如果你也在 怎样代写深度学习Deep Learning 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。深度学习Deep Learning(也称为深度结构化学习)是更广泛的机器学习方法系列的一部分,它是基于人工神经网络的表征学习。学习可以是监督的、半监督的或无监督的。人工神经网络(ANNs)的灵感来自于生物系统的信息处理和分布式通信节点。人工神经网络与生物大脑有各种不同之处。具体来说,人工神经网络倾向于静态和符号化,而大多数生物体的生物脑是动态(可塑性)和模拟的。
深度学习Deep Learning架构,如深度神经网络、深度信念网络、深度强化学习、递归神经网络、卷积神经网络和变形金刚,已被应用于包括计算机视觉、语音识别、自然语言处理、机器翻译、生物信息学、药物设计、医学图像分析、气候科学、材料检测和棋盘游戏程序等领域,它们产生的结果与人类专家的表现相当,在某些情况下甚至超过了人类专家。
深度学习Deep Learning代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的机器学习Machine Learning作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此机器学习Machine Learning作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在计算机Quantum computer代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的计算机Quantum computer代写服务。我们的专家在深度学习Deep Learning代写方面经验极为丰富,各种深度学习Deep Learning相关的作业也就用不着 说。
计算机代写|深度学习代写Deep Learning代考|Per-Task Evaluation
Figure 5.7 shows the results of the four different MTL and the ST model for the prediction of the overall MOS only. For each training run, the epoch with the best result for predicting the overall MOS was used as a result. The individual 10 training runs are then presented as boxplots. It can be seen that the prediction performance is very similar between the different models, where the model MTL-TD with taskspecific time-dependency and pooling blocks achieved slightly better results than the single-task model or the MTL models that share most of the layers. However, based on the figure it can be concluded that using the quality dimension as auxiliary tasks does not notably improve the prediction of the overall MOS. One reason for this could be that the signal distortions of the individual quality dimensions are already covered by the overall quality. Therefore, the model does not seem to learn new information from predicting quality dimensions that it could leverage to improve the prediction of the overall MOS. Also, the regularisation effect of the MTL model appears to be small, possibly because the noise of the ratings is correlated between the dimensions and overall MOS since they are rated by the same test participant.
Quality Dimensions
Figure 5.8 shows the results for predicting the individual quality dimensions. Again for each training run, the epoch with the best result for predicting the corresponding dimension was used as a result. The results of 10 training runs are then presented as boxplots. Additionally, to the MTL and ST models, in this experiment, also an ST model that is pretrained on the overall MOS is included. In this transferlearning approach, the model was first trained to predict the overall MOS. After that, it was fine-tuned to predict one of the quality dimensions. This overall MOS pretrained model is denoted as ST-PT. In the four plots of Fig. 5.8 the most variation in results can be seen for the dimension Coloration. The Coloration ST model with a median PCC of 0.69 is outperformed by the other MTL models with medians around 0.71. This shows that the model can benefit from the additional information that it receives through the other tasks. In fact, the ST-PT model that is pretrained to predict overall MOS obtains the best median PCC. Therefore, it can be concluded that the model mostly benefits from the additional information gained from the overall MOS prediction rather than by the other quality dimensions.
The MTL models in the plot are sorted from sharing all of the layers to only sharing parts of the $\mathrm{CNN}$ from left to right. The Coloration MTL model with the best results is MTL-POOL, where the performance notably decreases for each stage, of which less of the network is shared across tasks. However, MTL-FC that shares all of the layers achieves a slightly lower PCC, showing that in this case, it is better to not completely share the network layers between all tasks.
For the other quality dimensions, the results of the different models are closer together, and only small differences between the ST and the MTL models can be observed. However, there is a clear trend that the models MTL-POOL and MTL-TD achieve a slightly higher PCC than the ST models for the dimensions Noisiness, Discontinuity, and Loudness, whereas there is a notable improvement for the Coloration dimension. This shows that the prediction of the dimension scores can indeed benefit from the additional knowledge that is learned by considering other types of distortions as well.
