如果你也在 怎样代写图像压缩image compression这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。图像压缩image compression是一种应用于数字图像的数据压缩,以减少其存储或传输的成本。算法可以利用视觉感知和图像数据的统计特性,与用于其他数字数据的通用数据压缩方法相比,提供更优越的结果。
图像压缩image compression可以是有损或无损的。无损压缩是存档的首选,通常用于医学成像、技术图纸、剪贴画或漫画。有损压缩方法,特别是在低比特率下使用时,会引入压缩伪影。有损方法特别适用于自然图像,如照片,在这种应用中,为了实现比特率的大幅降低,可以接受微小的(有时难以察觉的)保真度损失。产生可忽略的差异的有损压缩可以被称为视觉上的无损。
my-assignmentexpert™ 图像压缩image compression作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的图像压缩image compression作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此图像压缩image compression作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图像压缩image compression代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图像压缩image compression相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的图像压缩image compression及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考|Sparse Prediction Problem Formulation
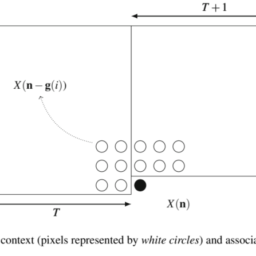
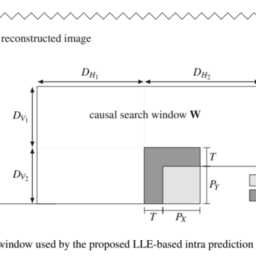
Consider the $N$-pixel region $\mathbf{S}$, the union of the $N_{p}$-pixel block $\mathbf{P}$ to be predicted, and the $N_{c}$-pixel approximation support (or template) $\mathbf{C}$, as illustrated in Fig. 2.9. Note that the pixels from the block $\mathbf{P}$ to be predicted are unknown, and the ones of the template $\mathbf{C}$ are the previously reconstructed pixels. By using an appropriate dictionary, the sparse prediction method estimates the best linear approximation for the known template $\mathbf{C}$ and keeps the same model to approximate the corresponding unknown block $\mathbf{P}$.
Let vector $\mathbf{b}$ be composed by the $N$ pixel values of region $\mathbf{S}$, stacked in a column (assuming zero value for unknown pixels of block $\mathbf{P}$ ). Also, let an $N \times M$ matrix $\mathbf{A}$ represent the dictionary matrix, a horizontal concatenation of $M$ basis functions represented as column vectors, $\mathbf{a}_{m}$, with $m=0, \ldots, M-1$. An over-complete dictionary is used, i.e. the number of atoms (or basis functions) $M$ is greater than the size $N$ of each function.
数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考|Matching Pursuit Methods
The MP algorithm can be used to compute sparse signal representations by iteratively selecting the dictionary atoms. This method provides a possible approximate solution to the problem in Eq. (2.3), which can be rewritten as:
$$
\min \left{|\mathbf{x}|_{0}:\left|\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}\right|_{2}^{2} \leq \rho\right},
$$
with some admissible approximation error $\rho \geq 0$.
MP procedure iteratively generates a sequence of possible solutions $\mathbf{x}{k}$, which present an increasing number of non-zero components. In first iteration, $\mathbf{x}{0}=\mathbf{0}$ and the initial residual vector is given by $\mathbf{r}{0}=\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}{0}=\mathbf{b}{c}$. At iteration $k$, MP selects the basis function, $\mathbf{a}{c_{m_{k}}}$ (with $m_{k}$ referring to the column index number), which has the highest correlation with the residual $\mathbf{r}{k-1}=\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}{k-1}$. The optimal dictionary atom $\mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}$ can be found by
$$
m_{k}=\arg \max {m} \frac{\left|\mathbf{a}{c_{m}}^{T} \mathbf{r}{k-1}\right|}{\left|\mathbf{a}{c_{m}}\right|_{2}} .
$$
The residual vector at iteration $k$ is then computed as
$$
\mathbf{r}{k}=\mathbf{r}{k-1}-\frac{\mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}^{T} \mathbf{r}{k-1}}{\mathbf{a}{c_{m_{k}}}^{T} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}=\mathbf{r}{k-1}-x{m_{k}} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}
$$
where $x_{m_{k}}$ is the weight of the new atom, which is added to $\mathbf{x}{k-1}$ in order to generate the new sparse solution vector $\mathbf{x}{k}$. MP proceeds with this algorithm until $| \mathbf{b}{c}-$ $\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}_{k} |^{2} \leq \rho$ is satisfied.
