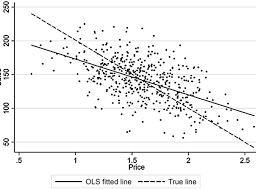
如果你也在 怎样代写统计Statistics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。统计Statistics是数学的一个分支,涉及到矢量空间和线性映射。它包括对线、面和子空间的研究,也涉及所有向量空间的一般属性。
统计学Statistics是一门关于发展和研究收集、分析、解释和展示经验数据的方法的科学。统计Statistics是一个高度跨学科的领域;统计Statistics的研究几乎适用于所有的科学领域,各科学领域的研究问题促使新的统计方法和理论的发展。在开发方法和研究支撑这些方法的理论时,统计学家利用了各种数学和计算工具。
统计Statistics领域的两个基本概念是不确定性和突变。我们在科学(或更广泛的生活)中遇到的许多情况,其结果是不确定的。在某些情况下,不确定性是因为有关的结果尚未确定(例如,我们可能不知道明天是否会下雨),而在其他情况下,不确定性是因为虽然结果已经确定,但我们并不知道(例如,我们可能不知道我们是否通过了某项考试)。
my-assignmentexpert™ 统计Statistics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的统计Statistics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此统计Statistics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在统计Statistics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在统计Statistics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种统计Statistics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的统计Statistics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- Date Analysis数据分析
- Actuarial Science 精算科学
- Bayesian Statistics 贝叶斯统计
- Generalized Linear Model 广义线性模型
- Macroeconomic statistics 宏观统计学
- Microeconomic statistics 微观统计学
- Logistic regression 逻辑回归
- linear regression 线性回归
We now have a basic understanding of simple and multiple LRMs, including how to interpret their slope coefficients, intercepts, $p$-values, and CIs, as well as some of their practical implications. Let’s next consider the assumptions of the model. We learned about some of these assumptions in Chapter 3. We’ll revisit them, introduce a new one, and mention some special situations when they might not be satisfied. The following is a brief overview because several of the subsequent chapters examine the assumptions in detail.
- Independence: the errors of prediction are independent of one another. This affects the bias and efficiency of the estimates. We can understand this assumption better now that we’ve examined a couple of LRMs. For example, when analyzing state-level data, we assume the errors of prediction are independent across states. But is this true? States that share borders are similar in many ways relative to states that are far apart. The errors in prediction are likely to be similar in adjacent states but different in states that are far away from one another. When we collect data over time, errors of prediction from those time points closer together are usually more alike than those farther apart. A simple way to predict whether the errors of prediction are not independent is when the units of observation in a dataset are also not independent. In this situation, the careful researcher will take steps to address the likely dependence of the errors. Chapter 8 provides more information about the independence assumption.
- Homoscedasticity (constant variance): the variance of the errors is constant for all combinations of Xs. Homoscedasticity means “same scatter.” Its antonym is heteroscedasticity (“different scatter”). This important assumption, when not satisfied, has implications for the efficiency of the LRM slope coefficients. We’ll learn more about this critical issue in Chapter $9 .$
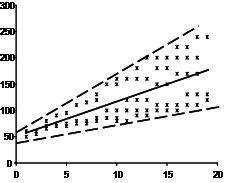
- Collinearity: no combination of the Xs has a perfect association-they are not perfectly collinear. This assumption is not listed in Chapter 3 since the simple LRM includes only one explanatory variable. Revisit the overlapping circles in Figure $4.4$ and you can visualize what collinearity implies. Suppose circles $x_{1}$ and $x_{2}$ overlap completely. Is it possible to estimate the covariance between $x_{1}$ and $y$ exclusive of $x_{2}$ ? No, because no variability is left over in $x_{1}$ once we consider its association with $x_{2}$. We’ll discover in Chapter 10 that even a higher degree of collinearity among explanatory variables can lead to unusual results in LRMs.
