my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 $100 \%$ 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的ECON经济学作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于economics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此经济作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在经济学作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的经济代写服务。我们的专家在经济学 代写方面经验极为丰富,各种economics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的econ代写服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 微观经济学
- 货币银行学
- 数量经济学
- 宏观经济学
- 经济统计学
- 经济学理论
- 商务经济学
- 计量经济学
- 金融经济学
- 国际经济学
- 健康经济学
- 劳动经济学
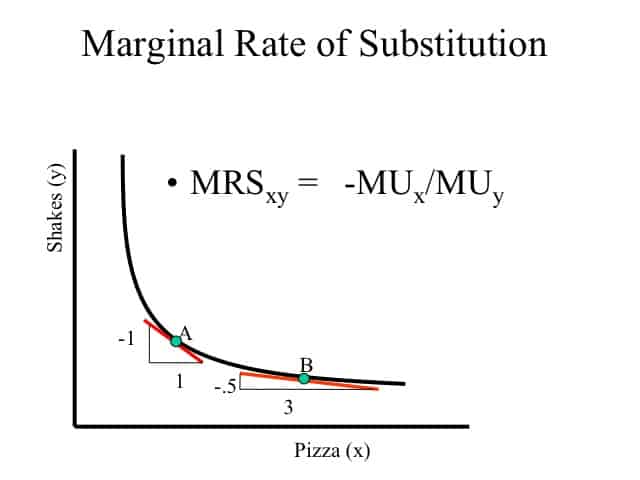
Base case|Econ经济作业代写Economics代考
Imagine two goods consumed at a marginal rate of substitution $M R S$ and produced at a marginal rate of transformation $M R T$. We now show that optimality implies $M R S=M R T$. Assume, to the contrary, that the marginal rate of substitution (for a consumer) is lower than the marginal rate of transformation (for a producer):
$M R S=\left|\frac{d x_{2}}{d x_{1}}\right|^{\text {indifference curve }}<\left|\frac{d x_{2}}{d x_{1}}\right|^{\text {transformation curve }}=M R T .$ If the producer reduces the production of good 1 by one unit, he can increase the production of good 2 by $M R T$ units. The consumer has to renounce the one unit of good 1 , and he needs at least $M R S$ units of good 2 to make up for this. By $M R T>M R S$ the additional production of good 2 (come about by producing one unit less of good 1) more than suffices to compensate the consumer. Thus, the inequality of marginal rate of substitution and marginal rate of transformation points to a Pareto-inefficient situation.
Perfect competition|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
4.2. Perfect competition. We want to apply the formula
$$
M R S \stackrel{!}{=} M R T
$$
to the case of perfect competition. For the output space, we have the condition
$$
p \stackrel{!}{=} M C .
$$
We have derived “price equals marginal cost” as the profit-maximizing condition on p. 240 and have discussed the welfare-theoretic implications on p. 310 .
First-degree price discrimination|Econ经济作业代写Economics代考
In the case of a Cournot monopoly, the “price equals marginal cost” rule is violated. However, firstdegree price discrimination fulfills this rule as shown on pp. 306 .
Cournot monopoly|Econ经济作业代写Economics代考
A trivial violation of Pareto optimality ensues if a single agent acts in a non-optimal fashion. Just consider consumer and producer as a single person. For the Cournot monopolist, the $M R S \stackrel{!}{=} M R T$ formula can be rephrased as the equality between
- the monetary marginal willingness to pay for selling – this is the marginal revenue $M R=\frac{d R}{d y}$ (see above p. 389$)$ – and
Household optimum|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
The exercise helps us understand that the marginal rate of transformation is the price ratio,
$$
M R T=\frac{p_{1}}{p_{2}},
$$
that we also know under the heading of “marginal opportunity cost”. (Alternatively, consider the transformation function $x_{2}=f\left(x_{1}\right)=\frac{m}{p_{2}}-\frac{p_{1}}{p_{2}} x_{1}$.) Seen this way, $M R S \stackrel{!}{=} M R T$ is nothing but the famous condition for household optimality dervied on pp. 137 .
External effects and the Coase theorem.|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
\begin{tabular}{c|c|c|}
number of steers & marginal profit & marginal crop loss \
\hline 1 & 4 & 1 \
2 & 3 & 2 \
3 & 2 & 3 \
4 & 1 & 4
\end{tabular}
The cattle raiser’s marginal profit from steers is a decreasing function of the number of steers while the marginal crop loss increases. Let us begin with the case where the cattle raiser is liable. He can pay the farmer up to 4 (thousand Euros) for allowing him to have one cattle destroy crop. Since the farmer’s compensating variation is 1 , the two can easily agree on a price of 2 or 3 .