As previously stated, the optimal solution estimated for the template area $\mathbf{C}$ may not be the best one for the block $\mathbf{P}$. For a more efficient prediction of block $\mathbf{P}$, some methods propose to explicitly select the solution that provides the best prediction results for block $\mathbf{P}$, from a set of possible solutions. For example, in [67] all the intermediate solutions $\mathbf{x}{k}$, for $k=1, \ldots, k{\max }$, where $k_{\max }$ is the value of $k$ that satisfied the maximum error $\rho$, are saved and tested to predict the block $\mathbf{P}$. The optimum solution $\mathbf{x}{\text {opt }}$ that minimises the block prediction error, given by $| \mathbf{b}{p}-$ $\mathbf{A}{p} \mathbf{x}{k} |_{2}^{2}$, is selected.
In order to reproduce the prediction process in the decoder side, the iteration $k^{*}$ associated to the optimum solution $\mathbf{x}{\text {opt }}$ should be explicitly transmitted. The prediction block is calculated as $\hat{\mathbf{b}}{p}=\mathbf{A}{p} \mathbf{x}{\text {opt }}$. Algorithm $2.1$ summarises the described sparse image prediction procedure using MP algorithm.
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|Template Matching Algorithm
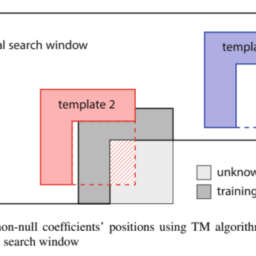
The TM algorithm 105 can be interpreted as a particular case of the presented sparse prediction method using MP, in which only one iteration is performed and the weighting coefficient is equal to 1 . In practice, TM algorithm can be formulated as a search procedure which compares the reference template with all equally shaped candidate templates existing in a causal search window (the atoms of the dictionary). The prediction of the unknown block is given by the reconstructed block associated (or adjacent) to the candidate template, which resulted in the lowest matching error. Typically, the reconstructed pixels belonging to the neighbourhood of the block to be predicted are used as reference template, equivalently to the area $\mathbf{C}$, of Fig. 2.9.
Improved variations of TM algorithm have been proposed and implemented in H.264/AVC standard, e.g. TM based on the averaging of multiple predictors 106 and TM using adaptive illumination compensation methods 129. The use of TM algorithm in addition to the traditional intra prediction modes has shown to be advantageous to predict textured areas. Applications of BMA for intra image prediction have also shown to provide effective prediction results 127. The principle of both methods is to reuse repeated patterns along the image. However, BMA requires some kind of signalling to indicate the optimal matched block in the causal reconstructed area, while TM provides an implicit way to find the matching block in the decoder. Hybrid approaches combining both BMA and TM for intra prediction have also been investigated in the past 15.
图像压缩代写
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|SPARSE PREDICTION PROBLEM FORMULATION
考虑ñ-像素区域小号, 的联合ñp-像素块磷被预测,并且ñC-像素近似支持这r吨和米pl一种吨和 C,如图 2.9 所示。请注意,来自块的像素磷要预测的都是未知的,而模板的C是先前重建的像素。通过使用适当的字典,稀疏预测方法估计已知模板的最佳线性近似C并保持相同的模型来逼近对应的未知块磷.
让向量b由ñ区域像素值小号, 堆叠成一列一种ss在米一世nG和和r这在一种l在和F这r在nķn这在np一世X和ls这Fbl这Cķ$磷$. 另外,让一个ñ×米矩阵一种表示字典矩阵,水平串联米表示为列向量的基函数,一种米, 和米=0,…,米−1. 使用了一个过完备字典,即原子数这rb一种s一世sF在nC吨一世这ns 米大于尺寸ñ每个功能的。
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|MATCHING PURSUIT METHODS
MP 算法可用于通过迭代选择字典原子来计算稀疏信号表示。该方法为方程式中的问题提供了可能的近似解。2.3,可以改写为:
$$
\min \left{|\mathbf{x}|_{0}:\left|\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}\right|_{2}^{2} \leq \rho\right},
$$
with some admissible approximation error $\rho \geq 0$.
