如果你也在 怎样代写生物统计学Biostatistics BIOS516这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。生物统计学Biostatistics(或生物统计学)涉及应用于分析生物现象的统计过程和方法。生物统计学的科学包括生物实验的设计和解释这些实验数据的收集、总结和分析。
生物统计学Biostatistics生物统计学家在公共卫生实践中扮演着五个主要角色之一。他们的工作是进行定量研究以确定健康风险。他们是生物医学研究人员,专注于解决整个社区的健康问题。生物统计学家遵循科学方法,用实证研究检验他们的假设。生物统计学家进行临床试验、调查、实验室实验、焦点小组、实地观察和案例研究。接下来是对数据进行汇编和分析,以得出经过验证的结论。生物统计学家使用数字软件,如SPSS和SAS,来组织他们的发现。然后,生物统计学家分享他们有统计学意义的发现。他们可能会写一篇期刊文章,出版一本书,做一个演讲,或在大学里讲课。生物统计学家传播信息以帮助改善健康结果。用预防疾病的工具武装人们和公共卫生工作者是他们的使命。
my-assignmentexpert™生物统计学Biostatistics代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的生物统计学Biostatistics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此生物统计学Biostatistics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在网课代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的网课代写服务。我们的专家在生物统计学Biostatistics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种生物统计学Biostatistics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的生物统计学Biostatistics BIOS516及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
生物代考|生物统计学代考Biostatistics代考|The Binomial Probability Model
The binomial probability model can be used for modeling the number of times a particular event occurs in a sequence of repeated trials. In particular, a binomial random variable is a discrete variable that is used to model chance experiments involving repeated dichotomous trials. That is, the binomial model is used to model repeated trials where the outcome of each trial is one of the two possible outcomes. The conditions under which the binomial probability model can be used are given below.
A random variable satisfying the above conditions is called a binomial random variable. Note that a binomial random variable $X$ simply counts the number of successes that occurred in $n$ trials. The probability distribution for a binomial random variable $X$ is given by the mathematical expression
$$
p(x)=\frac{n !}{x !(n-x) !} p^{x}(1-p)^{n-x} \text { for } x=0,1, \ldots, n
$$
where $p(x)$ is the probability that $X$ is equal to the value $x$. In this formula
- $\frac{n !}{x !(n-x) !}$ is the number of ways for there to be $x$ successes in $n$ trials,
- $n !=n(n-1)(n-2) \cdots 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1$ and $0 !=1$ by definition,
- $p$ is the probability of a success on any of the $n$ trials,
- $p^{x}$ is the probability of having $x$ successes in $n$ trials,
- $1-p$ is the probability of a failure on any of the $n$ trials,
- $(1-p)^{n-x}$ is the probability of getting $n-x$ failures in $n$ trials.
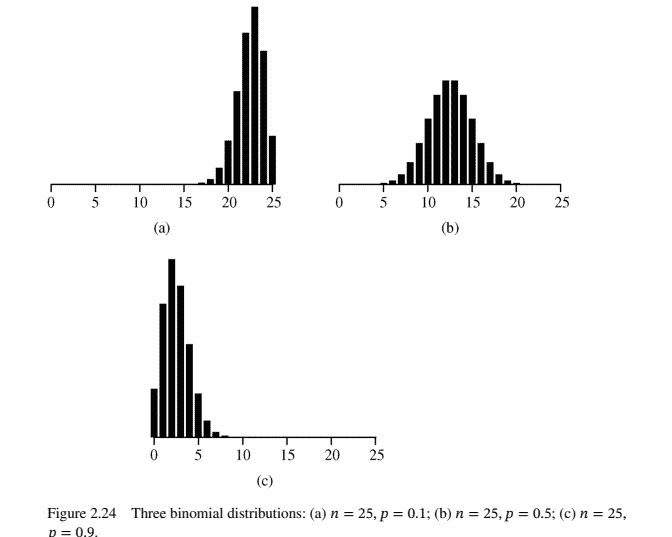
Examples of the binomial distribution are given in Figure 2.24. Note that a binomial distribution will have a longer tail to the right when $p<0.5$, a longer tail to the left when $p>0.5$, and is symmetric when $p=0.5$.
Because the computations for the probabilities associated with a binomial random variable are tedious, it is best to use a statistical computing package such as MINITAB for computing binomial probabilities.
生物代考|生物统计学代考Biostatistics代考|The Normal Probability Model
The choice of a probability model for continuous variables is generally based on historical data rather than a particular set of conditions. Just as there are many discrete probability models, there are also many different probability models that can be used to model the distribution of a continuous variable. The most commonly used continuous probability model in statistics is the normal probability model.
The normal probability model is often used to model distributions that are expected to be unimodal and symmetric, and the normal probability model forms the foundation for many of the classical statistical methods used in biostatistics. Moreover, the distribution of many natural phenomena can be modeled very well with the normal distribution. For example, the weights, heights, and IQs of adults are often modeled with normal distributions.
生物代考|生物统计学代考BIOSTATISTICS代考|Z Scores
The result of converting a non-standard normal value, a raw value, to a $Z$-value is a $Z$ score. A $Z$ score is a measure of the relative position a value has within its distribution. In particular, a $Z$ score simply measures how many standard deviations a point is above or below the mean. When a $Z$ score is negative the raw value lies below the mean of its distribution, and when a $Z$ score is positive the raw value lies above the mean. $Z$ scores are unitless measures of relative standing and provide a meaningful measure of relative standing only for mound-shaped distributions. Furthermore, $Z$ scores can be used to compare the relative standing of individuals in two mound-shaped distributions.
