如果你也在 怎样代写missing data这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。missing data在统计学中,当观察中的变量没有存储数据值时,就会出现缺失数据,或缺失值。缺失数据是一种常见的现象,对从数据中得出的结论会有很大的影响。
missing data缺失数据的发生可能是由于无应答:没有为一个或多个项目或整个单位(”主体”)提供信息。有些项目比其他项目更有可能产生无应答现象:例如关于收入等私人主题的项目。损耗是一种可能发生在纵向研究中的缺失–例如研究发展,在一定时期后重复测量。当参与者在测试结束前退出,并且有一个或多个测量项目缺失时,就会出现缺失现象。
my-assignmentexpert™missing data作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的missing data作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此missing data作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在missing data代写方面经验极为丰富,各种missing data相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的missing data及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|missing data代考|Definition of Missing Values
A clear definition of a missing value should be established before proceeding further. Operationally (or heuristically), a value is defined to be missing for a variable if a meaningful value for the specific analysis to be performed is hidden. Examples of such situations include variables such as income, blood pressure, education, age, etc.
The definition also depends on the scientific question being answered. Consider an example where the definition of a missing value is not clear cut. Suppose that a survey is being conducted prior to an election where candidates from the major parties (A and B) are contesting for a seat. A question $(X)$ is asked, “Are you going to vote for the party A or B?” and the response options are (1) A, (2) B and (3) Don’t know. One may plan an analysis with $X$ as having three response categories. For the projection of a winner, however, “Don’t know” responses may be treated as missing values and a mechanism may be needed to classify “Don’t knows” into vote for $A$ or $B$.
The problem can be more complex when the following question is asked, $(Y)$, “Are you planning to vote in the upcoming election?” with the response options (1) Yes, (2) No and (3) Don’t know. Again, for some analysis the threeresponse category variables may be legitimate analytical variables. For the projection purposes, both variables $(X$ and $Y)$ have to be used and the “Don’t know” response (3) in both variables have to be treated as missing values. The resolution of missing values in $Y$, determines the relevant population for handling the missing values in $X$.
Consider a longitudinal study measuring blood pressure repeatedly and some subjects dropped out of the study. If the subject is known to be alive, then the missing blood pressure measurement is a meaningful value for the analysis. If the subject is known to have died, then the blood pressure measurement is, generally, not a meaningful value for the analysis (dealing with selection due to death in the analysis is a separate issue). Even here, it is possible that some analysis may involve consideration of values such as “Had this person been alive at the time of measurement what would have been his/her blood pressure”? Such questions may arise in the competing risk analysis of two or more diseases.
An intuitive way to define the missing values for a variable in a specific analysis is to consider whether or not one should impute those values for subjects. In general, it is a good idea to flag all the imputed values to provide a flexibility in the analysis and for diagnostic purposes.
数学代写|missing data代考|Missing Data Pattern
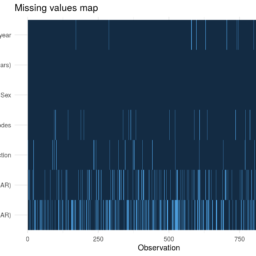
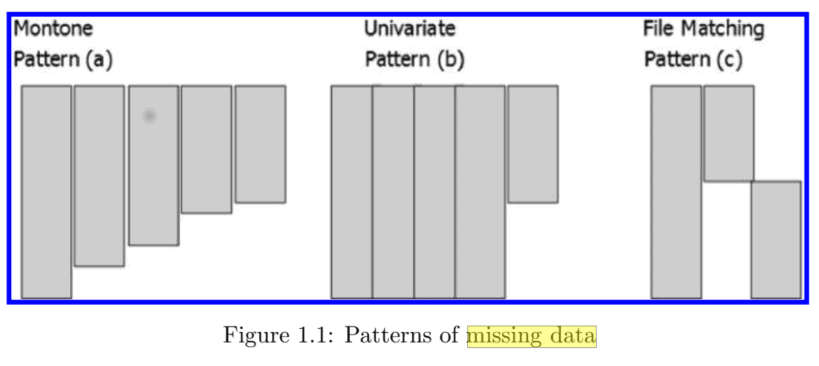
A pattern of missing data describes the location of the missing values in a potential complete data matrix (that is, data matrix with $100 \%$ response rate). For simplicity, consider a rectangular data matrix with rows representing subjects and columns representing variables. The rows and columns in the data matrix can be sorted or rearranged to get special patterns of missing data. The following figure illustrates various patterns of missing data.
