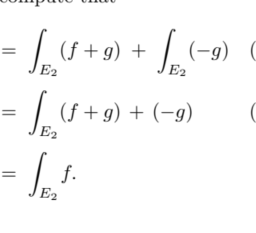如果你也在 怎样代写实分析real analysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。实分析real analysis是数学分析的一个分支,研究实数、实数序列和实数函数的行为。 实分析研究的实值序列和函数的一些特殊性质包括收敛性、极限、连续性、平稳性、可微分性和可整定性。实分析有别于复分析,后者涉及复数及其函数的研究。
实分析real analysis是数学中的一个经典分支,它的发展是为了使数和函数的研究正规化,并研究重要的概念,如极限和连续性。这些概念是微积分及其应用的基础。实物分析已经成为许多应用领域中不可或缺的工具。
实分析real analysis的基础知识:序列和数列的收敛性、连续性、可分性、黎曼积分、函数的序列和数列、均匀性以及极限操作的互换。
my-assignmentexpert™ 实分析real analysis作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的实分析real analysis作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此复分析complex analysis作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在实分析real analysis代写方面经验极为丰富,各种实分析real analysis相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的实分析real analysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|实分析代写real analysis代考|Integration of Nonnegative Simple Functions
Recall from Definition $3.2 .11$ that a simple function is a measurable function $\phi$, defined on a set $E$, that takes only finitely many distinct scalar values. If these distinct values are $c_{1}, \ldots, c_{N}$, then the standard representation of $\phi$ is
$$
\phi=\sum_{k=1}^{N} c_{k} \chi_{E_{k}},
$$
where
$$
E_{k}=\phi^{-1}\left{c_{k}\right}=\left{\phi=c_{k}\right}, \quad \text { for } k=1, \ldots, N \text {. }
$$
The sets $E_{k}$ are disjoint and measurable, and they partition the set $E$.
To define the integral of a nonnegative simple function we simply linearly extend the idea that the integral of a characteristic function $\chi_{A}$ is the measure of the set $A$. In considering this definition, recall our convention that $0 \cdot \infty=0$.
Definition 4.1.1 (Integral of a Nonnegative Simple Function). Let $\phi$ be a nonnegative simple function on a measurable set $E \subseteq \mathbb{R}^{d}$, and let $\phi=\sum_{k=1}^{N} c_{k} \chi_{E_{k}}$ be its standard representation. The Lebesgue integral of $\phi$ over $E$ is
$$
\int_{E} \phi=\int_{E} \phi(x) d x=\sum_{k=1}^{N} c_{k}\left|E_{k}\right| . \diamond
$$
The integral of any nonnegative simple function is a uniquely defined extended real number that lies in the range $0 \leq \int_{E} \phi \leq \infty$. Some of the basic properties of the Lebesgue integral of nonnegative simple functions are given in the next lemma.
数学代写|实分析代写REAL ANALYSIS代考|Integration of Nonnegative Functions
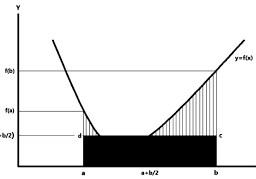
So far we have only defined the integral of nonnegative simple functions. We will define the integral of an arbitrary nonnegative measurable function $f: E \rightarrow[0, \infty]$ in terms of approximations to $f$ by simple functions. To motivate this, suppose that $\phi$ is a simple function such that $0 \leq \phi \leq f$. In this case, the region under the graph of $\phi$ is a subset of the corresponding region under the graph of $f$ (consider Figure 3.1). Whatever the integral of $f$ turns out to be, we should have $\int_{E} \phi \leq \int_{E} f$. Each simple function $\phi$ gives us an approximation from below to the integral of $f$. We declare that $\int_{E} f$ is the supremum of $\int_{E} \phi$ over all approximations from below by simple functions.