- Normality: the errors are a normally distributed random variable with a mean of zero. This statement includes two assumptions-normality and mean of zero-that are combined for convenience. The first part is considered a weak assumption since, even when contravened, the model performs fairly well, especially in large samples. ${ }^{13}$ The second part-that the mean is zero-is important for estimating the correct intercept. As we learned earlier, though, the intercept in many models is of little use since its value often falls outside the range of the explanatory and outcome variables. Chapter 11 provides a detailed discussion of the normality assumption. ${ }^{14}$
- Linearity: the mean value of $Y$ for each specific combination of the $X$ s is a linear function of the Xs. In other words, the regression surface is assumed flat in three dimensions (see Figure 4.3). In simple LRMs we assume straight-line relationships in two dimensions, but multiple LRMs include two or more explanatory variables so we must move to higher dimensions. One way to understand this is to imagine three-dimensional space and then visualize the difference between a flat surface and a curved surface. We assume that the relationship between the $X$ s and $Y$ is not curved. In Chapter 11 , we’ll learn about some tools for analyzing relationships that are not linear.
我们现在对简单和多重 LRM 有了基本的了解,包括如何解释它们的斜率系数、截距、p-values 和 CI,以及它们的一些实际含义。接下来让我们考虑模型的假设。我们在第 3 章中了解了其中的一些假设。我们将重新审视它们,引入一个新假设,并提及一些可能不满足的特殊情况。以下是一个简短的概述,因为随后的几章将详细检查这些假设。
- 独立性:预测误差相互独立。这会影响估计的偏差和效率。现在我们已经检查了几个 LRM,我们可以更好地理解这个假设。例如,在分析州级数据时,我们假设预测误差在各个州之间是独立的。但这是真的吗?与相距较远的州相比,共享边界的州在许多方面都相似。预测中的误差在相邻状态中可能相似,但在相距较远的状态中可能不同。当我们随着时间的推移收集数据时,距离较近的时间点的预测误差通常比距离较远的时间点更相似。预测预测误差是否不独立的一种简单方法是数据集中的观察单位也不是独立的。在这种情况下,细心的研究人员将采取措施解决错误的可能依赖性。第 8 章提供了有关独立性假设的更多信息。
- Homoscedasticity(常数方差):误差的方差对于 Xs 的所有组合都是常数。同方差性意味着“相同的分散”。它的反义词是异方差(“不同的分散”)。如果不满足这一重要假设,则会对 LRM 斜率系数的效率产生影响。我们将在本章中了解更多关于这个关键问题的信息9.
- 共线性:X 的组合没有完美的关联——它们不是完美的共线。由于简单 LRM 仅包含一个解释变量,因此第 3 章未列出该假设。重温图中重叠的圆圈4.4你可以想象共线性意味着什么。假设圆圈X1和X2完全重叠。是否可以估计之间的协方差X1和和不包括X2? 不,因为在X1一旦我们考虑它与X2. 我们将在第 10 章中发现,即使解释变量之间存在更高程度的共线性,也会导致 LRM 中出现不寻常的结果。
- 正态性:误差是均值为零的正态分布随机变量。该陈述包括两个假设——正态性和零均值——为方便起见将它们组合在一起。第一部分被认为是一个弱假设,因为即使违反,该模型也表现得相当好,尤其是在大样本中。13第二部分——均值为零——对于估计正确的截距很重要。然而,正如我们之前所了解的,许多模型中的截距几乎没有用处,因为它的值通常超出解释变量和结果变量的范围。第 11 章详细讨论了正态性假设。14
- 线性度:平均值和对于每个特定的组合Xs 是 Xs 的线性函数。换句话说,回归表面在三个维度上被假定为平坦的(见图 4.3)。在简单的 LRM 中,我们假设二维的直线关系,但多个 LRM 包含两个或多个解释变量,因此我们必须转向更高的维度。理解这一点的一种方法是想象三维空间,然后可视化平面和曲面之间的差异。我们假设两者之间的关系X沙和不是弯曲的。在第 11 章中,我们将学习一些用于分析非线性关系的工具。
统计作业代写Statistics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
matlab代写
MATLAB是一个编程和数值计算平台,被数百万工程师和科学家用来分析数据、开发算法和创建模型。
MATLAB is a programming and numeric computing platform used by millions of engineers and scientists to analyze data, develop algorithms, and create models.