计算机代写|深度学习代写Deep Learning代考|All-Tasks Evaluation
In this experiment, the different MTL models are compared on their overall performance across all four dimensions and the overall MOS. To this end, the average PCC $\overline{r_{\mathrm{ALL}}}=$ is calculated for each epoch of a training run, then the epoch with the best average PCC on the validation set is used as result. The average PCC is calculated as follows:
$$
\overline{r_{\mathrm{ALL}}}=\frac{r_{\mathrm{MOS}}+r_{\mathrm{NOI}}+r_{\mathrm{COL}}+r_{\mathrm{DIS}}+r_{\mathrm{LOUD}}}{5} .
$$
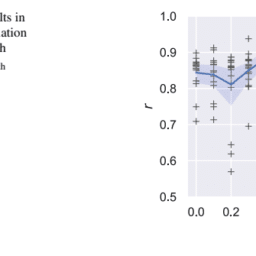
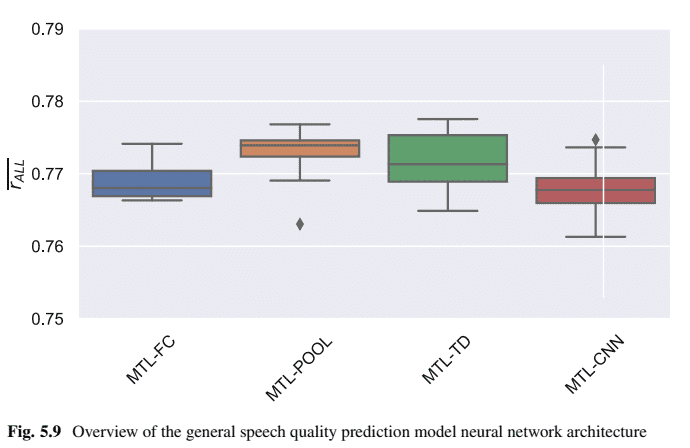
The results are shown in Fig. 5.9, where MTL-POOL obtains the best PCC. Again the differences between the models are only marginal; however, sharing some of the layers gives on average a slightly better performance than sharing all of the layers or sharing only a few layers. It can be concluded that the different tasks that the model learns are indeed quite similar to each other. Still, there is some difference between them so that the model benefits from having at least its own task-specific pooling layer for each of the quality dimensions and the overall quality. In case parts of the CNN are shared as well, the model performance decreases again, showing that sharing only the low-level CNN features is not enough to leverage the possible (but small) MTL performance increase.
深度学习代写
计算机代写|深度学习代写DEEP LEARNING代考|TRAINING AND EVALUATION METRIC
所呈现的模型使用 Adam 优化器进行端到端训练,批量大小为 60 ,学习率为 0.001 。训练提前停止了 15 个时期,其中 PCC
Pearson’scorrelationcoef ficient和均方根误差rootmean – squareerror在验证集上进行了检查。当PCC 或 RMSE方面的验证集性能在超过 15 个epoch 后仍末改善时,停止训练。
对于训练和评估,来自 Sect的数据集。3.1 被应用。对于训练,使用了模拟和实时训练集NISQA_TRAIN_SIM和 NISQA_TRAIN_LIVE。该模型在验证 数据集NISQA_VAL_SIM和 NISQA_VAL_LIVE 上进行评估。由于训练集和验证集来自相同的分布,因此理论上数据集之间不存在主观偏差,因此末对 评估应用多项式映射。此外,由于 MOS 值在数据集中的最小值和最大值之间分布相对均匀,因此本节仅使用 PCC 作为评估指标。
实时数据集的结果特别令人感兴趣,因为它们更“真实”,因此可以更好地表明模型在现实世界中的表现有多准确。然而,实时验证集比模拟数据 集小得多。正因为如此,PCC分别为模拟和实时数据集计算。之后,计算两个数据集的平均值并将其用于模型评估,如下所示:
$$
r=\frac{r_{\mathrm{val} _} \text {sim }+r_{\text {val_live }}}{2}
$$
计算机代写深度学习代写DEEP LEARNING代考|FRAMEWISE MODEL
在本小节中,模型训练针对不同的框架模型运行,这些模型计算每个单独的 Mel-spec段的特征。在图 3.7 的左侧,呈现了具有自注意力时间依赖模 型和注意力池池模型但三种不同的框架模型的语音质量模型的结果。箱线图最左侧的 CNN-SA-AP 使用CNN对于逐帧建模,FFN-SA-AP 模型使用前 馈网络进行逐帧建模,而 Skip-SA-AP 模型将Melspec段直接应用于自注意力网络,而无需逐帧建模。可以看出CNN平均 PCC 约为 0.87 的模型明显
优于其他两个模型,其中没有框架建模的模型仅获得约 0.77 的PCC。前馈网络有助于提高性能,但无法达到与 CNN类似的结果。 对片段进行下采样。有趣的是,可以注意到,Transformer 模型获得的结果与具有前馈网络的自注意力模型大致相同 $F F N-S A-A P$. 深度 LSTM 模型的性能优于低复杂度的 SA 模型,但仍优于 Transformer 模型。总体而言,可以得出结论,作为框架模型,CNN 的性能优于
Transformer/self-attention 和LSTM 网络

计算机代写|深度学习代写Deep Learning代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。