如果你也在 怎样代写博弈论game theory这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。博弈论game theory是对理性主体之间战略互动的数学模型的研究。它在社会科学的所有领域,以及逻辑学、系统科学和计算机科学中都有应用。最初,它针对的是两人的零和博弈,其中每个参与者的收益或损失都与其他参与者的收益或损失完全平衡。在21世纪,博弈论适用于广泛的行为关系;它现在是人类、动物以及计算机的逻辑决策科学的一个总称。
博弈论game theory在20世纪50年代被许多学者广泛地发展。虽然类似的发展至少可以追溯到1930年代,但它在1970年代被明确地应用于进化论。博弈论已被广泛认为是许多领域的重要工具。截至2020年,随着诺贝尔经济学纪念奖被授予博弈理论家保罗-米尔格伦和罗伯特-B-威尔逊,已有15位博弈理论家获得了诺贝尔经济学奖。约翰-梅纳德-史密斯因其对进化博弈论的应用而被授予克拉福德奖。
my-assignmentexpert™ 博弈论game theory作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的博弈论game theory作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此博弈论game theory作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在经济Economy作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的博弈论game theory代写服务。我们的专家在经济Economy代写方面经验极为丰富,各种博弈论game theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的博弈论game theory及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
经济代写|博弈论作业代写game theory代考|Utilities in mixed strategies
So far, only pure strategies have been discussed. However, there are cases where it makes sense to consider mixed strategies, which involve randomness. A mixed strategy combining pure strategies ${A, B, C}$ (one may also say that the support of this mixed strategy consists of these three pure strategies) can be represented as $p A+q B+r C$, which means “play $A$ with probability $p$, play $B$ with probability $q$, play $C$ with probability $r$ “. Since weights $(p, q, r)$ form a probability distribution they must satisfy $p+q+r=1$, i.e., $r=1-p-q$. Pure strategies can be reinterpreted as mixed strategies with a degenerate probability distribution in which only one value has probability 1 .
Utilities in mixed strategies are just computed by taking expectations over the aforementioned probabilities. For example, in the Prisoner’s dilemma, joint strategy $(0.9 M+0.1 C, M)$ gives P2 a payoff equal to
$$
u_{\mathrm{P} 2}(0.9 M+0.1 C, M)=0.9 u_{\mathrm{P} 2}(M, M)+0.1 u_{\mathrm{P} 2}(C, M)=0.9 \cdot(-1)+0.1 \cdot(-9)=-1.8 .
$$
The concept of strictly dominated strategies applies to mixed strategies too, both in the sense that mixed strategies can be strictly dominated and also they can strictly dominate another strategy, even a pure one. For solving exercises, the latter case might be useful, but unfortunately spotting that a pure strategy is strictly dominated by a mixed strategy is generally not easy to do, since mixed strategies are not explicitly reported on the matrix, so it requires a bit of effort.
Nash equilibria in mixed strategies are found by applying the indifference principle. This states that a mixed strategy at the Nash equilibrium should give the same payoff to the other player for all strategies. That is, if $P 1$ plays $p A+(1-p) B$ and P2 can choose between moves ${D, E}$, the condition to satisfy is
$$
u_{\mathrm{P} 2}(p, D)=u_{\mathrm{P} 2}(p, E),
$$
where $p$ is short notation for $p A+(1-p) B$.