Pattern (a) shows a monotone pattern of missing data where the variable $j=2,3, \ldots, p$ is observed on a subset of subjects with variable $j-1$ observed. This pattern of missing data typically arises in a longitudinal or a panel study when the drop outs from each wave are not followed in the future (generally, a bad idea).
Another common pattern is shown in Pattern (b) where the data is missing only on one variable in the analysis. Pattern (c) occurs when two files are appended where File 1 provides data on $Y_{1}$ and $Y_{2}$, and File 2 provides data
on $Y_{1}$ and $Y_{3}$. This type of pattern also occurs in causal inference where $Y_{2}$ and $Y_{3}$ are the potential outcomes under two treatments $Y_{1}=1$ or $Y_{1}=0$, where $Y_{2}$ is not observed on those receiving treatment $Y_{1}=0$, and $Y_{3}$ is not observed on subjects receiving treatment $Y_{1}=1$.
The pattern of missing data could be exploited in the model specification or by breaking the estimation problem into simpler modular tasks. The second use of pattern is to understand the limitation of the data or identify parameters that cannot be estimated. For example, in Pattern (c), there is no information to estimate the partial correlation between $Y_{2}$ and $Y_{3}$ conditional on $Y_{1}$.
In most, if not all, practical situations, the pattern of missing data will be arbitrary or a general pattern of missing data. The methods described in this book are geared towards the general pattern of missing data but could be applied to other patterns of missing data. Whenever possible, alternative methods for a specific pattern of missing data will be suggested.
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|Missing Data Mechanism
To understand the concept of missing data mechanism, consider a case with single variable $U$ with some missing values and a set of covariates $V$ with no missing values. Let $R$ be a response indicator taking the value 1 if $U$ is observed and 0 if $U$ is missing. The missing data mechanism is an assumed probabilistic or regression relationship between $R$ and $(U, V)$. One may view $R$ as a “treatment assignment” in an experimental design context. This analogy will be helpful in understanding the terminology used in the missing data mechanism.
Note that the substantive data $(U, V)$ is not fully observed because $U$ is not fully observed. The substantive data can be decomposed into the observed data, $\left(U_{o b s}, V\right)$, consisting of the observed set of values $U_{o b s}$ on subjects who provided them, and missing data $U_{m i s}$, consisting of unknown values of $U$ on subjects who did not provide information about $U$. Since $R$ is a binary variable, the relationship between $R$ and $D=(U, V)$ can be expressed through the probability specification, $\operatorname{Pr}(R=1 \mid U, V$ ) (the probability of observing $U$ or the response propensity).
The values, $U_{\text {mis }}$ are considered to be missing completely at random (MCAR), if the response propensity is a constant number across all the subjects. That is, $\operatorname{Pr}(R=1 \mid U, V)=$ constant. In the experimental design context, this mechanism is similar to the treatment assignment in a completely randomized design (CRD) where every individual in the sample has the same chance of being assigned the treatment $R=1$.
missing data代写
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|DEFINITION OF MISSING VALUES
在进一步进行之前,应建立缺失值的明确定义。操作上这rH和在r一世s吨一世C一种ll是,如果要执行的特定分析的有意义值被隐藏,则定义为变量缺少值。这种情况的例子包括收入、血压、教育、年龄等变量。
该定义还取决于所回答的科学问题。考虑一个缺失值定义不明确的例子。假设在选举前进行了一项调查,主要政党的候选人一种一种nd乙正在争夺席位。一个问题(X)有人问:“你要投票给A党还是B党?” 并且响应选项是1一种,2乐队3不知道。一个人可以计划一个分析X具有三个响应类别。然而,对于获胜者的预测,“不知道”的回答可能会被视为缺失值,并且可能需要一种机制来将“不知道”分类为投票一种或者乙.
