。
运筹学领域提供了比普通软件和数据分析工具更强大的决策方法。此外,运筹学可以根据特定的业务流程或用例进行定制,以确定哪些技术最适合解决问题。
运筹学可以应用于各种活动,比如:计划和时间管理(Planning and Time Management),城乡规划(Urban and Rural Planning),企业资源计划(ERP)与供应链管理(Supply Chain Management)等等。 如有代写代考需求,欢迎同学们联系Assignmentexpert™,我们期待为你服务!