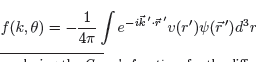数学代写|Review Questions 离散代考
离散数学在计算领域有广泛的应用,例如密码学、编码理论、 形式方法, 语言理论, 可计算性, 人工智能, 理论 数据库和软件的可靠性。 离散数学的重点是理论和应用,而不是为了数学本身而研究数学。 一切算法的基础都是离散数学一切加密的理论基础都是离散数学
编程时候很多奇怪的小技巧(特别是所有和位计算相关的东西)核心也是离散数学
其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
离散数学代写
Logic programming languages describe what is to be done, rather than how it should be done. These languages are concerned with the statement of the problem to be solved, rather than how the problem will be solved. These languages use mathematical logic as a tool in the statement of the problem definition. Logic is a useful tool in developing a body of knowledge (or theory), and it allows rigorous mathematical deduction to derive further truths from the existing set of truths. The theory is built up from a small set of axioms or postulates, and the rules of inference derive further truths logically.
The objective of logic programming is to employ mathematical logic to assist with computer programming. Many problems are naturally expressed as a theory, and the statement of a problem to be solved is often equivalent to determining if a new hypothesis is consistent with an existing theory. Logic provides a rigorot
Computation in logic programming is essentially logical deduction, and logic programming languages use first-order ${ }^{6}$ predicate calculus. They employ theorem proving to derive the desired truth from an initial set of axioms. These proofs are constructive $^{7}$ in that more an actual object that satisfies the constraints is produced rather than a pure existence theorem. Logic programming specifies the objects, the relationships between them and the constraints that must be satisfied for the problem.
- The set of objects involved in the computation,
- The relationships that hold between the objects,
- The constraints of the particular problem.
The language interpreter decides how to satisfy the particular constraints. Artificial Intelligence influenced the development of logic programming, and John McCarthy ${ }^{8}$ demonstrated that mathematical logic could be used for expressing knowledge. The first logic programming language was Planner developed by Carl Hewitt at MIT in 1969 . It uses a procedural ap rather than MoCarthy’s declarative approach.
The best-known logic programming language is Prolog, which was developed in the early $1970 \mathrm{~s}$ by Alain Colmerauer and Robert Kowalski. It stands for programming in logic. It is a goal-oriented language that is based on predicate logic. Prolog became an ISO standard in 1995. The language attempts to solve a goal by tackling the subgoals that the goal consists of:
$\overline{{ }^{6} \text { First-order logic allows quantification over objects but not functions or relations. Higher-order }}$ logics allow quantification of functions and relations ${ }^{7}$ For example, the statement $\exists x$ such that $x=\sqrt{4}$ states that there is an $x$ such that $x$ is the square root of 4 , and the constructive existence yields that the answer is that $x=2$ of $x-2$, i.e. constuctive existence provides more the tuth of the st ten satisfying the existence criteria is explicitly produced.
${ }^{8}$ John McCarthy received the Turing Award in 1971 for his contributions to Artificial Intelligence. He also developed the programming language LISP.
$16.6$ Logic and AI
283
goal : – subgoal $_{1}, \ldots$, subgoal $_{n}$.
That is, in order to prove a particular goal, it is sufficient to prove subgoal $_{1}$ through subgoal $_{n}$. Each line of a Prolog program consists of a rule or a fact, and the language specifies what exists rather than how. The following program fragment has one rule and two facts:
Grandmother $(G, S)$ :- parent $(P, S)$, mother $(G, P)$.
Mother (Sarah, Isaac).
Parent (Isaac, Jacob).
The first line in the program fragment is a rule that states that $\mathrm{G}$ is the grandmother of $\mathrm{S}$ if there is a parent $\mathrm{P}$ of $\mathrm{S}$ and $\mathrm{G}$ is the mother of $\mathrm{P}$. The next two statements are facts stating that Isaac is a parent of Jacob, and that Sarah is the mother of Isaac. A particular goal clause is true if all of its subclauses are true goalclause $\left(\mathrm{V}{\mathrm{g}}\right):-$ clause ${1}\left(\mathrm{~V}{1}\right), \ldots$ clause ${\mathrm{m}}\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{m}}\right)$.
A Horn clause consists of a goal clause and a set of clauses that must be proven separately. Prolog finds solutions by unification, i.e. by binding a variable to a value. For an implication to succeed, all goal variables $\mathrm{Vg}$ on the left side of:- must find a solution by binding variables from the clauses which are activated on the right side. But if a variable cannot be bound for a given clause, then that clause fails. Following the failure, Prolog backtracks, and this involves going back to the left to previous clauses to continue trying to unify with alternative bindings. Backtracking gives Prolog the ability to find multiple solutions to a given query or goal.
Logic programming languages generally use a simple searching strategy to consider the following alternatives:
- If a goal succeeds and there are more goals to achieve, then remember any untried alternatives and go on to the next goal.
- If a goal is achieved and there are no more goals to achieve, then stop with success.
- If a goal fails and there are alternative ways to solve it, then try the next one.
