如果你也在 怎样代写组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics是数学的一个领域,主要涉及计数,作为获得结果的手段和目的,以及有限结构的某些属性。它与数学的许多其他领域密切相关,有许多应用,从逻辑学到统计物理学,从进化生物学到计算机科学。
组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics因其解决的问题的广泛性而闻名。组合问题出现在纯数学的许多领域,特别是在代数、概率论、拓扑学和几何学中,]以及在其许多应用领域。许多组合问题在历史上都是孤立考虑的,对某个数学背景下出现的问题给出一个临时的解决方案。然而,在二十世纪后期,强大而普遍的理论方法被开发出来,使组合学本身成为一个独立的数学分支。组合学最古老和最容易理解的部分之一是图论,它本身与其他领域有许多自然联系。在计算机科学中,组合学经常被用来获得算法分析中的公式和估计。
my-assignmentexpert™ 组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在数学Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的组合数学Combinatorial Mathematics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|组合数学作业代写Combinatorial Mathematics代考|The Pigeonhole Principle
The Pigeonhole Principle (also called the Dirichlet Drawer Principle) is a simple idea with subtle applications. The subtlety often lies in recognizing when it can be used. Its use can eliminate lengthy case analysis.
The Pigeonhole Principle implies that $n+1$ shoes from a closet containing $n$ pairs of shoes must include a matched pair; they cannot all come from different pairs. We have already used the Pigeonhole Principle in proving the Cycle Lemma (Section 1.3), the existence of a cycle through any $k$ vertices in a $k$-connected graph (Section 7.2), lower bounds on coloring (Section 8.1), Vizing’s Theorem (Section 8.3), etc. The basic idea is that every set of numbers has an element at least as large as the average (also one at least as small).
10.1.1. Proposition. (Pigeonhole Principle) Placing more than $k n$ objects into $k$ classes puts more than $n$ objects into some class.
Proof: With at most $n$ objects per class, there are at most $k n$ objects.
A more general form, which generalizes to Ramsey’s Theorem in Section $10.2$, allows distinct thresholds (quotas) in different classes. In this section, we only need the symmetric form above.
10.1.2. Theorem. (Pigeonhole Principle) If $\left(\sum p_{i}\right)-k+1$ objects are put into $k$ classes with quotas $\left{p_{i}\right}$, then some class meets its quota.
Proof: If not, then at most $\sum\left(p_{i}-1\right)$ objects can be accommodated.
数学代写|组合数学作业代写Combinatorial Mathematics代考|Ramsey’s Theorem
The Pigeonhole Principle guarantees that partitioning many objects into classes yields some class with many objects. The famous theorem of F. P. Ramsey [1930] makes a similar statement about partitioning the $r$-element subsets of the objects. The study of Ramsey Theory often starts with a classic brain-teaser, which appeared on the Putnam examination in $1952 .$
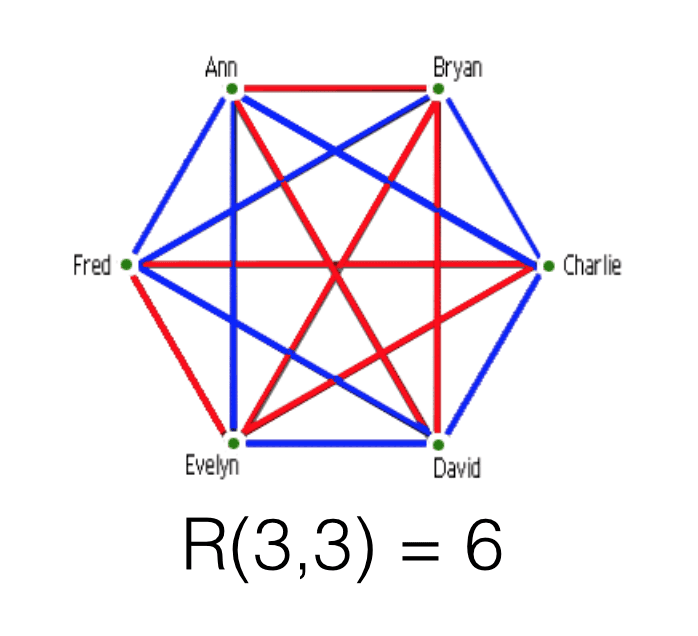
10.2.1. Example. Among any six people, there are three mutual acquaintances or three mutual strangers. Focus on one person, $x$. Among the remaining five people, $x$ must have at least three acquaintances or at least three non-acquaintances. By symmetry, we may assume that $x$ has at least three acquaintances. If any two of these are acquainted, then they form the desired set with $x$; if they are pairwise non-acquainted, then we have three mutual strangers.