统计代写
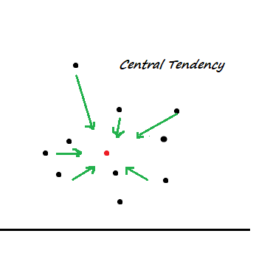
生活中,统计学无处不在。它遍布世界的每一个角落,应用于每一个领域。不管是普通人的生活,还是最高精尖的领域,它都不曾缺席。
自从人类发明统计学这一学科以来,原本复杂多样、无法预测的数据,变成了可预测的、直观的正态分布。
我们的确不可能精准的预测到每一个数据的变化,但是我们可以精准的预测到大部分数据的变化。当然,那些散落在中心之外的数据我们无法把握,可尽管如此,我们也拥有了接近神的能力,打破了神与人的壁垒,这就是统计学的魅力。
同时,它又作为众多学生的噩梦学科,在学科难度榜上居高不下 。大量的统计公式、概念和题目导致了ohysics作业繁杂又麻烦。现在有我们UprivateTA™机构为您提供优质statistics assignment代写服务,帮您解决作业难题!
统计作业代写
生活中,统计学无处不在。它遍布世界的每一个角落,应用于每一个领域。不管是普通人的生活,还是最高精尖的领域,它都不曾缺席。
自从人类发明统计学这一学科以来,原本复杂多样、无法预测的数据,变成了可预测的、直观的正态分布。
我们的确不可能精准的预测到每一个数据的变化,但是我们可以精准的预测到大部分数据的变化。当然,那些散落在中心之外的数据我们无法把握,可尽管如此,我们也拥有了接近神的能力,打破了神与人的壁垒,这就是统计学的魅力。
同时,它又作为众多学生的噩梦学科,在学科难度榜上居高不下 。大量的统计公式、概念和题目导致了ohysics作业繁杂又麻烦。现在有我们UprivateTA™机构为您提供优质statistics assignment代写服务,帮您解决作业难题!
my-assignmentexpert™这边统计代写的质量怎么样?保不保分?靠不靠谱? 一般能写到多少分?
各国各学校的学术标准都有所差异,即使是统计作业,给分也存在一定的主观性因素,有时Teacher和TA的改分并不能够做到完全公正,所有的作业分数都存在一定的运气成分,TA对于步骤把控的严格程度可能和给分的TA今天的心情以及他的性格正相关。一般情况下,MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™出品的作业平均正确率在93%以上。
我在MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™这里购买了代写服务,然后最后这门课的成绩挂了怎么办?
若是因为各种因素结合导致在此购买的统计作业的成绩未达到事先指定的标准,MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™承诺免费重写/修改,并且无条件退款。
最快什么时候写完? 很急的任务可以做吗?
最急的统计论文,可在24小时以内完成,加急的论文价格会比普通的订单稍贵,因此建议各位提前预定,不要拖到deadline临近再下订单。
最急的统计quiz和统计exam代考,在写手档期ok的情况下,可以在下单之后一小时之内进行,不过不提倡这样临时找人,因为加急的quiz和exam代考价格会比普通的订单贵更重要的是可能找不到人,因此建议各位提前预定,不要拖到deadline临近再下订单。
最急的统计assignment,在写手档期ok的情况下,可以在下单之后三小时之内完成,价格在一般的assignment基础上收一个加急费用,如果一份assignment发下来不确定自己能不能完成也能提前和我们联系,报价是不收取任何费用的,如果后续有需要,也方便我们安排写手档期。