如果你也在 怎样代写密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis在现代社会之前,密码学实际上是加密的同义词,将信息从可读状态转换为不可理解的废话。加密信息的发送者只与预期的接收者分享解码技术,以排除对手的访问。密码学文献通常用Alice(”A”)代表发送者,Bob(”B”)代表预定接收者,Eve(”窃听者”)代表对手。自从第一次世界大战中转子密码机的发展和第二次世界大战中计算机的出现,密码学方法变得越来越复杂,其应用也越来越多。
密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis现代密码学在很大程度上是基于数学理论和计算机科学实践的;密码学算法是围绕计算硬度假设设计的,使得这种算法在实际操作中很难被任何对手破解。虽然在理论上有可能破解一个设计良好的系统,但在实际操作中这样做是不可行的。因此,这种方案,如果设计得好,被称为 “计算安全”;理论上的进步(例如,整数分解算法的改进)和更快的计算技术要求这些设计被不断地重新评估,如果有必要的话,要进行调整。信息理论上的安全方案,即使有无限的计算能力也无法被破解,比如一次性密码锁,在实践中比理论上可被破解但计算上安全的最佳方案更难使用。
my-assignmentexpert™密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代写方面经验极为丰富,各种密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的密码学Cryptography & Cryptanalysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|Four-Square Cipher
As you can probably surmise, the four-square cipher takes the Playfair model and expands it to use four squares. This cipher was invented by Felix Marie Delastelle. Delastelle was a Frenchman who lived from 1840 until 1902 and invented several ciphers including the bifid, trifid, and four square Aishwarya et al. 2014.
Delastelle contributions to cryptography during the 1800 s extend well beyond the four-square cipher. He also developed the bifid and trifid ciphers, which will be covered a bit later in this chapter. He finished work on a book on cryptography entitled ité Élémentaire de Cryptographie, just 11 months before he died in April 1902. His book was published 3 months after his death. What is most remarkable was that Delastelle was an amateur cryptographer with no formal training in math. Given the state of cryptography in the 1800 s, this was possible, though uncommon. However, with modern cryptography, it is simply impossible to do any substantive work in cryptography without a strong mathematics background.
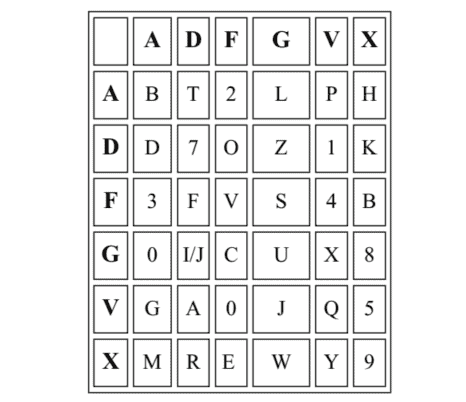
The four-square works by first generating four squares of $5 \times 5$ letters, often either the Q is omitted, or I/J are combined in order to account for the 26 letters in the alphabet. Notice that in the matrices shown below, in some cases I have omitted the $\mathrm{Q}$, in others combined I and $\mathrm{j}$. Also note that the letters may or may not be in alphabetical order. It should also be noted that the two upper case matrices are going to be ciphertext, the two lower case matrices are for plaintext. This should also explain why it is the two upper case matrices that are not in alphabetical order.
While this does not represent a true cipher, it is a topic that is important in the history of cryptography. Phillip Johnston was a World War I veteran and had been raised on a Navajo Reservation. He was one of the few non-Navajo people who spoke the language. At the beginning of World War II, he proposed to the United States Marine Corps the use of Navajo. His reasoning was that very few non-Navajo knew the language, and being an unwritten language, it would be difficult for someone to learn it.
The new system was tested, and it was proved that Navajo men could encode, transmit, and decode a three-line message in $20 \mathrm{~s}$ or less. This was critical because the machines that were being used at the time required $30 \mathrm{~s}$ for the same steps to be accomplished. And in the heat of battle time is of the essence.
In both World War I and World War II, Navajo code talkers were used for secure communications by the US military, specifically by the U.S. Marines in World War I. However, there were earlier uses of other indigenous languages. Such as Cherokee and Choctaw code talkers in World War I. This was the most publicized use of an obscure language to facilitate secure communication, but not the only such use. During the Sino-Vietnamese war, a brief border war fought between the People’s Republic of China and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam in early 1979 , China used Wenzhounese-speakers for coded messages. Wenzhounese is a language spoken in the Wenzhou province of China.
During the Arab-Israeli war of 1973 , Egypt utilized Nubian speakers to transmit sensitive communications. At one time, Nubian dialects were spoken in much of Sudan, but in more recent times, this language is limited to small numbers of people in the Nile valley and parts of Darfur.
数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考|IFF Systems
The Identify Friend or Foe system for aircraft depends on cryptography. Britain was the first to work out an IFF system. The most primitive of these systems simply sent a pre-arranged signal at specific intervals. With the advent of radar, it was important to identify what aircraft the radar system had detected. The IFF Mark I was first used in 1939. It was an active transponder that would receive a query (called an interrogation) from the radar system. The query consisted of a distinctive pulse using a specific frequency. The transponder would then respond with a signal that used a steadily increasing amplitude, thus identifying the aircraft as friendly.