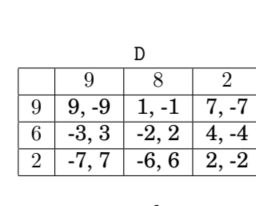
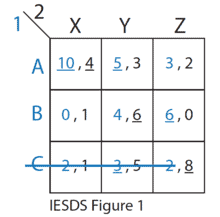
Example: In the game of “Odds and Evens” both players choose a number, usually between 0 and 5 , and do so simultaneously (as in rock-paper-scissors). The number can indeed be odd $(O)$ or even $(E)$. One player, say P1, wins and gets payoff $+1$ if the sum of the numbers is even; then the other, P2, wins instead if the sum is odd. The loser gets payoff $-1$. Conveniently, it turns out that the sum relationships on the $\mathbb{Z}_{2}$ field, i.e., between odd and even numbers satisfy certain mathematical properties that allow to represent just the choice of $O$ or $E$ as the pure strategies and the normal form of the game is shown through the following bi-matrix
经济代写|博弈论作业代写GAME THEORY代考|games with a structure
In general, games with a structure like that, i.e., one player likes when the selections are the same, but the other prefers that they are different, are called discoordination games. Compare this with a coordination game, where both players want instead them to be the same. A discoordination game does not have Nash equilibria in pure strategies, since all the joint strategies imply that one of the player has a regret and wants to change the outcome. However, an equilibrium in mixed strategies can be found by applying the indifference principle. P1 should play a mixed strategy $p O+(1-p) E$ such that P2’s payoff is the same playing either $O$ or $E$. This concept leads to
$$
u_{P 2}(p, O)=u_{P 2}(p, E)
$$
that is
$$
p u_{P 2}(O, O)+(1-p) u_{P 2}(E, O)=p u_{P 2}(O, E)+(1-p) u_{P 2}(E, E)
$$
Plugging in the numbers,
$$
p(-1)+(1-p)(+1)=p(+1)+(1-p)(-1)
$$
which is solved as $p=1 / 2$.
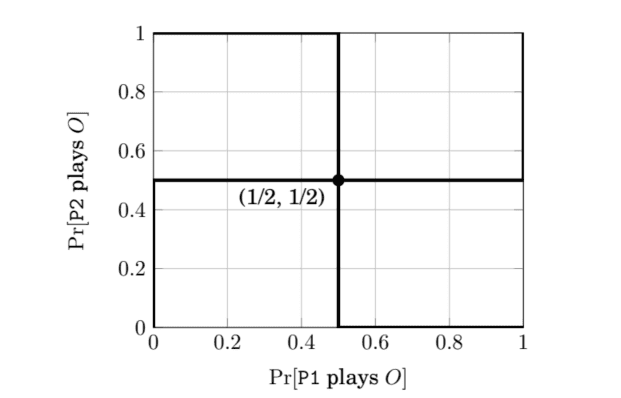
Likewise, P2 should play a mixed strategy $q O+(1-q) E$ such that P1’s payoff is the same playing either $O$ or $E$. For symmetry reasons, $q=p=1 / 2$. This means that the best thing a player can do is to randomly play even or odd with equal probability, which explains why the “Odds and Evens” game is used as a poor man’s replacement for a fair coin flip (indeed, a very poor man if it is penniless).
Notice that for all $p<1 / 2$, for P2 is more convenient to play $E$, while for all $p>1 / 2 O$ is P2’s best response. P2’s best response can thus be represented as a step function of $p$. Since the opposite applies to P1 (for $p<1 / 2$ he should always play $O$, for $p>1 / 2$ always $E$ ), a plot of both best responses looks as follows.Now, the most famous game theoretic result, Nash theorem, states the existence of at least one NE, possibly in mixed strategies, for each static game of complete information where the players have a finite set of available actions. Unfortunately, this is just an existence theorem, and does not say whether this NE is unique, or there are many. This implies that in certain situations the theorem can be promptly used to justify the existence of an NE in mixed strategy, for example, in discoordination games that are without NE in pure strategies, hence, they must have one in mixed strategies, but not to limit their number.
博弈论代写
经济代写|博弈论作业代写GAME THEORY代考|UTILITIES IN MIXED STRATEGIES
到目前为止,只讨论了纯策略。但是,在某些情况下考虑混合策略是有意义的,其中涉及随机性。结合纯策略的混合策略一种,乙,C 这n和米一种是一种ls这s一种是吨H一种吨吨H和s在pp这r吨这F吨H一世s米一世X和ds吨r一种吨和G是C这ns一世s吨s这F吨H和s和吨Hr和和p在r和s吨r一种吨和G一世和s可以表示为p一种+q乙+rC,意思是“玩一种有概率p, 玩乙有概率q, 玩C有概率r“。由于权重(p,q,r)形成他们必须满足的概率分布p+q+r=1, IE,r=1−p−q. 纯策略可以重新解释为具有退化概率分布的混合策略,其中只有一个值的概率为 1 。
混合策略中的效用只是通过对上述概率的期望来计算的。例如,在囚徒困境中,联合战略(0.9米+0.1C,米)给 P2 的收益等于
在磷2(0.9米+0.1C,米)=0.9在磷2(米,米)+0.1在磷2(C,米)=0.9⋅(−1)+0.1⋅(−9)=−1.8.
