微积分(Calculus),数学概念,是高等数学中研究函数的微分(Differentiation)、积分(Integration)以及有关概念和应用的数学分支。它是数学的一个基础学科,内容主要包括极限、微分学、积分学及其应用。微分学包括求导数的运算,是一套关于变化率的理论。它使得函数、速度、加速度和曲线的斜率等均可用一套通用的符号进行讨论。积分学,包括求积分的运算,为定义和计算面积、体积等提供一套通用的方法
my-assignmentexpert™ 微积分calculus作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的微积分calculus作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于economics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此微积分calculus作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在经济学作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的微积分calculus代写服务。我们的专家在微积分calculus学 代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微积分calculus相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的econ代写服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 单变量微积分
- 多变量微积分
- 傅里叶级数
- 黎曼积分
- ODE
- 微分学
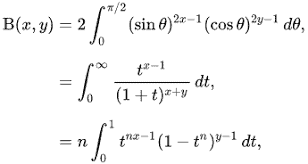
微积分代考calculus代写|Gamma Function
We show that for $x>0$, the improper integral
$$
\Gamma(x):=\int_{0}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
converges. The function $\Gamma(x), x>0$, is called the gamma function.
Let $x>0$. Note that
$$
t^{x-1} e^{-t} \leq t^{x-1} \quad \forall t>0
$$
and by the result in Example 4.1.8(ii), the improper integral $\int_{0}^{1} t^{x-1} \mathrm{~d} t$ converges. Hence, by comparison test (Theorem 4.2.1),
$$
\int_{0}^{1} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t \text { converges. }
$$
Also, we observe that
$$
\frac{t^{x-1} e^{-t}}{t^{-2}} \rightarrow 0 \text { as } t \rightarrow \infty
$$
and by the result in Example 4.1.3, the integral $\int_{1}^{\infty} t^{-2} \mathrm{~d} t$ converges. Hence, by Theorem 4.2.4, $\int_{1}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t$ converges. Thus,
$$
\Gamma(x):=\int_{0}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=\int_{0}^{1} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t+\int_{1}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
converges for every $x>0$. Recall from Example 4.1.5 that $\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=1$. Hence, we have
$$
\Gamma(1)=1 .(1)
$$
Also, using integration by parts, we obtain
$$
\Gamma(x+1)=x \Gamma(x) \quad \forall x>1 \text {.(2) }
$$
Indeed, for $x>1$, we have
$$
\int t^{x} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=-t^{x} e^{-t}+\int x t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
Since $t^{x} e^{-t} \rightarrow 0$ as $t \rightarrow 0$ and also as $t \rightarrow \infty$, we obtain
$$
\Gamma(x+1)=\int_{0}^{\infty} t^{x} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=x \int_{0}^{\infty} t^{x-1} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=x \Gamma(x) .
$$
Combining (1) and (2), we obtain
$$
\Gamma(n+1)=n ! \quad \forall n \in \mathbb{N} .
$$
We may also observe that
$$
\Gamma(1 / 2)=\int_{0}^{\infty} t^{-1 / 2} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
Using the change of variable, $y=t^{1 / 2}$, we have $d y=\frac{1}{2 t^{1 / 2}} \mathrm{~d} t$, it can be seen that
$$
\int_{0}^{\infty} t^{-1 / 2} e^{-t} \mathrm{~d} t=2 \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-y^{2}} \mathrm{~d} y .
$$
It is known (can be proved using the method of calculus of two variables) that
$$
\int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-x^{2}} \mathrm{~d} x=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{2}
$$
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|Beta Function
We show that for $x>0, y>0$, the improper integral
$$
\beta(x, y):=\int_{0}^{1} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
converges. The function $\beta(x, y)$ for $x>0, y>0$ is called the beta function.
Clearly, the above integral is proper for $x \geq 1$ and $y \geq 1$. In order to treat the remaining cases, we consider the integrals
$$
\int_{0}^{1 / 2} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \mathrm{~d} t, \quad \int_{1 / 2}^{1} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
We note that if $0<t \leq 1 / 2$, then $(1-t)^{y-1} \leq 2^{1-y}$ so that
$$
t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \leq t^{x-1} 2^{1-y} \leq 2 t^{x-1} \text { for } 0<t<\frac{1}{2}
$$
Now, $\int_{0}^{1 / 2} t^{x-1} \mathrm{~d} t$ converges, by the result in Example 4.1.8(ii). Hence, by comparison test (Theorem 4.2.1), $\int_{0}^{1 / 2} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \mathrm{~d} t$ converges.