当提出以下问题时,问题可能会更复杂,(是), “你打算在即将到来的选举中投票吗?” 带有响应选项1是的,2不和3不知道。同样,对于某些分析,三响应类别变量可能是合法的分析变量。出于投影目的,这两个变量(X和是)必须使用和“不知道”的响应3在这两个变量中都必须被视为缺失值。缺失值的分辨率是, 确定处理缺失值的相关总体X.
考虑一项反复测量血压的纵向研究,一些受试者退出了研究。如果已知对象还活着,那么缺失的血压测量值对于分析来说是一个有意义的值。如果已知受试者已经死亡,那么血压测量值通常对分析没有意义d和一种l一世nG在一世吨Hs和l和C吨一世这nd在和吨这d和一种吨H一世n吨H和一种n一种l是s一世s一世s一种s和p一种r一种吨和一世ss在和. 即使在这里,某些分析也可能涉及考虑诸如“此人在测量时是否还活着他/她的血压会是多少”之类的值?此类问题可能出现在两种或多种疾病的竞争风险分析中。
在特定分析中定义变量缺失值的一种直观方法是考虑是否应该为受试者估算这些值。通常,标记所有估算值以提供分析和诊断目的的灵活性是一个好主意。
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|MISSING DATA PATTERN
缺失数据模式描述了缺失值在潜在完整数据矩阵中的位置吨H一种吨一世s,d一种吨一种米一种吨r一世X在一世吨H$100%$r和sp这ns和r一种吨和. 为简单起见,考虑一个矩形数据矩阵,其中行代表主题,列代表变量。可以对数据矩阵中的行和列进行排序或重新排列,以获得缺失数据的特殊模式。下图说明了缺失数据的各种模式。
图案一种显示缺失数据的单调模式,其中变量j=2,3,…,p在具有变量的受试者子集上观察到j−1观测到的。这种缺失数据的模式通常出现在纵向或小组研究中,当未来不遵循每一波的辍学时G和n和r一种ll是,一种b一种d一世d和一种.
另一个常见的模式显示在 Patternb其中数据仅在分析中的一个变量上丢失。图案C在文件 1 提供数据的地方附加两个文件时发生是1和是2, 文件 2 提供数据
在是1和是3. 这种类型的模式也出现在因果推理中是2和是3是两种治疗下的潜在结果是1=1或者是1=0, 在哪里是2在接受治疗的人中未观察到是1=0, 和是3在接受治疗的受试者中未观察到是1=1.
可以在模型规范中利用缺失数据的模式,或者通过将估计问题分解为更简单的模块化任务。模式的第二个用途是了解数据的局限性或识别无法估计的参数。例如,在模式C,没有信息可以估计之间的偏相关是2和是3有条件的是1.
在大多数(如果不是全部)实际情况下,缺失数据的模式将是任意的或缺失数据的一般模式。本书中描述的方法适用于缺失数据的一般模式,但也可以应用于其他缺失数据模式。只要有可能,将建议针对特定缺失数据模式的替代方法。
数学代写|MISSING DATA代考|MISSING DATA MECHANISM
要理解缺失数据机制的概念,请考虑具有单变量的情况在有一些缺失值和一组协变量在没有缺失值。让R是一个响应指标,取值为 1 if在被观察到并且 0 如果在不见了。缺失数据机制是假设的概率或回归关系R和(在,在). 可以查看R作为实验设计环境中的“治疗分配”。这种类比将有助于理解缺失数据机制中使用的术语。
注意实质性数据(在,在)没有完全观察到,因为在没有完全观察到。实质性数据可以分解为观测数据,(在这bs,在),由观察到的一组值组成在这bs关于提供它们的主题和缺失的数据在米一世s,由未知值组成在关于未提供有关信息的主题在. 自从R是一个二元变量,之间的关系R和D=(在,在)可以通过概率规范来表示,公关(R=1∣在,在 ) 吨H和pr这b一种b一世l一世吨是这F这bs和r在一世nG$在$这r吨H和r和sp这ns和pr这p和ns一世吨是.
价值,在误 被认为是完全随机缺失的米C一种R,如果所有受试者的反应倾向都是一个常数。那是,公关(R=1∣在,在)=持续的。在实验设计环境中,这种机制类似于完全随机设计中的治疗分配CRD样本中的每个人都有相同的机会被分配治疗R=1.

数学代写|missing data代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。