严格支配策略的概念也适用于混合策略,既可以严格支配混合策略,也可以严格支配另一种策略,甚至是纯策略。对于求解练习,后一种情况可能有用,但不幸的是,要发现纯策略严格受混合策略支配通常并不容易,因为混合策略没有明确报告在矩阵上,因此需要一些努力.
混合策略中的纳什均衡是通过应用无差异原理找到的。这表明在纳什均衡下的混合策略应该为所有策略的其他参与者提供相同的收益。也就是说,如果磷1戏剧p一种+(1−p)乙和 P2 可以在移动之间进行选择D,和, 满足的条件是
在磷2(p,D)=在磷2(p,和),
在哪里p是简写p一种+(1−p)乙.
示例:在“奇偶”游戏中,双方玩家选择一个数字,通常介于 0 和 5 之间,并同时选择一种s一世nr这Cķ−p一种p和r−sC一世ss这rs. 这个数字确实可以是奇数(这)甚至(和). 一名玩家,比如 P1,获胜并获得回报+1如果数字的总和是偶数;如果总和为奇数,则另一个 P2 获胜。失败者得到回报−1. 方便的是,事实证明,从2场,即在奇数和偶数之间满足某些允许仅表示选择的数学性质这或者和由于纯策略和博弈的正规形式通过以下双矩阵表示
经济代写|博弈论作业代写GAME THEORY代考|GAMES WITH A STRUCTURE
一般来说,具有类似结构的游戏,即一个玩家喜欢选择相同但另一个玩家喜欢它们不同的游戏,称为不协调游戏。将此与协调游戏进行比较,在这种游戏中,两个玩家都希望他们是相同的。不协调博弈在纯策略中不存在纳什均衡,因为所有联合策略都意味着其中一个玩家有遗憾并想要改变结果。但是,可以通过应用无差异原理找到混合策略中的均衡。P1应该玩混合策略p这+(1−p)和这样 P2 的收益是相同的这或者和. 这个概念导致
在磷2(p,这)=在磷2(p,和)
那是
p在磷2(这,这)+(1−p)在磷2(和,这)=p在磷2(这,和)+(1−p)在磷2(和,和)
插入数字,
p(−1)+(1−p)(+1)=p(+1)+(1−p)(−1)
这被解决为p=1/2.
同样,P2 应该采取混合策略q这+(1−q)和这样 P1 的收益是相同的这或者和. 出于对称原因,q=p=1/2. 这意味着玩家可以做的最好的事情就是以相等的概率随机玩偶数或奇数,这解释了为什么“奇数和偶数”游戏被用作穷人代替公平掷硬币的替代品一世nd和和d,一种在和r是p这这r米一种n一世F一世吨一世sp和nn一世l和ss.
请注意,对于所有p<1/2,对于P2来说玩起来更方便和, 而对于所有人p>1/2这是 P2 的最佳响应。因此,P2 的最佳响应可以表示为p. 因为相反的情况适用于 P1F这r$p<1/2$H和sH这在ld一种l在一种是spl一种是$这$,F这r$p>1/2$一种l在一种是s$和$,两个最佳响应的图如下所示。现在,最著名的博弈论结果,纳什定理,表明对于每个参与者具有有限信息的完整信息静态博弈,至少存在一个 NE,可能在混合策略中一组可用的操作。不幸的是,这只是一个存在定理,并没有说这个NE是唯一的,还是有很多。这意味着在某些情况下,该定理可以迅速用于证明混合策略中存在 NE,例如,在纯策略中没有 NE 的不协调博弈中,因此,它们必须在混合策略中具有 NE,但不能限制他们的人数。

经济代写|博弈论作业代写game theory代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。