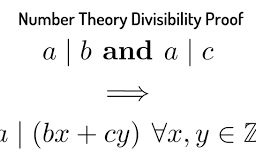统计代写|The Coupling Inequality 抽样理论代考
统计代写
A coupling between random variables $X$ and $Y$ can be used to evaluate how close the distribution of $X$ is from the distribution of $Y$. A natural way to compare the two distributions is to compute
$$
|P(X=k)-P(Y=k)|
$$
for every positive integer $k$ and see how large this difference can be. We will actually use a more stringent metric. Instead of comparing the distributions for individual $k$ ‘s, we will compare them on sets of integers. More precisely, let $D$ be a set of positive integers and then we will bound
$$
|P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D)|=\left|\sum_{k \in D}(P(X=k)-P(Y=k))\right|
$$
3 The Coupling Inequality
233
The following probability property will be useful. Recall that for any events $A$ and $B$,
$$
P(A)=P(A \cap B)+P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
Hence,
$$
P(A) \leq P(B)+P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
and therefore,
$$
P(A)-P(B) \leq P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
Let $D$ be a set of positive integers, and using the inequality above for
$$
A={X \in D} \text { and } B={Y \in D}
$$
we get
$$
P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D) \leq P(X \in D, Y \notin D)
$$
Since the event ${X \in D, Y \notin D}$ is included in the event ${X \neq Y}$,
$$
P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D) \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
Similarly,
$$
P(Y \in D)-P(X \in D) \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
Therefore,
$$
|P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D)| \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
This is the coupling inequality. It gives an upper bound on how far away the distribution of $X$ is from the distribution of $Y$.
Note that the inequality holds for any $D$. It does not matter if we are comparing the distributions of $X$ and $Y$ on a small set $D$ or on a large set $D$. The bound $P(X \neq$ $Y$ ) does not depend on $D$.
We now apply the coupling inequality to two Poisson distributions.
Example 1 We use the coupling from Sect. 2. Let $X$ be a mean $a$ Poisson random variable. Let $V$ be a mean $b-a$ Poisson random variable independent of $X$ and $Y=X+V$. Then, $Y$ is a Poisson random variable with mean $b$.
随机变量 $X$ 和 $Y$ 之间的耦合可用于评估 $X$ 的分布与 $Y$ 的分布的接近程度。比较两种分布的一种自然方法是计算
$$
|P(X=k)-P(Y=k)|
$$
对于每个正整数 $k$,看看这种差异有多大。我们实际上将使用更严格的指标。我们将在整数集上比较它们,而不是比较单个 $k$ 的分布。更准确地说,让 $D$ 是一组正整数,然后我们将绑定
$$
|P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D)|=\left|\sum_{k \in D}(P(X=k)-P(Y=k))\right|
$$
3 耦合不等式
233
以下概率属性将很有用。回想一下,对于任何事件 $A$ 和 $B$,
$$
P(A)=P(A \cap B)+P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
因此,
$$
P(A) \leq P(B)+P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
因此,
$$
P(A)-P(B) \leq P\left(A \cap B^{c}\right)
$$
令 $D$ 是一组正整数,并使用上面的不等式
$$
A={X \in D} \text { 和 } B={Y \in D}
$$
我们得到
$$
P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D) \leq P(X \in D, Y \notin D)
$$
由于事件${X\in D, Y\notin D}$包含在事件${X\neq Y}$中,
$$
P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D) \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
相似地,
$$
P(Y \in D)-P(X \in D) \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
所以,
$$
|P(X \in D)-P(Y \in D)| \leq P(X \neq Y)
$$
这就是耦合不等式。它给出了 $X$ 的分布与 $Y$ 的分布相距多远的上限。
请注意,不等式适用于任何 $D$。我们是在小集合 $D$ 上还是在大集合 $D$ 上比较 $X$ 和 $Y$ 的分布并不重要。有界 $P(X \neq$ $Y$ ) 不依赖于 $D$。
我们现在将耦合不等式应用于两个泊松分布。
示例 1 我们使用 Sect 的耦合。 2. 令 $X$ 为均值 $a$ 泊松随机变量。令 $V$ 为独立于 $X$ 和 $Y=X+V$ 的平均 $b-a$ 泊松随机变量。那么,$Y$ 是一个均值为 $b$ 的泊松随机变量。
统计代考
其他相关科目课程代写:组合学Combinatorics集合论Set Theory概率论Probability组合生物学Combinatorial Biology组合化学Combinatorial Chemistry组合数据分析Combinatorial Data Analysis
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
抽样理论(sampling theory)是关于从总体中抽取具有代表性的和适当的样本以得出有效推论的原则和分析技术的一种统计学理论。包括两个主题:(1)样本如何抽取,即抽样方法的问题。如随机抽样、分层抽样、分层等比抽样、系统抽样、群类抽样、有限总体抽样等;(2)样本大小的问题。
计量经济学代考
计量经济学是以一定的经济理论和统计资料为基础,运用数学、统计学方法与电脑技术,以建立经济计量模型为主要手段,定量分析研究具有随机性特性的经济变量关系的一门经济学学科。 主要内容包括理论计量经济学和应用经济计量学。 理论经济计量学主要研究如何运用、改造和发展数理统计的方法,使之成为经济关系测定的特殊方法。
相对论代考
相对论(英語:Theory of relativity)是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由愛因斯坦创立,依其研究对象的不同可分为狭义相对论和广义相对论。 相对论和量子力学的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,它们共同奠定了现代物理学的基础。
编码理论代写
编码理论(英语:Coding theory)是研究编码的性质以及它们在具体应用中的性能的理论。编码用于数据压缩、加密、纠错,最近也用于网络编码中。不同学科(如信息论、电机工程学、数学、语言学以及计算机科学)都研究编码是为了设计出高效、可靠的数据传输方法。这通常需要去除冗余并校正(或检测)数据传输中的错误。
编码共分四类:[1]
数据压缩和前向错误更正可以一起考虑。
复分析代考
学习易分析也已经很冬年了,七七八人的也续了圧少的书籍和论文。略作总结工作,方便后来人学 Đ参考。
复分析是一门历史悠久的学科,主要是研究解析函数,亚纯函数在复球面的性质。下面一昭这 些基本内容。
(1) 提到复变函数 ,首先需要了解复数的基本性左和四则运算规则。怎么样计算复数的平方根, 极坐标与 $x y$ 坐标的转换,复数的模之类的。这些在高中的时候囸本上都会学过。
(2) 复变函数自然是在复平面上来研究问题,此时数学分析里面的求导数之尖的运算就会很自然的 引入到复平面里面,从而引出解析函数的定义。那/研究解析函数的性贡就是关楗所在。最关键的 地方就是所谓的Cauchy一Riemann公式,这个是判断一个函数是否是解析函数的关键所在。
(3) 明白解析函数的定义以及性质之后,就会把数学分析里面的曲线积分 $a$ 的概念引入复分析中, 定义几乎是一致的。在引入了闭曲线和曲线积分之后,就会有出现复分析中的重要的定理: Cauchy 积分公式。 这个是易分析的第一个重要定理。