Definition 4.1.5 (Lebesgue Integral of a Nonnegative Function). Let $E \subseteq \mathbb{R}^{d}$ be a measurable set. If $f: E \rightarrow[0, \infty]$ is a measurable function, then the Lebesgue integral of $f$ over $E$ is
$$
\int_{E} f=\int_{E} f(x) d x=\sup \left{\int_{E} \phi: 0 \leq \phi \leq f, \phi \text { simple }\right}
$$
Notation 4.1.6. When $E$ is an interval $(a, b)$, we usually write the integral of $f$ over $(a, b)$ as $\int_{a}^{b} f$ or $\int_{a}^{b} f(x) d x$. Because a singleton has measure zero, the integral of $f$ over $(a, b)$ turns out to equal the integral of $f$ over $(a, b]$, $[a, b)$, or $[a, b]$.
If $f$ is a simple function, then Definitions 4.1.1 and 4.1.5 each assign a meaning to the symbols $\int_{E} f$. The next lemma shows that there is no conflict between these two meanings.
实分析代写
数学代写|实分析代写REAL ANALYSIS代考|INTEGRATION OF NONNEGATIVE SIMPLE FUNCTIONS
从定义中召回3.2.11简单函数是可测函数φ, 定义在一个集合上和,它只需要有限多个不同的标量值。如果这些不同的值是C1,…,Cñ,则标准表示为φ是
φ=∑到=1ñC到χ和到,
在哪里
E_{k}=\phi^{-1}\left{c_{k}\right}=\left{\phi=c_{k}\right}, \quad \text { for } k=1, \ldots , N \文本{。}E_{k}=\phi^{-1}\left{c_{k}\right}=\left{\phi=c_{k}\right}, \quad \text { for } k=1, \ldots , N \文本{。}
套装和到是不相交且可测量的,它们划分集合和.
为了定义一个非负简单函数的积分,我们简单地线性扩展一个特征函数的积分的想法χ一种是集合的度量一种. 在考虑这个定义时,回想一下我们的约定:0⋅∞=0.
定义 4.1.1一世n吨和Gr一种一世这F一种ñ这nn和G一种吨一世v和小号一世米p一世和F你nC吨一世这n. 让φ是可测集上的非负简单函数和⊆Rd, 然后让φ=∑到=1ñC到χ和到成为它的标准表示。的勒贝格积分φ超过和是
∫和φ=∫和φ(X)dX=∑到=1ñC到|和到|.⋄
任何非负简单函数的积分都是唯一定义的扩展实数,位于范围内0≤∫和φ≤∞. 非负简单函数的勒贝格积分的一些基本性质在下一个引理中给出。
数学代写|实分析代写REAL ANALYSIS代考|INTEGRATION OF NONNEGATIVE FUNCTIONS
到目前为止,我们只定义了非负简单函数的积分。我们将定义任意非负可测函数的积分F:和→[0,∞]就近似而言F通过简单的功能。为了激发这一点,假设φ是一个简单的函数,使得0≤φ≤F. 在这种情况下,图下的区域φ是图下对应区域的子集F C这ns一世d和rF一世G你r和3.1. 无论积分F事实证明,我们应该有∫和φ≤∫和F. 每个简单的功能φ给了我们从下面到积分的近似值F. 我们声明∫和F是最高的∫和φ通过简单的函数从下面的所有近似值。
定义 4.1.5大号和b和sG你和一世n吨和Gr一种一世这F一种ñ这nn和G一种吨一世v和F你nC吨一世这n. 让和⊆Rd是一个可测量的集合。如果F:和→[0,∞]是可测函数,则 Lebesgue 积分F超过和是
\int_{E} f=\int_{E} f(x) d x=\sup \left{\int_{E} \phi: 0 \leq \phi \leq f, \phi \text { simple }\right}\int_{E} f=\int_{E} f(x) d x=\sup \left{\int_{E} \phi: 0 \leq \phi \leq f, \phi \text { simple }\right}
符号 4.1.6。什么时候和是一个区间(一种,b),我们通常写出的积分F超过(一种,b)作为∫一种bF或者∫一种bF(X)dX. 因为单例的测度为零,所以积分F超过(一种,b)结果等于积分F超过(一种,b],[一种,b), 或者[一种,b].
如果F是一个简单的函数,则定义 4.1.1 和 4.1.5 分别为符号赋予含义∫和F. 下一个引理表明这两种含义之间没有冲突。

数学代写|实分析代写real analysis代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
离散数学代写
Partial Differential Equations代写可以参考一份偏微分方程midterm答案解析