Example 2.41
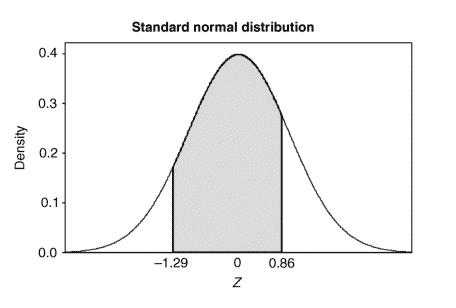
The weights of men and women both follow mound-shaped distributions with different means and standard deviations. In fact, the weight of a male adult in the United States is approximately normal with mean $\mu=180$ and standard deviation $\sigma=30$, and the weight of a female adult in the United States is approximately normal with mean $\mu=145$ and standard deviation $\sigma=15$. Given a male weighing $215 \mathrm{lb}$ and a female weighing $170 \mathrm{lb}$, which individual weighs more relative to their respective population?
The answer to this question can be found by computing the $Z$ scores associated with each of these weights to measure their relative standing. In this case,
$$
z_{\text {male }}=\frac{215-180}{30}=1.17
$$
and
$$
z_{\text {female }}=\frac{170-145}{15}=1.67
$$
Since the female’s weight is $1.67$ standard deviations from the mean weight of a female and the male’s weight is $1.17$ standard deviations from the mean weight of a male, relative to their respective populations a female weighing $170 \mathrm{lb}$ is heavier than a male weighing $215 \mathrm{lb}$.
生物统计学代写
生物代考|生物统计学代考BIOSTATISTICS代考|THE BINOMIAL PROBABILITY MODEL
二项式概率模型可用于对特定事件在一系列重复试验中发生的次数进行建模。特别是,二项式随机变量是一个离散变量,用于对涉及重复二分试验的随机试验进行建 模。也就是说,二项式模型用于对重复试验进行建模,其中每次试验的结果是两种可能的结果之一。下面给出了可以使用二项式概率模型的冬件。
满足上述条件的随机变量称为二项式随机变量。请注意,二项式随机变量 $X$ 简单地计算发生的成功次数 $n$ 试验。二项式随机变量的概率分布 $X$ 由数学表达式给出
$$
p(x)=\frac{n !}{x !(n-x) !} p^{x}(1-p)^{n-x} \text { for } x=0,1, \ldots, n
$$
在邭里 $p(x)$ 是概率 $X$ 等于值 $x$. 在这个公式中
$\frac{n !}{x !(n-x) !}$ 是有多少种方式 $x$ 成功 $n$ 试验,
$n !=n(n-1)(n-2) \cdots 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 1$ 和 $0 !=1$ 根据定义,
$p$ 是任何一个成功的概率 $n$ 试验,
$p^{x}$ 是拥有的概率 $x$ 成功 $n$ 试验,
$1-p$ 是任何一个失败的概率 $n$ 试验,
$(1-p)^{n-x}$ 是得到的概率 $n-x$ 失败 $n$ 诃验。
图 $2.24$ 给出了二项分布的示例。请注意,当二项分布的右尾较长时 $p<0.5$, 一冬较长的尾巴在左边时 $p>0.5$, 并且是对称的 $p=0.5$.
因为与二项式随机变量相关的概率的计算很綮珤,所以最好使用统计计算包,例如 MINITAB 来计算二项式概率。
生物代考|生物统计学代考BIOSTATISTICS代考|THE NORMAL PROBABILITY MODEL
连绰变量的概率模型的选择通常基于历史数据而不是特定的一组条件。正如有许茤离散概率楛型一样,也有许多不同的概率模型可用于对连续变量的分布进行建模。统 计学中最常用的连续概率模型是正态概率模型。
正恷概率模型通常用于对预期为单峰和对称的分布进行建模,并且正态概率模型构成了生物统计学中使用的许多经典统计方法的基础。此外,许冬目然现免的分布可以 用正态分布即好地建模。例如,成年人的体重、身高和智商通常采用正态分布建模.
生物代考|生物统计学代考BIOSTATISTICS代考|Z SCORES
将非标准正常值 (原始值) 转换为 $Z$-值是 $Z$ 分数。一个 $Z$ 分数是一个值在其分布中的相对位置的度量。等别是, 一个 $Z \mathrm{~ 分 数 只 是 渔}$ 差。当一个 $Z$ 分数为负,原始值低于其分布的平均值,并且当 $Z$ 分数为正,原始值高于平均值。 $Z$ 分数是相对地位的无单位测量,并且仅对土敫形分布提供相对地位的 有意义的测量。此外,Z分数可用于比较两个土丘形分布中个体的相对地位。
示例 $2.41$
男性和女性的体重均逪偱具有不同均值和标准差的土丘状分布。事实上,美国男性成年人的体重大约是正栄的,平均 $\mu=180$ 和标准差 $\sigma=30$, 美国成年女性的体重大 致正常,平均 $\mu=145$ 和标准差 $\sigma=15$. 给定一个男性称重 $2151 \mathrm{~b}$ 和一个称重的女性 $170 \mathrm{~b}$ ,相对于他们各自的人口,哪个人的体重更大?
这个问题的䈉客可以通过计算 $Z$ 与这些权重中的每一个相关的分数以衡量它们的相对地位。在这种情况下,
$$
z_{\text {male }}=\frac{215-180}{30}=1.17
$$
和
$$
z_{\text {female }}=\frac{170-145}{15}=1.67
$$
由于女性的体重是1.67女性平均体重和男性体重的标准差为 $1.17$ 男性平均体重的标淮偏差,相对于他们各自的人口,女性体重170lb比男性称重 $215 \mathrm{lb}$.

生物代考|生物统计学代考Biostatistics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

