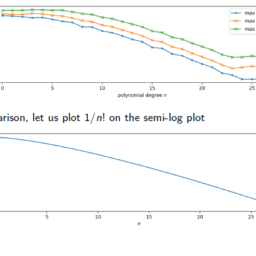
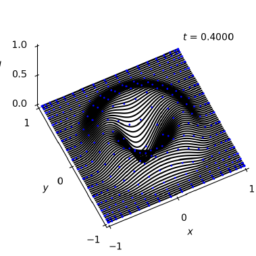
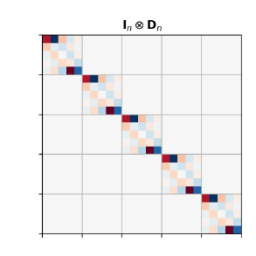
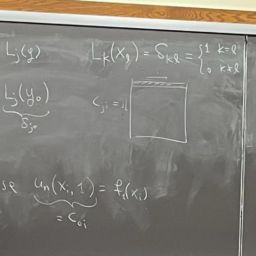数学代写|Example Polynomial approximation 数值分析代写
数值分析代写
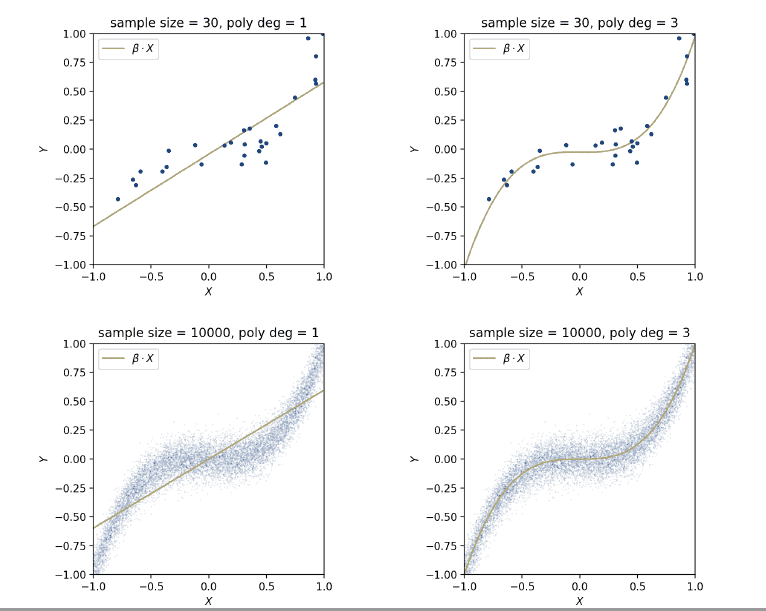
Determine the input and output variables $X$ and $Y$
Collect training data set containing observations $\left(x_{i}, y_{i}\right)$ where $i=1, \ldots, N$.
Choose a model to use for relating $X$ to $Y$
(e.g. linear model)
Choose a loss function to minimize
(e.g. residual sum of squares)
Solve the minimization problem to find the parameters
(e.g. normal equations)
Consider our inverse problem involving the PDE
$$
\nabla \cdot K \nabla u=0 \quad \text { in }(-1,1)^{2}
$$
Our input $X$ will be set as an observation of the measurement operator (Dirichlet-to-Neumann map $\Lambda$ ) on the boundary
For example let $\left(x_{i_{r}}, y_{j_{r}}\right), r=1, \ldots, R$ denote points on the boundary of the domain.
Then for each Dirichlet boundary condition $f_{\el
l, r}$ on the boundary, we would have the Neumann data $g_{\ell, r}$.
Input and output for the inverse conductivity problem
Then each observation of the Dirichlet-to-Neumann map will be given as
$$
\left[\begin{array}{c}
f_{1, \ell} \
f_{2, \ell} \
\vdots \
f_{R, \ell} \
g_{1, \ell} \
g_{2, \ell} \
\vdots \
g_{R, \ell}
\end{array}\right], \quad \ell=1, \ldots, L .
$$
Collecting all such measurements $\ell=1, \ldots, L$, with some choice of $f_{\ell}$, forms one observation of our input $x_{i}$
$$
x_{i}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc}
f_{1,1} & f_{1,2} & \cdots & f_{1, L} \
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \
f_{R, 1} & f_{R, 1} & \cdots & f_{R, L} \
g_{1,1} & g_{1,2} & \cdots & g_{1, L} \
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \
g_{R, 1} & g_{R, 2} & \cdots & g_{R, L}
\end{array}\right]
$$
数值分析代考
确定输入和输出变量 $X$ 和 $Y$
收集包含观测值的训练数据集 $\left(x_{i}, y_{i}\right)$ 其中 $i=1, \ldots, N$。
选择用于关联 $X$ 和 $Y$ 的模型
(例如线性模型)
选择一个损失函数来最小化
(例如残差平方和)
解决最小化问题以找到参数
(例如正规方程)
考虑我们涉及 PDE 的逆问题
$$
\nabla \cdot K \nabla u=0 \quad \text { in }(-1,1)^{2}
$$
我们的输入 $X$ 将被设置为边界上的测量算子(Dirichlet-to-Neumann map $\Lambda$)的观察值
例如让 $\left(x_{i_{r}}, y_{j_{r}}\right), r=1, \ldots, R$ 表示域边界上的点。
然后对于每个 Dirichlet 边界条件 $f_{\el
l, r}$ 在边界上,我们将有 Neumann 数据 $g_{\ell, r}$。
反电导率问题的输入和输出
然后 Dirichlet-to-Neumann 映射的每个观测值将被给出为
$$
\left[\begin{数组}{c}
f_{1, \ell} \
f_{2, \ell} \
\vdots \
f_{R, \ell} \
g_{1, \ell} \
g_{2, \ell} \
\vdots \
g_{R, \ell}
\end{array}\right], \quad \ell=1, \ldots, L 。
$$
收集所有这些测量值 $\ell=1、\ldots、L$,并选择 $f_{\ell}$,形成我们输入 $x_{i}$ 的一个观察结果
$$
x_{i}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc}
f_{1,1} & f_{1,2} & \cdots & f_{1, L} \
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \
f_{R, 1} & f_{R, 1} & \cdots & f_{R, L} \
g_{1,1} & g_{1,2} & \cdots & g_{1, L} \
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \
g_{R, 1} & g_{R, 2} & \cdots & g_{R, L}
\end{数组}\right]
$$

数学代写| Chebyshev polynomials 数值分析代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
时间序列分析代写
统计作业代写
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程