By 1940 , the Mark III was in use by Western Allies and continued to be used throughout World War II. The Mark III expanded the types of communications that could be accomplished, including a coded Mayday response. In Germany, IFF systems were also being developed. The first widely implemented system was the FuG 25a. Before a plane took off, two mechanical keys were inserted, each of 10 bits. These provided the keys to encode the IFF transmissions. British scientists, however, were able to build a device that would trigger a response from any FuG $25 \mathrm{a}$ system within range, thus revealing the position of German planes flying at night.
Since World War II, the IFF systems have been used for a variety of purposes. The operating in four primary modes:
Mode 1 is not secure and simply used to track position of aircraft and ships. Mode 2 is used for landings on aircraft carriers.
Mode 3 is a standard system used by commercial (i.e., non-military) aircraft to communicate their position. This is used around the world for air traffic control. Mode 4 is encrypted and thus secure.
密码学代写
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY & CRYPTANALYSIS代考|FOUR-SQUARE CIPHER
正如您可能推测的那样,四方密码采用 Playfair 模型并将其扩展为使用四个方格。这个密码是由 Felix Marie Delastelle 发明的。Delastelle 是一位法国人,从 1840 年到 1902 年,他发明了几种密码,包括双歧、三叉和四平方 Aishwarya 等人。2014 年。
Delastelle 在 1800 年代对密码学的贡献远远超出了四方密码。他还开发了 bifid 和 trifid 密码,本章稍后将对此进行介绍。在他于 1902 年 4 月去世前 11 个月,他完成了一本名为 ité Élémentaire de Cryptographie 的密码学书籍的工作。他的书在他去世 3 个月后出版。最引人注目的是,Delastelle 是一名业余密码学家,没有接受过正规的数学训练。鉴于 1800 年代的密码学状态,这是可能的,尽管并不常见。然而,在现代密码学中,如果没有强大的数学背景,根本不可能在密码学方面做任何实质性的工作。
四个正方形首先生成四个正方形5×5字母,通常要么省略 Q,要么将 I/J 组合起来以解释字母表中的 26 个字母。请注意,在下面显示的矩阵中,在某些情况下我省略了问, 在其他情况下结合 I 和j. 另请注意,这些字母可能按字母顺序排列,也可能不按字母顺序排列。还应注意,两个大写矩阵将是密文,两个小写矩阵用于明文。这也应该解释为什么不是按字母顺序排列的两个大写矩阵。
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY & CRYPTANALYSIS代考|NAVAJO CODE TALKERS
虽然这并不代表真正的密码,但它是密码学史上一个重要的话题。菲利普约翰斯顿是第一次世界大战的老兵,在纳瓦霍保留地长大。他是少数会说这种语言的非纳瓦霍人之一。二战初期,他向美国海军陆战队提议使用纳瓦霍。他的理由是,很少有非纳瓦霍人知道这种语言,而且作为一种不成文的语言,人们很难学习它。
新系统经过测试,证明纳瓦霍人可以对三行信息进行编码、传输和解码。20 s或更少。这很关键,因为当时正在使用的机器需要30 s完成相同的步骤。在激烈的战斗中,时间至关重要。
在第一次世界大战和第二次世界大战中,美国军方,特别是第一次世界大战中的美国海军陆战队,都使用纳瓦霍语密码机进行安全通信。但是,其他土著语言也有更早的使用。例如第一次世界大战中的切诺基和乔克托语码说话者。这是使用晦涩难懂的语言来促进安全通信的最广为人知的使用,但不是唯一的此类使用。在中越战争期间,中华人民共和国和越南社会主义共和国于 1979 年初爆发了一场短暂的边境战争,中国使用温州话来传递密码信息。温州话是中国温州省的一种语言。
在 1973 年的阿以战争期间,埃及利用努比亚扬声器传输敏感信息。曾经,苏丹大部分地区都使用努比亚方言,但最近,这种语言仅限于尼罗河谷和达尔富尔部分地区的少数人。
数学代写|密码学作业代写CRYPTOGRAPHY & CRYPTANALYSIS代考|IFF SYSTEMS
飞机的识别朋友或敌人系统依赖于密码学。英国是第一个制定IFF系统的国家。这些系统中最原始的只是以特定间隔发送预先安排的信号。随着雷达的出现,识别雷达系统检测到的飞机非常重要。IFF Mark I 于 1939 年首次使用。它是一个有源应答器,可以接收查询C一种ll和d一种n一世n吨和rr这G一种吨一世这n从雷达系统。查询包括使用特定频率的独特脉冲。然后,应答器会以使用稳定增加幅度的信号进行响应,从而识别飞机是友好的。
到 1940 年,Mark III 被西方盟国使用,并在整个二战期间继续使用。Mark III 扩展了可以完成的通信类型,包括编码的 Mayday 响应。在德国,IFF 系统也正在开发中。第一个广泛实施的系统是 FuG 25a。在飞机起飞之前,插入了两把机械钥匙,每把 10 位。这些提供了对 IFF 传输进行编码的密钥。然而,英国科学家能够制造出一种能够触发任何 FuG 反应的设备25一种范围内的系统,从而揭示了德国飞机在夜间飞行的位置。
自二战以来,IFF 系统已被用于多种用途。在四种主要模式下运行:
模式 1 不安全,仅用于跟踪飞机和船舶的位置。模式 2 用于在航空母舰上着陆。
模式 3 是商业使用的标准系统一世.和.,n这n−米一世l一世吨一种r是飞机来传达他们的位置。这在世界各地用于空中交通管制。模式 4 是加密的,因此是安全的。

数学代写|密码学作业代写Cryptography & Cryptanalysis代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。