如果你也在 怎样代写图像压缩image compression这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。图像压缩image compression是一种应用于数字图像的数据压缩,以减少其存储或传输的成本。算法可以利用视觉感知和图像数据的统计特性,与用于其他数字数据的通用数据压缩方法相比,提供更优越的结果。
图像压缩image compression可以是有损或无损的。无损压缩是存档的首选,通常用于医学成像、技术图纸、剪贴画或漫画。有损压缩方法,特别是在低比特率下使用时,会引入压缩伪影。有损方法特别适用于自然图像,如照片,在这种应用中,为了实现比特率的大幅降低,可以接受微小的(有时难以察觉的)保真度损失。产生可忽略的差异的有损压缩可以被称为视觉上的无损。
my-assignmentexpert™ 图像压缩image compression作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的图像压缩image compression作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此图像压缩image compression作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图像压缩image compression代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图像压缩image compression相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的图像压缩image compression及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考|Dependent View Coding Tools
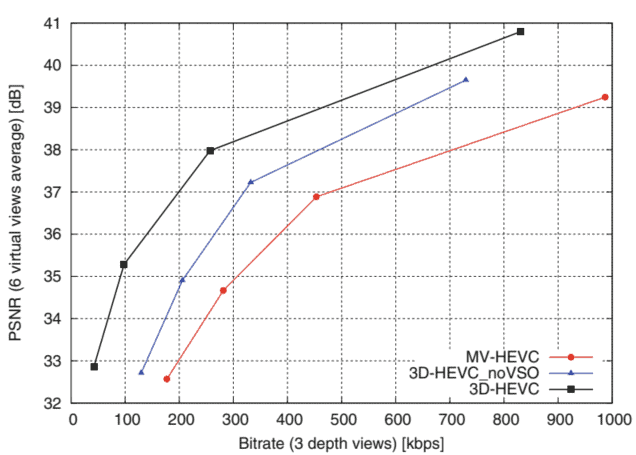
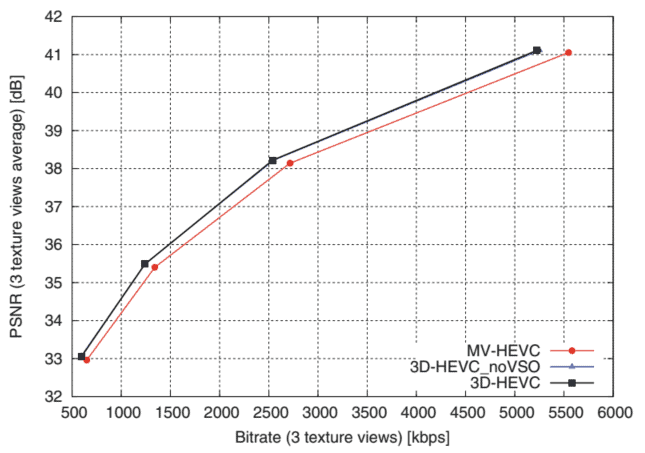
Similarly to MV-HEVC standard, the 3D-HEVC uses DCP to exploit inter-view dependencies for both texture video and depth map components. For an improved inter-view coding, 3D-HEVC also introduces modifications at the block-level tools, which allow to exploit the correlations of motion and residue information between multiple views. The most relevant tools include the Neighbouring Block-based Disparity Vector Derivation (NBDV), inter-view motion prediction, inter-view residual prediction and illumination compensation 14.
The main idea of the NBDV tool is to implicitly derive the disparity vector of the block, based on its spatial and temporal neighbourhood, in order to be used by other methods, namely the inter-view motion prediction and inter-view residual prediction. NBDV uses spatial candidates similar to the ones used in Advanced Motion Vector Prediction (AMVP) or merge modes of HEVC, plus a temporal neighbouring candidate. The first disparity vector found among the spatial and temporal candidates is returned by NBDV. When does not exist a disparity vector in the available candidates, a zero disparity vector is assumed. Note that this approach does not require any additional signalling symbol in the bitstream.
Regarding inter-view motion prediction, its main purpose is to include additional candidates into the list of the merge mode (see Sect. 2.3.2), which can use up to six candidates instead of the five candidates defined in HEVC standard. Two possible additional candidates are the disparity vector (and associated reference picture index) derived by the NBDV method, and the motion vector corresponding to the block pointed out by the NBDV vector.
The inter-view residual prediction is used to exploit similarities between the motion-compensated residue generated by two distinct views. Its procedure consists in predicting the motion-compensated residual signal of the predicted block using an already encoded view, namely the motion-compensated residual signal associated to the block that is pointed out by the NBDV disparity vector and the corresponding reference picture index.
The illumination compensation is used to compensate luminance variations often observed between views, for instance when the cameras have calibration differences. For this reason, this tool is only applied on blocks predicted from inter-view reference pictures. The illumination compensation is achieved by using a simple linear model, whose coefficients are implicitly estimated by solving a least-squares problem, based on the reconstructed samples in the block neighbourhood.
Other tools used to improve the compression of dependent texture video views using information of previously encoded depth maps from other views include the Depth-oriented Neighbouring Block-based Disparity Vector DoNBDV, the View Synthesis Prediction VSP and the Depth-Based Block Partitioning DBBP 14.