- If a goal fails and there are no alternate ways to solve it, and there is a previous

图论代考
逻辑编程语言描述了要做什么,而不是应该怎么做。这些语言关注的是要解决的问题的陈述,而不是如何解决问题。这些语言在问题定义的陈述中使用数学逻辑作为工具。逻辑是发展知识体系(或理论)的有用工具,它允许严格的数学推论从现有的一组真理中推导出更多的真理。该理论是从一小组公理或公设中建立起来的,推理规则从逻辑上推导出更多的真理。
逻辑编程的目标是使用数学逻辑来辅助计算机编程。许多问题自然而然地表达为理论,而对要解决的问题的陈述往往等同于确定一个新假设是否与现有理论一致。逻辑提供了严格的
逻辑编程中的计算本质上是逻辑演绎,逻辑编程语言使用一阶${}^{6}$谓词演算。他们使用定理证明从一组初始公理中推导出所需的真理。这些证明是建设性的$^{7}$,因为产生了更多满足约束的实际对象,而不是纯粹的存在定理。逻辑编程指定对象、对象之间的关系以及问题必须满足的约束。
- 计算中涉及的对象集,
- 对象之间的关系,
- 特定问题的约束。
语言解释器决定如何满足特定的约束。人工智能影响了逻辑编程的发展,John McCarthy ${ }^{8}$ 证明了数理逻辑可以用于表达知识。第一种逻辑编程语言是 1969 年由麻省理工学院的 Carl Hewitt 开发的 Planner。它使用程序 ap 而不是 MoCarthy 的声明式方法。
最著名的逻辑编程语言是 Prolog,它是由 Alain Colmerauer 和 Robert Kowalski 于 1970 年初开发的。它代表逻辑编程。它是一种基于谓词逻辑的面向目标的语言。 Prolog 于 1995 年成为 ISO 标准。该语言试图通过解决目标所包含的子目标来解决目标:
$\overline{{ }^{6} \text { 一阶逻辑允许对对象进行量化,但不允许对函数或关系进行量化。高阶 }}$ 逻辑允许量化函数和关系 ${ }^{7}$ 例如,语句 $\exists x$ 使得 $x=\sqrt{4}$ 表明存在 $x$使得 $x$ 是 4 的平方根,并且建设性存在产生答案是 $x-2$ 的 $x=2$,即建设性存在提供更多满足存在标准的 st 10 的真相是明确产生。
${ }^{8}$ John McCarthy 因对人工智能的贡献而于 1971 年获得图灵奖。他还开发了编程语言 LISP。
$16.6$ 逻辑和人工智能
283
目标:- 子目标 $_{1},\ldots$,子目标 $_{n}$。
也就是说,为了证明一个特定的目标,通过子目标 $_{n}$ 证明子目标 $_{1}$ 就足够了。 Prolog 程序的每一行都由一个规则或一个事实组成,并且该语言指定存在什么而不是如何存在。下面的程序片段有一个规则和两个事实:
祖母 $(G, S)$ :- 父母 $(P, S)$,母亲 $(G, P)$。
母亲(莎拉,艾萨克)。
父母(艾萨克,雅各布)。
程序片段的第一行是一条规则,如果 $\mathrm{S} 有父 $\mathrm{P}$,则 $\mathrm{G}$ 是 $\mathrm{S}$ 的祖母$ 和 $\mathrm{G}$ 是 $\mathrm{P}$ 的母亲。接下来的两个陈述是事实,说明以撒是雅各的父母,而撒拉是以撒的母亲。一个特定的目标子句如果其所有子句都为真,则其为真V}{1}\right), \ldots$ 子句 ${\mathrm{m}}\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{m}}\right)$。
Horn 子句由一个目标子句和一组必须单独证明的子句组成。 Prolog 通过统一找到解决方案,即将变量绑定到值。为了使暗示成功,所有目标变量 $\mathrm{Vg}$ 在左侧:- 必须通过绑定右侧激活的子句中的变量来找到解决方案。但是如果一个变量不能被一个给定的子句绑定,那么这个子句就会失败。失败后,Prolog 回溯,这涉及到向左返回到前面的子句以继续尝试与替代绑定统一。回溯使 Prolog 能够找到给定查询或目标的多个解决方案。
逻辑编程语言通常使用简单的搜索策略来考虑以下备选方案:
- 如果一个目标成功并且还有更多目标要实现,那么记住任何未尝试过的替代方案并继续下一个目标。
- 如果一个目标

数学代写| DISCRETE MATHEMATICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
抽象代数代考
抽象代数就是一门概念繁杂的学科,我们最重要的一点我想并不是掌握多少例子。即便是数学工作者也不会刻意记住Jacobson环、正则环这类东西,重要的是你要知道这门学科的基本工具和基本手法,对概念理解了没有,而这一点不需要用例子来验证,只需要看看你的理解和后续概念是否相容即可。
矩阵论代考matrix theory
数学,矩阵理论是一门研究矩阵在数学上的应用的科目。矩阵理论本来是线性代数的一个小分支,但其后由于陆续在图论、代数、组合数学和统计上得到应用,渐渐发展成为一门独立的学科。
密码学代考
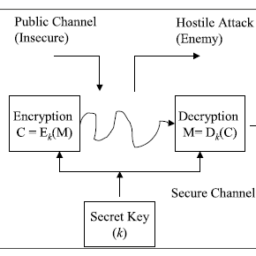
密码学是研究编制密码和破译密码的技术科学。 研究密码变化的客观规律,应用于编制密码以保守通信秘密的,称为编码学;应用于破译密码以获取通信情报的,称为破译学,总称密码学。 电报最早是由美国的摩尔斯在1844年发明的,故也被叫做摩尔斯电码。
- Cryptosystem
- A system that describes how to encrypt or decrypt messages
- Plaintext
- Message in its original form
- Ciphertext
- Message in its encrypted form
- Cryptographer
- Invents encryption algorithms
- Cryptanalyst
- Breaks encryption algorithms or implementations
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。