如果你也在 怎样代写密码学cryptography这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。密码学cryptography是在存在对抗行为的情况下安全通信技术的实践和研究。 更广泛地说,密码学是关于构建和分析防止第三方或公众阅读私人信息的协议;[信息安全的各个方面,如数据保密性、数据完整性、认证和不可抵赖性,是现代密码学的核心。现代密码学存在于数学、计算机科学、电子工程、通信科学和物理学等学科的交叉点。密码学的应用包括电子商务、基于芯片的支付卡、数字货币、计算机密码和军事通信。
密码学cryptography实际上是加密的同义词,将信息从可读状态转换为不可理解的废话。加密信息的发送者只与预期的接收者分享解码技术,以排除对手的访问。密码学文献通常用Alice(”A”)代表发送者,Bob(”B”)代表预定接收者,Eve(”窃听者”)代表对手。 自从第一次世界大战中转子密码机的发展和第二次世界大战中计算机的出现,密码学方法变得越来越复杂,其应用也越来越多。
my-assignmentexpert™ 密码学cryptography作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的密码学cryptography作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此密码学cryptography作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的密码学cryptography代写服务。我们的专家在数学Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种密码学cryptography相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的密码学cryptography及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:

数学代写|密码学作业代写cryptography代考|Differential Cryptanalysis
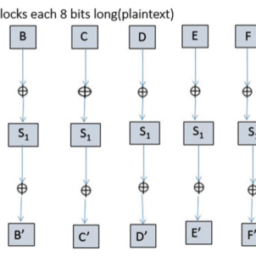
The idea of differential cryptanalysis is originally due to Eli Biham and Adi Shamir from the Weizmann Institute in Israel. ${ }^{1}$ It assumes a chosen plaintext attack model: the adversary can play with the encryption device as a black box, submitting chosen plaintexts and getting ciphertexts in return (see Fig. 4.1). The aim of the attack is to recover the secret key.
The basic idea of differential cryptanalysis is to investigate differential behaviors: we submit pairs of random plaintext blocks the difference of which is a fixed value $a$. We then look at the corresponding ciphertext difference until it is a fixed value $b$. A first analysis phase consists of looking for good $a$ and $b$ values in a heuristic way. A crucial quantity is the differential probability defined by
$$
\operatorname{DP}^{f}(a, b)=\operatorname{Pr}[f(X+a)=f(X)+b]
$$
where $f$ is the encryption function and $X$ is a uniformly distributed random variable. The higher this probability is, the more efficient the attack is. Additional dedicated tricks enable the analysis of complicated ciphers by using differentials on simplified variants.
We illustrate the differential cryptanalysis paradigm by the example of DES reduced to eight rounds instead of sixteen.
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY代考|Linear Cryptanalysis
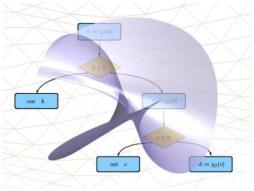
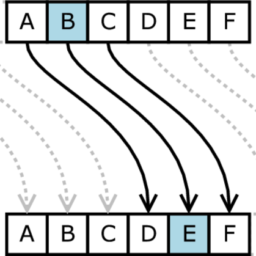
A dual idea to differential cryptanalysis was invented by Mitsuru Matsui at Mitsubishi Electronic (see Ref. $[124,125])$ based on previous works from Henri Gilbert and his colleagues of France Telecom (see Ref. $[74,75,178]$ ) and by the independent discovery of anomalies in the $S$-boxes of DES by Matt Franklin and Adi Shamir. ${ }^{2}$ It has been called linear cryptanalysis. In this method, instead of trying to keep track of difference propagation by chosen plaintext attacks, we try to keep track of Boolean information which is linearly obtained by a known plaintext attack: if we get one $(x, C(x))$ pair, we make a statistical analysis of the Boolean information $L(x, C(x))$ and deduce some information on the secret key (see Fig. 4.4).