Public goods|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
在古诺垄断的情况下,“价格等于边际成本”的规则被违反了。然而,一级价格歧视符合这一规则,如第 306 页所示。
COURNOT MONOPOLY|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
Consider two individuals $A$ and $B$ who consume a private good $x$ (quantities $x^{A}$ and $x^{B}$, respectively) and a public good $G$. We define $M R S^{A}$ and $M R S^{B}$ as the marginal willingness to pay for the public good in terms of the private good. The optimality condition is
$$
\begin{aligned}
& M R S^{A}+M R S^{B} \
=&\left|\frac{d x^{A}}{d G}\right|^{\text {indifference curve }}+\left|\frac{d x^{B}}{d G}\right|^{\text {indifference curve }} \
& \stackrel{!}{=}\left|\frac{d\left(x^{A}+x^{B}\right)}{d G}\right|^{\text {transformation curve }}=M R T
\end{aligned}
$$
Assume that this condition is not fulfilled. For example, let the marginal rate of transformation be smaller than the sum of the marginal rates of substitution. Then, it is a good idea to produce one additional unit of the public good. The two consumers need to forgo $M R T$ units of the private
BASE CASE|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
想象两种商品以边际替代率消费米R小号并以边际转化率生产米R吨. 我们现在证明最优性意味着米R小号=米R吨. 相反,假设边际替代率(对于消费者)低于边际转化率(对于生产者):
米R小号=|dX2dX1|无差异曲线 <|dX2dX1|转换曲线 =米R吨.如果生产者将商品 1 的产量减少一单位,他可以将商品 2 的产量增加一单位米R吨单位。消费者必须放弃一单位商品 1 ,他至少需要米R小号单位好2弥补了这一点。经过米R吨>米R小号商品 2 的额外生产(通过少生产一单位商品 1 来实现)足以补偿消费者。因此,边际替代率和边际转化率的不平等指向了帕累托无效率的情况。
PERFECT COMPETITION|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
4.2. 完美的竞争。我们想应用公式
米R小号=!米R吨
以完全竞争为例。对于输出空间,我们有条件
p=!米C.
我们推导出“价格等于边际成本”作为 p 的利润最大化条件。240 并讨论了关于 p.2 的福利理论含义。310 .
FIRST-DEGREE PRICE DISCRIMINATION|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
在古诺垄断的情况下,“价格等于边际成本”的规则被违反了。然而,一级价格歧视符合这一规则,如第 306 页所示。
COURNOT MONOPOLY|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
如果单个代理以非最优方式行事,则会发生对帕累托最优的微不足道的违反。只需将消费者和生产者视为一个人。对于古诺垄断者来说,米R小号=!米R吨公式可以改写为
- 为销售支付的货币边际意愿——这是边际收入米R=dRd和(见上文第 389 页)- 和
HOUSEHOLD OPTIMUM|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
这个练习帮助我们理解边际转化率是价格比率,
米R吨=p1p2,
我们在“边际机会成本”的标题下也知道。(或者,考虑转换函数X2=F(X1)=米p2−p1p2X1.) 这样看,米R小号=!米R吨只不过是第 137 页得出的家庭最优性的著名条件。
EXTERNAL EFFECTS AND THE COASE THEOREM.|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
\begin{tabular}{c|c|c|} 公牛数量 & 边际利润 & 边际作物损失 \ \hline 1 & 4 & 1 \ 2 & 3 & 2 \ 3 & 2 & 3 \ 4 & 1 & 4 \结束{表格}\begin{tabular}{c|c|c|} 公牛数量 & 边际利润 & 边际作物损失 \ \hline 1 & 4 & 1 \ 2 & 3 & 2 \ 3 & 2 & 3 \ 4 & 1 & 4 \结束{表格}
养牛者从阉牛的边际利润是阉牛数量的减函数,而边际作物损失增加。让我们从养牛者承担责任的案例开始。他可以向农民支付高达 4(千欧元)的费用,以允许他让一头牛毁坏庄稼。由于农夫的补偿变差为 1 ,因此两者很容易就 2 或 3 的价格达成一致。
PUBLIC GOODS|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
在古诺垄断的情况下,“价格等于边际成本”的规则被违反了。然而,一级价格歧视符合这一规则,如第 306 页所示。
COURNOT MONOPOLY|ECON经济作业代写ECONOMICS代考
考虑两个人一种和乙谁消费私人物品X(数量X一种和X乙, 分别) 和公共物品G. 我们定义米R小号一种和米R小号乙就私人物品而言,为公共物品支付的边际意愿。最优条件是
米R小号一种+米R小号乙 =|dX一种dG|无差异曲线 +|dX乙dG|无差异曲线 =!|d(X一种+X乙)dG|转换曲线 =米R吨
假设这个条件不满足。例如,让边际转化率小于边际替代率之和。然后,再生产一个单位的公共物品是个好主意。两个消费者需要放弃米R吨私人单位

matlab代写请认准UprivateTA™.
经济代写
计量经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
微观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
宏观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写