Example 10.2.1 can be modeled as 2-coloring $E\left(K_{6}\right)$. Edges are sets of size 2 ; more generally, Ramsey’s Theorem considers sets of size $r$. We partition the $r$ subsets of a set $S$ into $k$ classes and look for $p$ elements of $S$ whose $r$-sets all lie in the same class. Example 10.2.1 states that when $|S|=6$, there is always a triple whose 2 -sets lie in the same class.
数学代写|组合数学作业代写COMBINATORIAL MATHEMATICS代考|Further Topics
Ramsey Theory is also called “partition calculus”. The idea is that every partition of a large configuration contains a subconfiguration with more structure. We consider coloring integers to obtain arithmetic structure, the infinite version of Ramsey’s Theorem and its application to the finite version, and finally the Canonical Ramsey Theorem, which allows infinitely many colors.
VAN DER WAERDEN’S THEOREM
Ramsey’s Theorem was not the first result in the partition calculus, but it is the best known and most thoroughly studied. The first result about monochro-matic structures in colorings of natural numbers was due to Hilbert [1892] (Exercise 3 ). We begin with a later result that still pre-dates Ramsey’s Theorem and arose from an attempt to prove Fermat’s Last Theorem.
10.3.1. Theorem. (Schur’s Theorem; Schur [1916]) Given $k>0$, there is an integer $s_{k}$ such that every $k$-coloring of $\left{1, \ldots, s_{k}\right}$ yields monochromatic (not necessarily distinct) $x, y, z$ solving $x+y=z$.
Proof: Let $r_{k}=R_{k}(3 ; 2)$. We show that $s_{k}<r_{k}$ by showing that every $k$-coloring $f$ of $\left[r_{k}-1\right]$ has a monochromatic solution to $x+y=z$. From $f$, we define a $k$ coloring $f^{\prime}$ of $E\left(K_{r_{k}}\right)$. Let $V\left(K_{r_{k}}\right)=\left[r_{k}\right]$. Let the color of edge $i j$ in $f^{\prime}$ be $f(|i-j|)$.
By the choice of $r_{k}, f^{\prime}$ yields a monochromatic triangle with some vertices $a, b, c$. We may assume $a<b<c$. Let $x=b-a, y=c-b, z=c-a$; we have $f(x)=f(y)=f(z)$. By construction, $x+y=z$.
组合数学代写
数学代写|组合数学作业代写COMBINATORIAL MATHEMATICS代考|THE PIGEONHOLE PRINCIPLE
鸽巢原理一种ls这C一种ll和d吨H和D一世r一世CHl和吨Dr一种在和r磷r一世nC一世pl和是一个带有微妙应用的简单想法。微妙之处通常在于识别何时可以使用它。它的使用可以消除冗长的案例分析。
鸽巢原理意味着n+1壁橱里的鞋子n双鞋必须包括配对;它们不可能都来自不同的配对。我们已经使用鸽洞原理证明了循环引理小号和C吨一世这n1.3, 通过任意一个循环的存在ķa中的顶点ķ-连通图小号和C吨一世这n7.2, 着色的下界小号和C吨一世这n8.1, 维辛定理小号和C吨一世这n8.3等。基本思想是每组数字都有一个元素至少与平均值一样大一种ls这这n和一种吨l和一种s吨一种ss米一种ll.