We remind that all scalar linear mappings can be represented by a dot product with a constant vector: given $x \in{0,1}^{m}$ and a linear mapping $\varphi:{0,1}^{m} \rightarrow{0,1}$ there exists a unique $a$ such that for any $x$ we have
$$
\varphi(x)=a \cdot x=a_{1} x_{1} \oplus a_{2} x_{2} \oplus \cdots \oplus a_{m} x_{m}
$$
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY代考|Classical Security Strengthening
In order to measure the nonlinearity of a function $f$ we define
$$
\begin{aligned}
\operatorname{DP}^{f}(a, b) &=\operatorname{Pr}[f(X+a)=f(X)+b] \
\mathrm{DP}{\max }^{f} &=\max {a \neq 0, b} \operatorname{DP}^{f}(a, b) \
\operatorname{LP}^{f}(a, b) &=(2 \operatorname{Pr}[a \cdot X=b \cdot f(X)]-1)^{2} \
\mathrm{LP}{\max }^{f} &=\max {a, b \neq 0} \operatorname{LP}^{f}(a, b)
\end{aligned}
$$
where the probabilities hold over the uniform distribution of the random variable $X$. The nonlinearity for differential cryptanalysis corresponds to DP, and the nonlinearity for linear cryptanalysis corresponds to LP. DP ${ }^{f}(a, b)$ actually corresponds to the probability of the $a \rightarrow b$ differential characteristic for $f$. LP ${ }^{f}(a, b)$ corresponds to the LP bias of the $a \cdot x \oplus b \cdot f(x)$ bit. DP and LP are connected with the discrete Fourier transform.
密码学代写
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY代考|DIFFERENTIAL CRYPTANALYSIS
差分密码分析的想法最初是由以色列魏茨曼研究所的 Eli Biham 和 Adi Shamir 提出的。1它假设一个选择的明文攻击模型:攻击者可以将加密设备当作黑匣子,提交选择的明文并获得密文作为回报s和和F一世G.4.1. 攻击的目的是恢复密钥。
差分密码分析的基本思想是研究差分行为:我们提交成对的随机明文块,其差异是固定值一种. 然后我们看对应的密文差异,直到是固定值b. 第一个分析阶段包括寻找好的一种和b以启发式的方式取值。一个关键量是由下式定义的微分概率
DPF(一种,b)=公关[F(X+一种)=F(X)+b]
在哪里F是加密函数和X是一个均匀分布的随机变量。这个概率越高,攻击的效率就越高。其他专用技巧可以通过对简化变体使用差分来分析复杂密码。
我们通过将 DES 减少到 8 轮而不是 16 轮的例子来说明差分密码分析范式。
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY代考|LINEAR CRYPTANALYSIS
差分密码分析的双重思想是由三菱电子的 $[124,125])$ based on previous works from Henri Gilbert and his colleagues of France Telecom (see Ref. $[74,75,178]$ ) and by the independent discovery of anomalies in the $S$-boxes of DES by Matt Franklin and Adi Shamir. ${ }^{2}$ It has been called linear cryptanalysis. In this method, instead of trying to keep track of difference propagation by chosen plaintext attacks, we try to keep track of Boolean information which is linearly obtained by a known plaintext attack: if we get one $(x, C(x))$ pair, we make a statistical analysis of the Boolean information $L(x, C(x))$ 并推导出一些关于密钥的信息s和和F一世G.4.4.
我们提醒一下,所有标量线性映射都可以用一个具有常数向量的点积来表示:给定X∈0,1米和线性映射披:0,1米→0,1存在一个独特的一种这样对于任何X我们有
$$
\varphi(x)=a \cdot x=a_{1} x_{1} \oplus a_{2} x_{2} \oplus \cdots \oplus a_{m} x_{m}
$$
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY代考|CLASSICAL SECURITY STRENGTHENING
为了测量函数的非线性F我们定义
$$
\begin{aligned}
\operatorname{DP}^{f}(a, b) &=\operatorname{Pr}[f(X+a)=f(X)+b] \
\mathrm{DP}{\max }^{f} &=\max {a \neq 0, b} \operatorname{DP}^{f}(a, b) \
\operatorname{LP}^{f}(a, b) &=(2 \operatorname{Pr}[a \cdot X=b \cdot f(X)]-1)^{2} \
\mathrm{LP}{\max }^{f} &=\max {a, b \neq 0} \operatorname{LP}^{f}(a, b)
\end{aligned}
$$
其中概率保持随机变量的均匀分布X. 差分密码分析的非线性对应于DP,线性密码分析的非线性对应于LP。DPF(一种,b)实际上对应的概率一种→b差分特性为F. LPF(一种,b)对应于 LP 偏差一种⋅X⊕b⋅F(X)少量。DP 和 LP 与离散傅里叶变换相连。
数学代写|密码学作业代写cryptography代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。