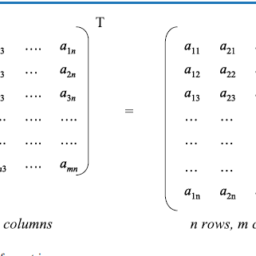
经济代写|Conclusion 宏观经济学代写
经济代写
3.6 Conclusion
This chapter began with a description of the financial architecture of India (commercial banks, capital market and moneylenders being the important players) and highlighted the presence of regulators such as the RBI, SEBI and IRDA. Subsequently, we discussed their active role in financial intermediation because they earn profits by lending dear and accepting deposits cheap. Following this, we discussed the meaning and role of money and the interest rate. In line with the recent developments in monetary economics, we introduced the endogenous money approach alongside the conventional exogenous money approach. This was followed by a brief discussion of the channels through which monetary policy influences other interest rates, as 62
MONEY AND INTEREST RATES
well as borrowing and lending decisions in the economy. Finally, we looked at the financial flows between India and the RoW; here, we discussed how exchange rates are determined and its links with monetary policy. Moreover, we also discussed, in brief, the nature of FIIs and FDI and their impact on the Indian economy via the RBI’s balance sheet and India’s capital account. And now, we shall move on to discuss the determination of aggregate income and employment in the next chapter.
Most textbooks position this chapter after the one on the theory of output and employment; do you think that the positioning matters in the way you understand macroeconomics?
Suggestions for further reading
It is strongly recommended that you read the 2014 Bank of England article ‘Money Creation in the Modern Economy’ cited in the chapter in its entirety; it is available for free download on the Bank of England website. For more advanced treatments of money and interest rates, consult the following: the book chapter ‘The Theory of Interest Rates’ by John Smithin in A Handbook of Alternative Monetary Economics, edited by Philip Arestis and Malcolm Sawyer in 2016 (Cheltenham: Edward Elgar) and Massimo Pivetti’s 1991 book An Essay on Money and Distribution (New York: Palgrave Macmillan). You can complement these readings with the chapter ‘The Social Device of Money’ from Amit Bhaduri’s 1986 textbook Macroeconomics: The Dynamics even further your understanding of money and interest rates, consult Tony Aspromourgos’s 2007 article ‘Interest as an Artefact of Self-validating Central Bank Beliefs’ in the journal Metroeconomica (2007, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 514-35). To understand money in the open economy with specific reference to India, look at the chapter ‘Managing Finance in Emerging Economies: The Case of India’ from Sunanda Sen’s 2014 book Dominant Finance and Stagnant Economies (New Delhi: Oxford University Press).
3.6 结论
本章首先描述了印度的金融架构(商业银行、资本市场和放债人是重要的参与者),并强调了 RBI、SEBI 和 IRDA 等监管机构的存在。随后,我们讨论了他们在金融中介中的积极作用,因为他们通过高价放贷和低价接受存款来赚取利润。在此之后,我们讨论了货币和利率的意义和作用。根据货币经济学的最新发展,我们引入了内生货币方法和传统的外生货币方法。随后简要讨论了货币政策影响其他利率的渠道,如 62
货币和利率
以及经济中的借贷决策。最后,我们研究了印度与世界其他地区之间的资金流动;在这里,我们讨论了汇率是如何确定的以及它与货币政策的联系。此外,我们还简要讨论了 FII 和 FDI 的性质以及它们通过 RBI 的资产负债表和印度的资本账户对印度经济的影响。现在,我们将在下一章继续讨论总收入和就业的决定。
大多数教科书将这一章放在关于产出和就业理论的那一章之后。你认为定位对你理解宏观经济学的方式很重要吗?
进一步阅读的建议
强烈建议您完整阅读本章引用的 2014 年英格兰银行文章“现代经济中的货币创造”;它可以在英格兰银行网站上免费下载。有关货币和利率的更高级处理方法,请参阅以下内容:John Smithin 在 A Handbook of Alternative Monetary Economics 中的“利率理论”一书,Philip Arestis 和 Malcolm Sawyer 于 2016 年编辑(切尔滕纳姆:Edward Elgar)和 Massimo Pivetti 1991 年出版的《金钱与分配论文集》(纽约:Palgrave Macmillan)。您可以使用 Amit Bhaduri 1986 年教科书《宏观经济学:动力学》中的“货币的社会设备”一章来补充这些阅读材料,进一步了解货币和利率,请参阅 Tony Aspromourgos 2007 年的文章“利息作为自我验证中央银行的人工制品” Beliefs’ in the Journal Metroeconomica (2007, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 514-35)。要了解开放经济中的货币并具体参考印度,请查看 Sunanda Sen 2014 年出版的《主导金融和停滞经济》一书(新德里:牛津大学出版社)中的“新兴经济体中的金融管理:印度案例”一章。
经济代考
宏观经济学,是以国民经济总过程的活动为研究对象,主要考察就业总水平、国民总收入等经济总量,因此,宏观经济学也被称做就业理论或收入理论。 宏观经济学研究的是经济资源的利用问题,包括国民收入决定理论、就业理论、通货膨胀理论、经济周期理论、经济增长理论、财政与货币政策。

其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
宏观经济学是经济学的一个分支,它研究的是一个整体经济,即市场或其他大规模运作的系统是如何运作的。宏观经济学研究经济范围内的现象,如通货膨胀价格水平经济增长,国民收入,国内生产总值,以及失业 .
计量经济学代考
计量经济学是以一定的经济理论和统计资料为基础,运用数学、统计学方法与电脑技术,以建立经济计量模型为主要手段,定量分析研究具有随机性特性的经济变量关系的一门经济学学科。 主要内容包括理论计量经济学和应用经济计量学。 理论经济计量学主要研究如何运用、改造和发展数理统计的方法,使之成为经济关系测定的特殊方法。
相对论代考
相对论(英語:Theory of relativity)是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由愛因斯坦创立,依其研究对象的不同可分为狭义相对论和广义相对论。 相对论和量子力学的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,它们共同奠定了现代物理学的基础。
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。
复分析代考
学习易分析也已经很冬年了,七七八人的也续了圧少的书籍和论文。略作总结工作,方便后来人学 Đ参考。
复分析是一门历史悠久的学科,主要是研究解析函数,亚纯函数在复球面的性质。下面一昭这 些基本内容。
(1) 提到复变函数 ,首先需要了解复数的基本性左和四则运算规则。怎么样计算复数的平方根, 极坐标与 $x y$ 坐标的转换,复数的模之类的。这些在高中的时候囸本上都会学过。
(2) 复变函数自然是在复平面上来研究问题,此时数学分析里面的求导数之尖的运算就会很自然的 引入到复平面里面,从而引出解析函数的定义。那/研究解析函数的性贡就是关楗所在。最关键的 地方就是所谓的Cauchy一Riemann公式,这个是判断一个函数是否是解析函数的关键所在。
(3) 明白解析函数的定义以及性质之后,就会把数学分析里面的曲线积分 $a$ 的概念引入复分析中, 定义几乎是一致的。在引入了闭曲线和曲线积分之后,就会有出现复分析中的重要的定理: Cauchy 积分公式。 这个是易分析的第一个重要定理。