如果你也在 怎样代写博弈论Game theory ECON7062这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。博弈论Game theory在20世纪50年代被许多学者广泛地发展。它在20世纪70年代被明确地应用于进化论,尽管类似的发展至少可以追溯到20世纪30年代。博弈论已被广泛认为是许多领域的重要工具。截至2020年,随着诺贝尔经济学纪念奖被授予博弈理论家保罗-米尔格伦和罗伯特-B-威尔逊,已有15位博弈理论家获得了诺贝尔经济学奖。约翰-梅纳德-史密斯因其对进化博弈论的应用而被授予克拉福德奖。
博弈论Game theory是对理性主体之间战略互动的数学模型的研究。它在社会科学的所有领域,以及逻辑学、系统科学和计算机科学中都有应用。最初,它针对的是两人的零和博弈,其中每个参与者的收益或损失都与其他参与者的收益或损失完全平衡。在21世纪,博弈论适用于广泛的行为关系;它现在是人类、动物以及计算机的逻辑决策科学的一个总称。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在经济Economy代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的经济Economy代写服务。我们的专家在博弈论Game theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种博弈论Game theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
经济代写|博弈论代考Game theory代写|Two-Player Cooperative Fishery Games Without Side Payments
Game theorist, Guillermo Owen, argues that the introduction of side payments (transferable utility) to the theory of cooperative games simplifies the analysis enormously (Owen 2013, 355). These authors can only agree and will demonstrate this fact in the context of cooperative fishery games. Owen continues that in the real world, however, side payments are, for reasons right or wrong, not always feasible. He does, as a consequence, find it necessary to devote a full chapter of his book on game theory to cooperative games without side payments (Owen 2013, Chap. 15).
In the real world of fisheries management, side payments and side payments like arrangements are beginning to appear more frequently. The acceptance of side payments has, however, been a slow process. The very name side payments has in the past had unfortunate connotations to policymakers, suggesting bribes, “kickbacks”, all in all quite unsavoury (Munro 2013). Economists have been undertaking a campaign among policymakers to convince them of the benefits of side payments.
Given this state of affairs, it is essential to be able to demonstrate that the theory of cooperative games has relevance and applicability in situations in which, for whatever reason, side payments are infeasible, or are willfully ignored. This then is the task before us.
The task shall be undertaken, not by talking in generalities, but rather by developing a specific fisheries model, in which side payments are explicitly not employed. The model that we shall bring to bear is a dynamic model, in fact exactly the same model that is employed in Chap. 3 , which we described as a dynamic version of the Gordon-Schaefer model (Gordon 1954). ${ }^3$
As we did on Chap. 3, let us start out with the sole owner perspective, to give us a benchmark. In Chap. 3, we saw the objective of the sole owner as being that of maximizing the present value of the net economic returns, resource rent, through time. Technically, given our assumptions, we were presented with a linear autonomous optimal control problem. We then talked about a “state” variable, $X(t)$, and a “control” variable. With regards to a “control” variable, it was maintained that we had a choice between $H(t)$ and $E(t)$. In Chap. 3, it was most convenient to let $E(t)$ be the “control” variable. In this chapter, convenience is best served by letting $H(t)$ play that role.
In Chap. 3, we expressed the sole owner’s objective functional as
$$
P V(E(t))=\int_0^{+\infty} e^{-\delta t}(p q X(t)-c) E(t) d t
$$
经济代写|博弈论代考Game theory代写|A Symmetric Cooperative Game
The two players are assumed to be identical in all respects. Let it be supposed that the players were initially playing competitively. After observing the costs of non-cooperation, and being able to communicate with one another, the two finally respond to the admonition of Article 63(1) of the $1982 \mathrm{UN}^{\text {Convention }}{ }^7$ to explore the possibility of managing the fishery resource cooperatively.
In so doing, we assume that they are not prepared to contemplate side payments. What will be found is that the refusal so to contemplate will have no negative consequences, simply because, in this case, side payments will have no useful role to play.
As in Chap. 3, let us denote the optimal biomass level, as perceived by players 1 and 2, as $X_1^* ; X_2^$ respectively. With symmetry prevailing, we have $X_1^=X_2^*$. The perceived optimal resource management programme of player 1 will be identical to that of player 2. If the two players decide that cooperation is worthwhile, ${ }^8$ they will, if rational, attempt to maximize the present value of the global resource rent through time, and then bargain over the division of the global resource rent. The game then is over that division.
