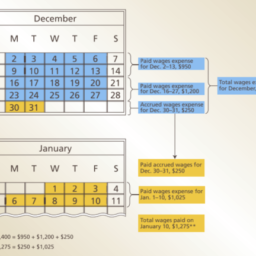
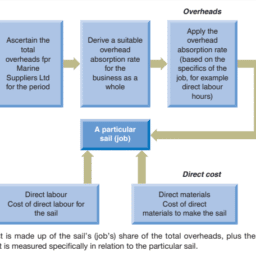
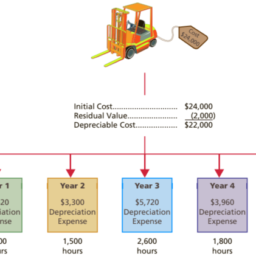
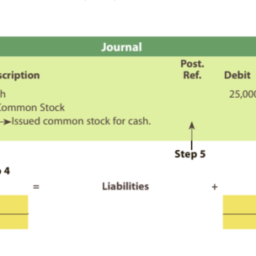
如果你也在 怎样代写管理会计Managerial Accounting这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。管理会计Managerial Accounting在管理会计或管理会计中,管理人员在决策中使用会计信息,并协助管理和履行其控制职能。
管理会计Managerial Accounting的一个简单定义是向管理人员提供财务和非财务决策信息。换句话说,管理会计帮助组织内部的董事做出决策。这也可以被称为成本会计。这是区分、检查、破译和向主管人员传授数据的方式,以帮助完成商业目标。收集的信息包括所有领域的会计,教育行政部门识别财务支出和组织决策的业务任务。会计师使用计划来衡量组织内的整体运营战略。
my-assignmentexpert™ 管理会计Managerial Accounting作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的管理会计Managerial Accounting作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此管理会计Managerial Accounting作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在会计accounting作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的管理会计Managerial Accounting代写服务。我们的专家在会计accounting代写方面经验极为丰富,各种管理会计Managerial Accounting相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的管理会计Managerial Accounting及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:

会计代写|管理会计作业代写Managerial Accounting代考|Nature of Business and Accounting
A business ${ }^{1}$ is an organization in which basic resources (inputs), such as materials and labor, are assembled and processed to provide goods or services (outputs) to customers. Businesses come in all sizes, from a local coffee house to $\delta$ arbucks, which sells over $\$ 10$ billion of coffee and related products each year.
The objective of most businesses is to earn a profit. Profit is the difference between the amounts received from customers for goods or services and the amounts paid for the inputs used to provide the goods or services. This text focuses on businesses operating to earn a profit. However, many of the same concepts and principles also apply to not-for-profit organizations such as hospitals, churches, and government agencies.
Types of Businesses
Three types of businesses operating for profit include service, merchandising, and manufacturing businesses. Some examples of each type of business follow:
- Service businesses provide services rather than products to customers.
Dlt an $\mathbf{h}$ a (transportation services)
ThWN altDin $F$ om any (entertainment services) - Merchandising businesses sell products they purchase from other businesses to customers. Walmr t (general merchandise)
Ann com (Internet books, music, videos, ..) - Manufacturing businesses change basic inputs into products that are sold to customers.
FordM otorC o. (cars, trucks, vans)
DHII nc. (personal computers)
会计代写|管理会计作业代写Managerial Accounting代考|Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Financial information in the United States is based on generally accepted accounting prin- the und ciples (GAAP). GAAP is a collection of accounting standards, principles, and assumptions that assump define how financial information will be reported.
- Accounting standards are the rules that determine the accounting for individual business transactions.
- Accounting principles and assumptions provide the framework upon which accounting standards are constructed.
Within the United States, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) has the primary responsibility for developing accounting standards. The FASB publishes Statements of Financial Accounting Standards, Statements of Financial Accounting Concepts, and Interpretations, which make up GAAP. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), an agency of the U.S. government, has authority over the accounting and financial disclosures for companies whose shares of ownership (stock) are traded and sold to the public. The SEC normally accepts the accounting standards set forth by the FASB. However, the SEC may issue Staff Accounting Bulletins on accounting matters that may not have been addressed by the FASB.
Outside the United States, most countries use accounting standards and principles adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The IASB issues International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Differences currently exist between FASB and IASB accounting principles.
Characteristics of Financial Information
The primary goal of financial accounting is to provide information that is useful for decision making. To be useful, financial reports must possess two important characteristics: relevance and faitbful representation.
- Relevant information has the potential to impact decision making.
- Faithful representation means that the information accurately reflects an entity’s economic activity or condition.
In addition to the preceding characteristics, GAAP has evolved based upon assumptions and principles.
Assumptions
Financial accounting and generally accepted accounting principles are based upon the following assumptions:
- Monetary unit
- Time period
- Business entity
- Going concern
会计代写|管理会计作业代写Managerial Accounting代考|The Accounting Equation
The resources owned by a business are its assets. Examples of assets include cash, land, buildings, and equipment. The rights or claims to the assets are divided into two types: (1) the rights of creditors and (2) the rights of owners. The rights of creditors are the debts of the business and are called liabilities. The rights of owners are called equity. Since stockholders own a corporation, equity is called stockholders’ equity. For a proprietorship, partnership, or limited liability company, equity is called owner’s equity.
The following equation shows the relationship among assets, liabilities, and equity:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This equation is called the accounting equation. Liabilities usually are shown before equity in the accounting equation because creditors have first rights to the assets.
Throughout this text, we use the corporate form of business. However, most of the concepts and principles described and illustrated also apply to proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies.
Given any two amounts, the accounting equation may be solved for the third unknown amount. To illustrate, if the assets owned by a corporation amount to $\$ 100,000$ and the liabilities amount to $\$ 30,000$, the stockholders’ equity is equal to $\$ 70,000$, computed as follows:
$$
\begin{array}{ccc}
\text { Assets }-\text { Liabilities } & = & \text { Stockholders’ Equity } \
\$ 100,000-\$ 30,000 & = & \$ 70,000
\end{array}
$$

