如果你也在 怎样代写无机化学Inorganic Chemistry CHEM302/402这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。无机化学Inorganic Chemistry关注的是无机化合物的属性和行为,其中包括金属、矿物和有机金属化合物。
无机化学Inorganic Chemistry涉及到无机和有机金属化合物的合成和行为。这个领域涵盖了非碳基的化合物,这些化合物是有机化学的主题。这两门学科之间的区别远非绝对,因为有机金属化学的分支学科有很多重叠。它在化学工业的各个方面都有应用,包括催化、材料科学、颜料、表面活性剂、涂料、药物、燃料和农业。
my-assignmentexpert™无机化学Inorganic Chemistry代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的无机化学Inorganic Chemistry作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此无机化学Inorganic Chemistry作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的作业代写服务。我们的专家在无机化学Inorganic Chemistry代写方面经验极为丰富,各种无机化学Inorganic Chemistry相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的无机化学Inorganic Chemistry CHEM302/402及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
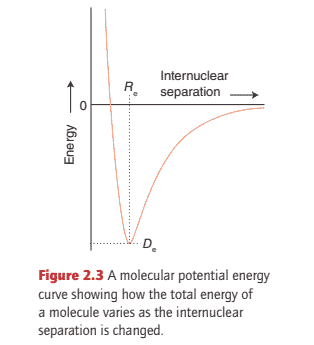
化学代写|无机化学代写Inorganic Chemistry代写|The hvdrogen molecule
The two-electron wavefunction for two widely separated $\mathrm{H}$ atoms is $\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(1) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(2)$, where $\chi_{\mathrm{A}}$ and $\chi_{\mathrm{B}}$ are H1s orbitals on atoms $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$. (Although $\chi$, chi, is also used for electronegativity, the context makes it unlikely that the two usages will be confused: $\chi$ is commonly used to denote an atomic orbital in computational chemistry.) When the atoms are close, it is not possible to know whether it is electron 1 or electron 2 that is on A. An equally valid description is therefore $\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(2) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(1)$, in which electron 2 is on A and electron 1 is on B. When two outcomes are equally probable, quantum mechanics instructs us to describe the true state of the system as a superposition of the wavefunctions for each possibility, so a better description of the molecule than either wavefunction alone is the linear combination of the two possibilities:
$$
\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(1) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(2)+\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(2) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(1)
$$
化学代写|无机化学代写Inorganic Chemistry代写|Homonuclear diatomic molecules
Key point: Electrons in atomic orbitals of the same symmetry but on neighbouring atoms are paired to form $\sigma$ and $\pi$ bonds.
A similar description can be applied to more complex molecules, and we begin by considering homonuclear diatomic molecules, diatomic molecules in which both atoms belong to the same element (dinitrogen, $\mathrm{N}{2}$, is an example). To construct the VB description of $\mathrm{N}{2}$, we consider the valence electron configuration of each atom, which from Section $1.6$ we know to be $2 s^{2} 2 p_{z}^{1} 2 p_{y}^{1} 2 p_{x}^{1}$. It is conventional to take the $z$-axis to be the internuclear axis, so we can imagine each atom as having a $2 \mathrm{p}{z}$ orbital pointing towards a $2 \mathrm{p}{z}$ orbital on the other atom, with the $2 \mathrm{p}{x}$ and $2 \mathrm{p}{y}$ orbitals perpendicular to the axis. A $\sigma$ bond is then formed by spin pairing between the two electrons in the opposing $2 \mathrm{p}{z}$ orbitals. Its spatial wavefunction is still given by eqn $2.1$, but now $\chi{\mathrm{A}}$ and $\chi_{\mathrm{B}}$ stand for the two $2 \mathrm{p}_{z}$ orbitals. A simple way of identifying a $\sigma$ bond is to envisage rotation of the bond around the internuclear axis: if the wavefunction remains unchanged, the bond is classified as $\sigma$.
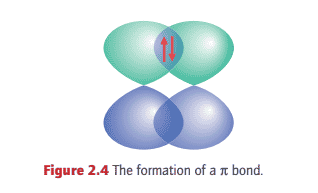
The remaining $2 \mathrm{p}$ orbitals cannot merge to give $\sigma$ bonds as they do not have cylindrical symmetry around the internuclear axis. Instead, the orbitals merge to form two $\pi$ bonds. A $\pi$ bond arises from the spin pairing of electrons in two $p$ orbitals that approach side by side (Fig. 2.4). The bond is so called because, viewed along the internuclear axis, it resembles a pair of electrons in a p orbital. More precisely, an electron in a $\pi$ bond has one unit of orbital angular momentum about the internuclear axis. A simple way of identifying a $\pi$ bond is to envisage rotation of the bond through $180^{\circ}$ around the internuclear axis. If the signs as indicated by the shading of the lobes of the orbital are interchanged, then the bond is classified as $\pi$.