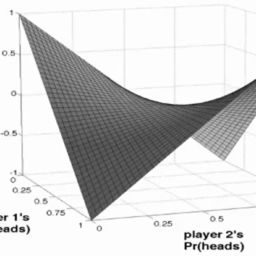
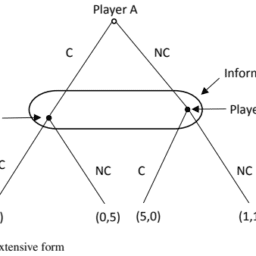
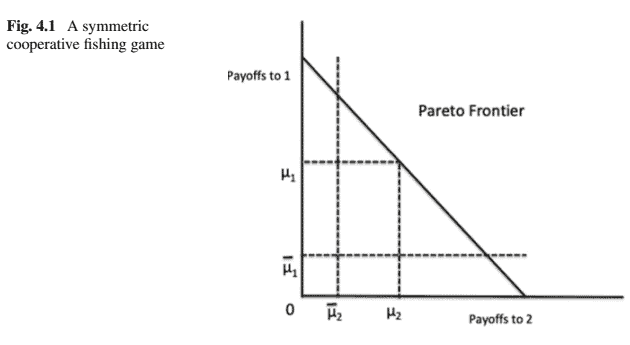
Consider now Fig. 4.1. The $45^{\circ}$ line is the Pareto Frontier. The sum of solution payoffs, $\mu_1, \mu_2$, at any one point on the Frontier is identical to the sum at any other point on the Frontier. A solution to the game is the Nash bargaining solution (see Definition 4.2). ${ }^9$
We need to say much more on the actual division of the net economic returns from the fishery, between players 1 and 2, arising from this Nash game. In order to do this, we must first present the concept of the cooperative surplus.
博弈论代写
经济代写|博弈论代考game theory代写|two-player渔业合作博弈的无侧重点支付
博弈理论家吉列尔莫-欧文(Guillermo Owen)认为,在合作博弈理论中引入边际支付的可转移效用,可以极大地简化分析,欧文2013,355。这些作者只能同意并将在合作渔业博弈的背景下证明这一事实。欧文继续说,然而,在现实世界中,由于正确或错误的原因,附带支付并不总是可行的。因此,他认为有必要在他的博弈论书中用一整章来讨论没有附带支付的合作博弈 Owen 2013 ,第15章。
在渔业管理的现实世界中,附带支付和类似附带支付的安排开始更频繁地出现。然而,接受边际支付是一个缓慢的过程。过去,附带付款这一名称对政策制定者来说有不幸的含义,意味着贿赂、”回扣”,总之是相当不光彩的,Munro2013。经济学家一直在决策者中开展活动,以说服他们相信边际支付的好处。
鉴于这种状况,必须能够证明合作博弈理论在以下情况下具有相关性和适用性:无论出于何种原因,附带支付是不可行的,或者被故意忽略。这就是我们面前的任务。
承担这项任务的方式不是泛泛而谈,而是建立一个具体的渔业模型,在这个模型中明确地不采用附带支付。我们将采用的模型是一个动态模型,实际上与第三章中采用的模型完全相同,我们将其描述为GordonSchaefer模型的动态版本,Gordon 1954。${ }^3$
和第三章一样,让我们从唯一所有者的角度开始,给我们一个基准。在第三章中,我们认为唯一所有者的目标是通过时间实现净经济收益(资源租金)的现值最大化。从技术上讲,鉴于我们的假设,我们面临的是一个线性自主最优控制问题。然后我们谈到了一个 “状态 “变量,$X(t)$,和一个 “控制 “变量。关于 “控制 “变量,有人认为我们可以在$H(t)$和$E(t)$之间进行选择。在第三章中,让$E(t)$作为 “控制 “变量是最方便的。在本章中,让$H(t)$扮演这个角色是最方便的。在第三章中,我们将唯一所有者的目标函数表示为
$$
P V(E(t))=int_0^{+infty} e^{-delta t}(p q X(t)-c) E(t) d t
$$
经济代写|博弈论代考|对称性合作博弈
假设两个玩家在各方面都是相同的。假设双方最初是竞争性的博弈。在观察了不合作的成本,并且能够相互沟通后,两人最终响应了1982年《联合国公约》第631条的告诫7,探索合作管理渔业资源的可能性。
在这样做的时候,我们假设他们不准备考虑附带付款。我们将发现,拒绝这样的考虑不会有任何负面的后果,因为在这种情况下,附带付款不会有任何作用。如果双方决定合作是值得的,那么,如果理性的话,他们将试图通过时间来最大化全球资源租金的现值,然后就全球资源租金的分割进行讨价还价。然后,博弈就在这个分割上。
现在考虑图4.1。45^{\circ}$线是帕累托边界。边界上任何一点的解决方案报酬之和$mu_1, \mu_2$与边界上任何其他点的报酬之和相同。该游戏的解决方案是纳什讨价还价解决方案,见De finition 4.2^{.9}$
我们需要进一步说明,在这个纳什博弈中,参与者1和2之间对渔业净经济收益的实际划分。为了做到这一点,我们必须首先提出合作盈余的概念。

经济代写|博弈论代考Game theory代写 请认准exambang™. exambang™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。