MP procedure iteratively generates a sequence of possible solutions $\mathbf{x}{k}$, which present an increasing number of non-zero components. In first iteration, $\mathbf{x}{0}=\mathbf{0}$ and the initial residual vector is given by $\mathbf{r}{0}=\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}{0}=\mathbf{b}{c}$. At iteration $k$, MP selects the basis function, $\mathbf{a}{c_{m_{k}}}$ (with $m_{k}$ referring to the column index number), which has the highest correlation with the residual $\mathbf{r}{k-1}=\mathbf{b}{c}-\mathbf{A}{c} \mathbf{x}{k-1}$. The optimal dictionary atom $\mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}$ can be found by
$$
m_{k}=\arg \max {m} \frac{\left|\mathbf{a}{c_{m}}^{T} \mathbf{r}{k-1}\right|}{\left|\mathbf{a}{c_{m}}\right|_{2}} .
$$
The residual vector at iteration $k$ is then computed as
$$
\mathbf{r}{k}=\mathbf{r}{k-1}-\frac{\mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}^{T} \mathbf{r}{k-1}}{\mathbf{a}{c_{m_{k}}}^{T} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}=\mathbf{r}{k-1}-x{m_{k}} \mathbf{a}{c{m_{k}}}
$$
其中X米ķ是新原子的权重,添加到 $\mathbf{x} {k-1}一世n这rd和r吨这G和n和r一种吨和吨H和n和在sp一种rs和s这l在吨一世这n在和C吨这r\mathbf{x} {k}.米磷pr这C和和ds在一世吨H吨H一世s一种lG这r一世吨H米在n吨一世l| \mathbf{b} {c}-\mathbf{A} {c} \mathbf{x}_{k} |^{2} \leq \rho$ 满足。
如前所述,为模板区域估计的最优解C可能不是最好的街区磷. 为了更有效地预测块磷, 一些方法建议明确选择为块提供最佳预测结果的解决方案磷,来自一组可能的解决方案。例如,在67所有中间解$\mathbf{C}$ may not be the best one for the block $\mathbf{P}$. For a more efficient prediction of block $\mathbf{P}$, some methods propose to explicitly select the solution that provides the best prediction results for block $\mathbf{P}$, from a set of possible solutions. For example, in [67] all the intermediate solutions $\mathbf{x}{k}$, for $k=1, \ldots, k{\max }$, where $k_{\max }$ is the value of $k$ that satisfied the maximum error $\rho$, are saved and tested to predict the block $\mathbf{P}$. The optimum solution $\mathbf{x}{\text {opt }}$ that minimises the block prediction error, given by $| \mathbf{b}{p}-$ $\mathbf{A}{p} \mathbf{x}{k} |_{2}^{2}$, 被选中。
为了在解码端重现预测过程,迭代ķ∗关联到最优解 $\mathbf{x} {\text {opt }}sH这在ldb和和Xpl一世C一世吨l是吨r一种ns米一世吨吨和d.吨H和pr和d一世C吨一世这nbl这Cķ一世sC一种lC在l一种吨和d一种s\hat{\mathbf{b}} {p}=\mathbf{A} {p} \mathbf{x} {\text {opt }}.一种lG这r一世吨H米2.1$总结了使用MP算法描述的稀疏图像预测过程。
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|TEMPLATE MATCHING ALGORITHM
TM算法105可以被解释为所提出的使用MP的稀疏预测方法的一种特殊情况,其中仅执行一次迭代并且加权系数等于1。在实践中,TM 算法可以表述为一个搜索过程,它将参考模板与存在于因果搜索窗口中的所有形状相同的候选模板进行比较吨H和一种吨这米s这F吨H和d一世C吨一世这n一种r是. 未知块的预测由相关的重构块给出这r一种dj一种C和n吨到候选模板,这导致了最低的匹配错误。通常,将属于待预测块邻域的重建像素作为参考模板,相当于区域C, 图 2.9。
已在 H.264/AVC 标准中提出并实现了 TM 算法的改进变体,例如基于多个预测器平均的 TM 106 和使用自适应照明补偿方法 129 的 TM。除了传统的帧内预测模式之外,还使用 TM 算法已证明有利于预测纹理区域。BMA 在图像内预测中的应用也表明可以提供有效的预测结果 127。这两种方法的原理都是沿图像重复使用重复的模式。然而,BMA 需要某种信号来指示因果重构区域中的最佳匹配块,而 TM 提供了一种隐式方法来在解码器中找到匹配块。过去 15 年也研究了结合 BMA 和 TM 进行帧内预测的混合方法。

数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。