数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考|Depth Map Coding Tools
In order to better represent depth maps and preserve the sharp edges, 3D-HEVC proposes additional tools for depth map intra and inter coding, as well as for inter-component prediction. Moreover, some tools inherited from MV-HEVC are modified or disabled when compressing depth maps. The modified tools include the motion and disparity compensation methods. Instead of quarter-sample accuracy, the full-sample accuracy is used, because the eight-tap interpolation filters tend to create artifacts at sharp edges. Similarly, the estimated vectors are encoded using full-sample accuracy. The disabled tools in 3D-HEVC for depth map coding include the in-loop filters, specifically the DBF and the SAO. The inter-view motion and inter-view residual prediction tools presented above are also disabled for depth map coding. In order to exploit inter-component dependencies, 3D-HEVC proposes some modifications to the dependent coding techniques mentioned in Sect. 3.3.2.1 and includes new coding tools as well.
Regarding intra coding methods for depth maps, 3D-HEVC maintains the directional prediction modes and transform-based residue coding present in the reference HEVC standard. However, new tools that better preserve depth map discontinuities have been introduced [14], namely the Depth Modelling Modes (DMMs), segment-wise DC coding (SDC) and single depth intra mode.
DMM takes an important role for depth map representation in 3D-HEVC standard. It consists in new intra prediction modes that partition the depth block into two non-rectangular regions, which are approximated by constant values. The partitioning information and the mean value of both regions are the unique information required by this model. DMM may exploit some inter-component dependencies by deriving the depth block partitioning information from the colocated block in the corresponding texture video view. Similarly to directional modes, the residual signal calculated between the DMM model and the original depth map might be encoded using transform coding.
图像压缩代写
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|DEPENDENT VIEW CODING TOOLS
与 MV-HEVC 标准类似,3D-HEVC 使用 DCP 来利用纹理视频和深度图组件的视图间依赖性。对于改进的视图间编码,3D-HEVC 还引入了块级工具的修改,允许利用多个视图之间的运动和残留信息的相关性。最相关的工具包括基于相邻块的视差向量推导ñ乙D在、视图间运动预测、视图间残差预测和光照补偿 14。
NBDV 工具的主要思想是基于块的空间和时间邻域隐式推导块的视差向量,以便被其他方法使用,即视图间运动预测和视图间残差预测。NBDV 使用类似于高级运动矢量预测中使用的空间候选一种米在磷或 HEVC 的合并模式,加上一个时间相邻候选。在空间和时间候选中找到的第一个视差向量由 NBDV 返回。当可用候选中不存在视差矢量时,假定视差矢量为零。请注意,这种方法不需要比特流中的任何附加信令符号。
关于视图间运动预测,其主要目的是在合并模式的列表中包含额外的候选者s和和小号和C吨.2.3.2,它最多可以使用六个候选项,而不是 HEVC 标准中定义的五个候选项。两个可能的附加候选者是视差向量一种nd一种ss这C一世一种吨和dr和F和r和nC和p一世C吨在r和一世nd和XNBDV方法导出的运动向量,以及NBDV向量所指向的块对应的运动向量。
视图间残差预测用于利用由两个不同视图生成的运动补偿残差之间的相似性。其过程在于使用已经编码的视图来预测预测块的运动补偿残余信号,即与由 NBDV 视差向量和相应参考图片索引指出的块相关联的运动补偿残余信号。
照明补偿用于补偿视图之间经常观察到的亮度变化,例如当相机具有校准差异时。出于这个原因,该工具仅适用于从视图间参考图片预测的块。光照补偿是通过使用一个简单的线性模型来实现的,该模型的系数是通过解决最小二乘问题来隐式估计的,基于块邻域中的重建样本。
用于使用来自其他视图的先前编码的深度图信息来改进相关纹理视频视图的压缩的其他工具包括面向深度的基于相邻块的视差向量 DoNBDV、视图合成预测 VSP 和基于深度的块分区 DBBP 14。
数学代写|图像压缩代写IMAGE COMPRESSION代考|DEPTH MAP CODING TOOLS
为了更好地表示深度图并保留锐利的边缘,3D-HEVC 提出了用于深度图帧内和帧间编码以及组件间预测的附加工具。此外,一些从 MV-HEVC 继承的工具在压缩深度图时会被修改或禁用。修改后的工具包括运动和视差补偿方法。代替四分之一样本精度,使用全样本精度,因为八抽头插值滤波器倾向于在锐利边缘产生伪影。类似地,估计的向量使用全样本精度进行编码。3D-HEVC 中用于深度图编码的禁用工具包括环路滤波器,特别是 DBF 和 SAO。上面介绍的视图间运动和视图间残差预测工具也被禁用用于深度图编码。为了利用组件间的依赖关系,3D-HEVC 对 Sect 中提到的依赖编码技术提出了一些修改。3.3.2.1 并且还包括新的编码工具。
关于深度图的帧内编码方法,3D-HEVC 保留了参考 HEVC 标准中存在的方向预测模式和基于变换的残差编码。但是,已经引入了更好地保留深度图不连续性的新工具14,即深度建模模式D米米s, 分段 DC 编码小号DC和单深度帧内模式。
DMM 在 3D-HEVC 标准中对深度图表示起重要作用。它包含将深度块划分为两个非矩形区域的新帧内预测模式,这些区域由常数值近似。两个区域的划分信息和均值是该模型所需的唯一信息。DMM 可以通过从对应的纹理视频视图中的同位块导出深度块分割信息来利用一些组件间依赖性。与定向模式类似,在 DMM 模型和原始深度图之间计算的残差信号可以使用变换编码进行编码。

数学代写|图像压缩代写image compression代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。