There are two $\pi$ bonds in $\mathrm{N}{2}$, one formed by spin pairing in two neighbouring $2 \mathrm{p}{x}$ orbitals and the other by spin pairing in two neighbouring $2 \mathrm{p}{y}$ orbitals. The overall bonding pattern in $\mathrm{N}{2}$ is therefore a $\sigma$ bond plus two $\pi$ bonds (Fig. 2.5), which is consistent with the structure $\mathrm{N} \equiv \mathrm{N}$. Analysis of the total electron density in a triple bond shows that it has cylindrical symmetry around the internuclear axis, with the four electrons in the two $\mathrm{p}$ bonds forming a ring of electron density around the central $\sigma$ bond.
无机化学代写
化学代写|无机化学代写INORGANIC CHEMISTRY代写|THE HVDROGEN MOLECULE
两个相距很远的两电子波函数 $\mathrm{H}$ 原子是 $\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(1) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(2)$ ,在哪里 $\chi_{\mathrm{A}}$ 和 $\chi_{\mathrm{B}}$ 是原子上的 $\mathrm{H} 1 \mathrm{~s}$ 轨道 $\mathrm{A}$ 和B. 当原子靠近时,不可能知道 $\mathrm{A}$ 上是电子 1 还是电子 $2_{2}$ 。因此,同样有效的描述是 $\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(2) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(1)$ ,其中电子 2 在 $\mathrm{A}$ 上,电子 1 在 $\mathrm{B}$ 上。当两个结果的可能性相同时, 量子力学指导我们将系统的真实状态描述为每种可能性的波函数的叠加,因此更好地描述了分子比任可一个波函数单独是两种可能性的线性组合:
$$
\psi=\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(1) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(2)+\chi_{\mathrm{A}}(2) \chi_{\mathrm{B}}(1)
$$
化学代写|无机化学代写INORGANIC CHEMISTRY代 写|HOMONUCLEAR DIATOMIC MOLECULES
关键点: 具有相同对称性但在相邻原子上的原子轨道中的电子配对形成 $\sigma$ 和 $\pi$ 债券。
英似的描述可以应用于更昆杂的分子,我们首先考虑同核双原子分子,其中两个原子属于同一元素的双原子分子 dinitrogen, \$N2\$, isanexample.构造VB描述N2, 我们考虑每个原子的价电子构型,从第 $1.6$ 我们知道是 $2 s^{2} 2 p_{z}^{1} 2 p_{y}^{1} 2 p_{x}^{1}$. 它是传统的采取 $z$-轴是核间轴,所以我们可以想彖每个嫄子都有一个 $2 \mathrm{p} z$ 指向 $a$ 的轨道 $2 \mathrm{p} z$ 在另一 个原子上的轨道,与 $2 \mathrm{p} x$ 和 $2 \mathrm{p} y$ 轨道垂直于轴。一个 $\sigma$ 然后通过相对的两个电子之间的自旋配对形成犍 $2 \mathrm{p} z$ 轨道。其空间波函数仍由 eqn 给出 $2.1$ ,但现在 $\chi \mathrm{A}$ 和 $\chi_{\mathrm{B}}$ 代表 两者 $2 p_{z}$ 轨道。一种简单的识别方法 $\sigma$ 键是设想键围绕核间轴旋转: 如果波函数保持不变,则键鿆分类为 $\sigma$.
剩余的 $2 \mathrm{p}$ 轨道不能合并给 $\sigma$ 键,因为它们在核间轴周围没有圆柱对称性。相反,轨道合并形成两个 $\pi$ 债券。一个键产生于两个电子的自旋配对 $p$ 并排接近的轨道 Fig. 2.4. 该键之所以如此命名,是因为沿核间轴观察,它荚似于 ap 轨道上的一对电子。更准确地说,一个电子在 $\pi$ 键具有一个关于核间轴的轨道角动量单位。一种简 单的识别方法 $\pi$ 债券是设相债券的轮换通过 $180^{\circ}$ 围绕核间轴。如果轨道叶的阴影所指示的符昊互换,则该键被分类为 $\pi$. ,与结构一玫 $\mathrm{N} \equiv \mathrm{N}$. 分析三键中的总电子密度表明,它围绕核间轴具有圆柱对称性,其中两个中的四个电子 $\mathrm{p}$ 键在中心周围形成一个电子密度环 $\sigma$ 纽带。

化学代写|无机化学代写Inorganic Chemistry代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。