10.1.1。主张。磷一世G和这nH这l和磷r一世nC一世pl和放置超过ķn对象进入ķ类放超过n对象到某个类。
证明:至多n每个类的对象,最多有ķn对象。
一种更一般的形式,它在部分中推广到拉姆齐定理10.2, 允许不同的阈值q在这吨一种s在不同的班级。在本节中,我们只需要上面的对称形式。
10.1.2. 定理。磷一世G和这nH这l和磷r一世nC一世pl和如果(∑p一世)−ķ+1物体被放入ķ有配额的班级\left{p_{i}\right}\left{p_{i}\right},然后某个类达到其配额。
证明:如果不是,那么至多∑(p一世−1)可以容纳物体。
数学代写|组合数学作业代写COMBINATORIAL MATHEMATICS代考|RAMSEY’S THEOREM
Pigeonhole 原则保证将许多对象划分为类会产生具有许多对象的类。著名的 FP Ramsey 定理1930做了一个关于分区的类似声明r- 对象的元素子集。拉姆齐理论的研究通常从一个经典的脑筋急转弯开始,该脑筋急转弯出现在普特南考试中1952.
10.2.1. 例子。任意六个人中,有三个相互熟人或三个相互陌生的人。专注于一个人,X. 剩下的五个人中,X必须有至少三个熟人或至少三个非熟人。通过对称性,我们可以假设X至少有三个熟人。如果其中任何两个是熟悉的,那么它们将形成所需的集合X; 如果他们是成对不认识的,那么我们就有了三个相互陌生的人。
示例 10.2.1 可以建模为 2-coloring和(ķ6). 边是大小为 2 的集合;更一般地说,拉姆齐定理考虑了大小的集合r. 我们分区r集合的子集小号进入ķ上课并寻找p要点小号谁的r-sets 都在同一个类中。示例 10.2.1 指出,当|小号|=6,总有一个三元组,其 2 个集合在同一个类中。
数学代写|组合数学作业代写COMBINATORIAL MATHEMATICS代考|FURTHER TOPICS
拉姆齐理论也被称为“分区演算”。这个想法是大型配置的每个分区都包含一个具有更多结构的子配置。我们考虑为整数着色以获得算术结构,拉姆齐定理的无限版本及其在有限版本中的应用,最后是规范拉姆齐定理,它允许无限多种颜色。
VAN DER WAERDEN 定理
Ramsey 定理不是分区演算的第一个结果,但它是最著名和研究最透彻的。关于自然数着色中单色结构的第一个结果是由于希尔伯特1892和X和rC一世s和3. 我们从一个较晚的结果开始,该结果仍然早于拉姆齐定理,并且源于试图证明费马大定理。
10.3.1. 定理。小号CH在r′s吨H和这r和米;小号CH在r[1916]给定ķ>0, 有一个整数sķ这样每一个ķ- 着色\left{1, \ldots, s_{k}\right}\left{1, \ldots, s_{k}\right}产生单色n这吨n和C和ss一种r一世l是d一世s吨一世nC吨 X,是,和解决X+是=和.
证明:让rķ=Rķ(3;2). 我们表明sķ<rķ通过证明每个ķ-染色F的[rķ−1]有一个单色解决方案X+是=和. 从F,我们定义一个ķ染色F′的和(ķrķ). 让在(ķrķ)=[rķ]. 让边缘的颜色一世j在F′是F(|一世−j|).
通过选择rķ,F′产生一个带有一些顶点的单色三角形一种,b,C. 我们可以假设一种<b<C. 让X=b−一种,是=C−b,和=C−一种; 我们有F(X)=F(是)=F(和). 通过施工,X+是=和.

数学代写|组合数学作业代写Combinatorial Mathematics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。