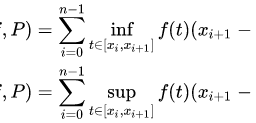微积分(Calculus),数学概念,是高等数学中研究函数的微分(Differentiation)、积分(Integration)以及有关概念和应用的数学分支。它是数学的一个基础学科,内容主要包括极限、微分学、积分学及其应用。微分学包括求导数的运算,是一套关于变化率的理论。它使得函数、速度、加速度和曲线的斜率等均可用一套通用的符号进行讨论。积分学,包括求积分的运算,为定义和计算面积、体积等提供一套通用的方法
my-assignmentexpert™ 微积分calculus作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的微积分calculus作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于economics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此微积分calculus作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在经济学作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的微积分calculus代写服务。我们的专家在微积分calculus学 代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微积分calculus相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的econ代写服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 单变量微积分
- 多变量微积分
- 傅里叶级数
- 黎曼积分
- ODE
- 微分学
微积分代考calculus代写|Convergence and Absolute Convergence
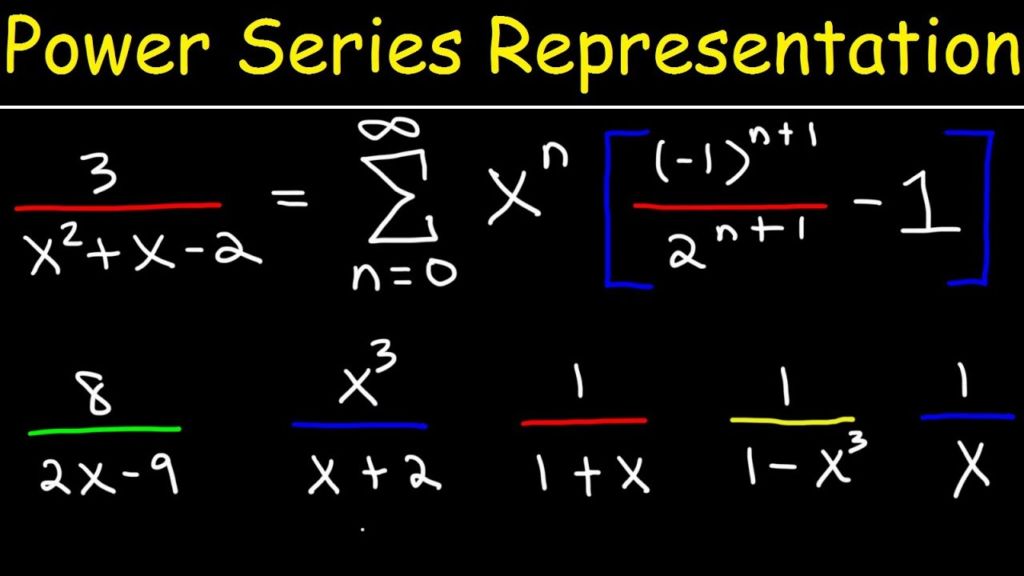
Example 5.3.2 Consider the power series $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{x^{n}}{n}$. In this case, we know that the series converges at $x=-1$ and diverges at $x=1$. Hence, its radius of convergence is 1 , and its domain of convergence is $[-1,1)$.
Example 5.3.3 Consider the power series $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{x^{n}}{n^{2}}$. We know that this series converges at $x=1$ and $x=-1$. Since
$$
\frac{\left|x^{n+1} /(n+1)^{2}\right|}{\left|x^{n} / n^{2}\right|}=|x| \frac{n^{2}}{(n+1)^{2}} \rightarrow|x| \text { as } n \rightarrow \infty,
$$
by ratio test the series $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\left|\frac{x^{n}}{n^{2}}\right|$ converges for $x$ with $|x|<1$ and diverges for $x$ with $|x|>1$. Therefore, the radius of convergence is 1 , and the domain of convergence is $[-1,1]$.
Example 5.3.4 Consider the power series $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{x^{n}}{n !}$. Since
$$
\frac{\left|x^{n+1} /(n+1) !\right|}{\left|x^{n} / n !\right|}=\frac{|x|}{n+1} \rightarrow 0 \text { as } n \rightarrow \infty
$$
by ratio test the series converges at every $x \in \mathbb{R}$. Hence, the radius of convergence is $\infty$, and the domain of convergence is $\mathbb{R}$. Note that in this case the function
$$
f(x)=e^{x}, \quad x \in \mathbb{R},
$$
represents the given power series.
$\diamond$
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|Term by Term Differentiation and Integration
In this subsection, we shall consider, without loss of generality, that a power series is of the form $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_{n} x^{n}$ with domain of convergence and radius of convergence are $D$ and $R$, respectively. Let
$$
f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_{n} x^{n}, \quad x \in D .
$$
Now, we address the following questions on the power series $\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_{n} x^{n}$.