To show the convergence of the second integral, consider the change of variable $s=1-t$. Then
$$
\int_{1 / 2}^{1} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1} \mathrm{~d} t=\int_{0}^{1 / 2} s^{y-1}(1-s)^{x-1} \mathrm{~d} s
$$
at the integral $\int_{0}^{1 / 2} s^{y-1}(1-s)^{x-1} \mathrm{~d} s$ converges. Thus, 4 Improper Integrals
274
$$
\beta(x, y):=\int_{0}^{1} t^{x-1}(1-t)^{1-y} \mathrm{~d} t, x>0, y>0
$$
converges for every $x>0, y>0$.
Beta function and gamma function are related by the relation,
$$
\beta(x, y)=\frac{\Gamma(x) \Gamma(y)}{\Gamma(x+y)}
$$
the proof of which is too much involved (see, e.g., [6]).
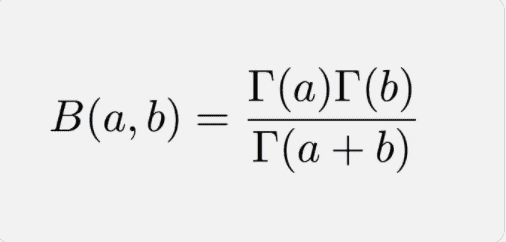
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|GAMMA FUNCTION
我们证明了X>0, 不正确的积分
Γ(X):=∫0∞吨X−1和−吨 d吨
收敛。功能Γ(X),X>0,称为伽马函数。
让X>0. 注意
吨X−1和−吨≤吨X−1∀吨>0
并且根据示例 4.1.8(ii) 中的结果,不正确的积分∫01吨X−1 d吨收敛。因此,通过比较测试(定理 4.2.1),
∫01吨X−1和−吨 d吨 收敛。
此外,我们观察到
吨X−1和−吨吨−2→0 作为 吨→∞
根据示例 4.1.3 中的结果,积分∫1∞吨−2 d吨收敛。因此,根据定理 4.2.4,∫1∞吨X−1和−吨 d吨收敛。因此,Γ(X):=∫0∞吨X−1和−吨 d吨=∫01吨X−1和−吨 d吨+∫1∞吨X−1和−吨 d吨
收敛于每个X>0. 回想一下示例 4.1.5,∫0∞和−吨 d吨=1. 因此,我们有
Γ(1)=1.(1)
此外,使用分部积分,我们得到
Γ(X+1)=XΓ(X)∀X>1.(2)
的确,对于X>1, 我们有
∫吨X和−吨 d吨=−吨X和−吨+∫X吨X−1和−吨 d吨
自从吨X和−吨→0作为吨→0也作为吨→∞, 我们获得
Γ(X+1)=∫0∞吨X和−吨 d吨=X∫0∞吨X−1和−吨 d吨=XΓ(X).
结合(1)和(2),我们得到
Γ(n+1)=n!∀n∈ñ.
我们还可以观察到
Γ(1/2)=∫0∞吨−1/2和−吨 d吨
利用变量的变化,和=吨1/2, 我们有d和=12吨1/2 d吨, 可以看出
∫0∞吨−1/2和−吨 d吨=2∫0∞和−和2 d和.
已知(可以用二元微积分法证明)
∫0∞和−X2 dX=圆周率2
微积分代考CALCULUS代写|BETA FUNCTION
我们证明了X>0,和>0, 不正确的积分
b(X,和):=∫01吨X−1(1−吨)和−1 d吨
收敛。功能b(X,和)为了X>0,和>0称为 beta 函数。
显然,上述积分适用于X≥1和和≥1. 为了处理剩余的情况,我们考虑积分
∫01/2吨X−1(1−吨)和−1 d吨,∫1/21吨X−1(1−吨)和−1 d吨
我们注意到,如果0<吨≤1/2, 然后(1−吨)和−1≤21−和以便
吨X−1(1−吨)和−1≤吨X−121−和≤2吨X−1 为了 0<吨<12
现在,∫01/2吨X−1 d吨收敛,由示例 4.1.8(ii) 中的结果。因此,通过比较测试(定理 4.2.1),∫01/2吨X−1(1−吨)和−1 d吨收敛。
为了显示第二个积分的收敛性,考虑变量的变化s=1−吨. 然后
∫1/21吨X−1(1−吨)和−1 d吨=∫01/2s和−1(1−s)X−1 ds
在积分∫01/2s和−1(1−s)X−1 ds收敛。因此,4个不正确的积分
274
b(X,和):=∫01吨X−1(1−吨)1−和 d吨,X>0,和>0
收敛于每个X>0,和>0.
Beta 函数和 gamma 函数由关系相关,
b(X,和)=Γ(X)Γ(和)Γ(X+和)
其证明涉及太多(参见,例如,[6])。

微积分note Integer Multiples of Irrational Numbers 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。