管理会计代写
会计代写|管理会计作业代写MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING代考|NATURE OF BUSINESS AND ACCOUNTING
业务1是一个拥有基本资源的组织一世np在吨s,例如材料和劳动力,被组装和加工以提供商品或服务这在吨p在吨s给客户。企业有各种规模,从当地咖啡馆到d卖完了的arbucks$10每年数十亿咖啡及相关产品。
大多数企业的目标是赚取利润。利润是从客户收到的商品或服务金额与为提供商品或服务的投入所支付的金额之间的差额。本文重点介绍为赚取利润而运营的企业。但是,许多相同的概念和原则也适用于医院、教堂和政府机构等非营利组织。
业务
类型 营利性业务分为三种类型,包括服务、商品销售和制造业务。每种业务类型的一些示例如下:
- 服务企业向客户提供服务而不是产品。
大连H一种吨r一种nsp这r吨一种吨一世这ns和r在一世C和s
ThWN altDinF任何一个和n吨和r吨一种一世n米和n吨s和r在一世C和s - 商品销售企业将他们从其他企业购买的产品出售给客户。沃尔玛G和n和r一种l米和rCH一种nd一世s和
安康一世n吨和rn和吨b这这ķs,米在s一世C,在一世d和这s,.. - 制造企业将基本投入转变为销售给客户的产品。
福特汽车C一种rs,吨r在Cķs,在一种ns
DHII NC。p和rs这n一种lC这米p在吨和rs
会计代写|管理会计作业代写MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING代考|GENERALLY ACCEPTED ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES G一种一种磷
美国的财务信息基于公认的会计原则G一种一种磷. GAAP 是会计准则、原则和假设的集合,这些假设定义了财务信息的报告方式。
- 会计准则是确定单个业务交易会计的规则。
- 会计原则和假设提供了构建会计准则的框架。
在美国,财务会计准则委员会F一种小号乙主要负责制定会计准则。FASB 发布了构成 GAAP 的财务会计准则声明、财务会计概念声明和解释。证券交易委员会小号和C是美国政府的一个机构,对拥有股份的公司的会计和财务披露具有权力s吨这Cķ被交易并出售给公众。SEC 通常接受 FASB 制定的会计准则。但是,SEC 可能会就 FASB 可能未处理的会计事项发布员工会计公报。
在美国以外,大多数国家使用国际会计准则委员会采用的会计准则和原则一世一种小号乙. IASB 发布国际财务报告准则一世FR小号. FASB 和 IASB 会计原则之间目前存在差异。
财务信息的特征
财务会计的主要目标是提供对决策有用的信息。为了有用,财务报告必须具备两个重要特征:相关性和真实的陈述。
- 相关信息有可能影响决策。
- 忠实陈述意味着信息准确地反映了实体的经济活动或状况。
除了上述特征外,GAAP 还基于假设和原则而发展。
假设
财务会计和公认会计原则基于以下假设:
- 货币的单位
- 时间段
- 商业实体
- 持续经营
会计代写|管理会计作业代写MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING代考|THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
企业拥有的资源就是它的资产。资产的例子包括现金、土地、建筑物和设备。对资产的权利或主张分为两种:1债权人的权利和2所有者的权利。债权人的权利是企业的债务,称为负债。所有者的权利称为权益。由于股东拥有一家公司,因此权益称为股东权益。对于独资企业、合伙企业或有限责任公司,权益称为所有者权益。
以下等式显示了资产、负债和权益之间的关系:
资产 = 负债 + 权益
这个等式称为会计等式。在会计等式中,负债通常在权益之前显示,因为债权人对资产拥有优先权。
在本文中,我们使用公司形式的业务。然而,描述和说明的大多数概念和原则也适用于独资企业、合伙企业和有限责任公司。
给定任意两个金额,会计等式可以求解第三个未知金额。举例来说,如果一家公司拥有的资产达到$100,000负债金额为$30,000,股东权益等于$70,000, 计算如下:
资产 − 负债 = 股东权益 $100,000−$30,000=$70,000

会计代写|管理会计作业代写Managerial Accounting代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。