- Is $f$ continuous on $D$ ?
- Is $f$ integrable on every interval $[a, b] \subseteq D$ ?
- If $f$ is integrable on $[a, b] \subseteq D$, then do we have the equality
$$
\int_{a}^{b} f(x) \mathrm{d} x=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_{n} \int_{a}^{b} x^{n} \mathrm{~d} x ?
$$ - Is $f$ differentiable on $(-R, R)$ ?
- If $f$ is differentiable on $(-R, R)$, and if $g=f^{\prime}$, then do we have the equality
$$
g(x)=\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} n a_{n} x^{n-1} \text { on }(-R, R) ?
$$
We show that the answers to all the above questions are in the affirmative. In this regard the following theorem is very crucial.
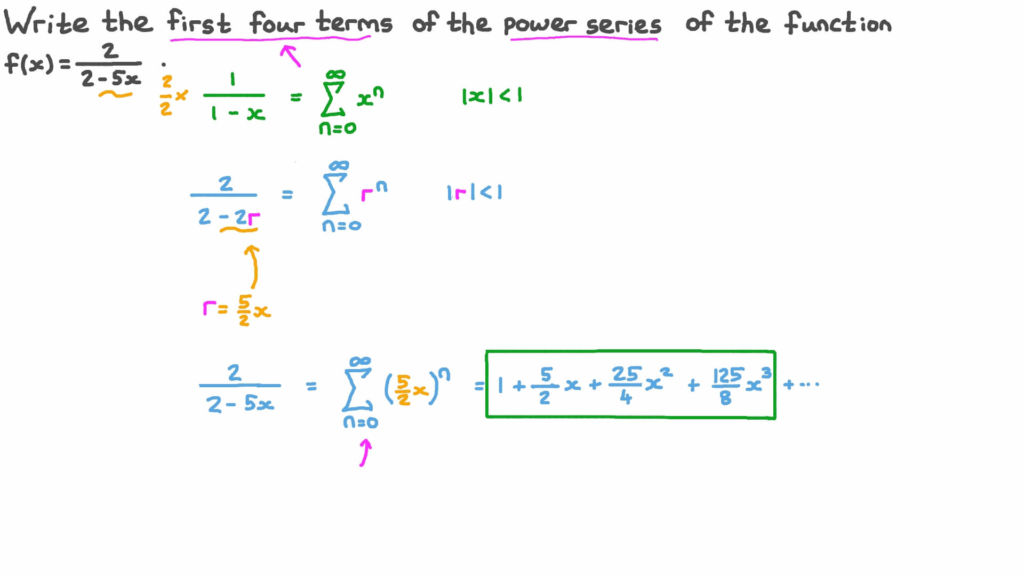
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|CONVERGENCE AND ABSOLUTE CONVERGENCE
例 5.3.2 考虑幂级数∑n=0∞Xnn. 在这种情况下,我们知道级数收敛于X=−1并且发散于X=1. 因此,它的收敛半径为 1 ,其收敛域为[−1,1).
例 5.3.3 考虑幂级数∑n=0∞Xnn2. 我们知道这个系列收敛于X=1和X=−1. 自从
|Xn+1/(n+1)2||Xn/n2|=|X|n2(n+1)2→|X| 作为 n→∞,
按比率测试系列∑n=0∞|Xnn2|收敛于X和|X|<1并且发散为X和|X|>1. 因此,收敛半径为 1 ,收敛域为[−1,1].
例 5.3.4 考虑幂级数∑n=0∞Xnn!. 自从
|Xn+1/(n+1)!||Xn/n!|=|X|n+1→0 作为 n→∞
通过比率测试,系列收敛于每个X∈R. 因此,收敛半径为∞, 收敛域是R. 请注意,在这种情况下,函数
F(X)=和X,X∈R,
表示给定的幂级数。
⋄
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|TERM BY TERM DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION
在本小节中,我们将不失一般性地考虑,幂级数的形式为∑n=0∞一种nXn收敛域和收敛半径分别为D和R, 分别。让
F(X)=∑n=0∞一种nXn,X∈D.
现在,我们解决以下关于幂级数的问题∑n=0∞一种nXn.
- 是F连续开D?
- 是F在每个区间上可积[一种,b]⊆D?
- 如果F可积在[一种,b]⊆D, 那么我们是否有等式
∫一种bF(X)dX=∑n=0∞一种n∫一种bXn dX? - 是F可微分(−R,R)?
- 如果F是可微的(−R,R), 而如果G=F′, 那么我们是否有等式
G(X)=∑n=1∞n一种nXn−1 在 (−R,R)?
我们证明以上所有问题的答案都是肯定的。在这方面,以下定理非常关键。

微积分note Integer Multiples of Irrational Numbers 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。