如果你也在 怎样金融数学Financial Mathematics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融数学Financial Mathematics是将数学方法应用于金融问题。(有时使用的同等名称是定量金融、金融工程、数学金融和计算金融)。它借鉴了概率、统计、随机过程和经济理论的工具。传统上,投资银行、商业银行、对冲基金、保险公司、公司财务部和监管机构将金融数学的方法应用于诸如衍生证券估值、投资组合结构、风险管理和情景模拟等问题。依赖商品的行业(如能源、制造业)也使用金融数学。 定量分析为金融市场和投资过程带来了效率和严谨性,在监管方面也变得越来越重要。
定量金融作为经济学的一个子领域,关注资产和金融工具的估值以及资源的配置。几个世纪的经验产生了关于经济运行方式和我们评估资产的方式的基本理论。模型描述了基本变量之间的关系,如资产价格、市场运动和利率。这些数学工具使我们能够得出原本难以发现或从直觉上无法立即看出的结论。模型应用的一个例子是银行的压力测试。 特别是在现代计算技术的帮助下,我们可以存储大量的数据并同时对许多变量进行建模,从而有能力对相当大和复杂的系统进行建模。因此,科学计算的技术,如数值分析、蒙特卡洛模拟和优化是金融数学的重要组成部分。
任何科学的很大一部分都是在对研究对象的基本了解的基础上建立可检验的假设,并通过可重复的研究来证明或反驳这些假设的能力。从这个角度来看,数学是代表理论的语言,并提供测试其有效性的工具。例如,在布莱克、斯科尔斯和默顿的期权定价理论中,提出了一个股票价格变动的模型,结合无风险投资将获得无风险收益率的理论,研究者们推断出可以给期权分配一个价值。
my-assignmentexpert™金融数学Financial Mathematics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的金融数学Financial Mathematics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融数学Financial Mathematics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在金融数学Financial Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的金融数学Financial Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在金融数学Financial Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种金融数学Financial Mathematics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的金融数学Financial Mathematics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 随机微积分 Stochastic calculus
- 随机分析 Stochastic analysis
- 随机控制理论 Stochastic control theory
- 微观经济学 Microeconomics
- 数量经济学 Quantitative Economics
- 宏观经济学 Macroeconomics
- 经济统计学 Economic Statistics
- 经济学理论 Economic Theory
- 计量经济学 Econometrics
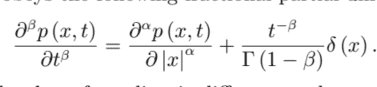
经济代写
数学代写|金融数学作业代写Financial Mathematics代考|Ultrahigh-frequency
An important area where fractional processes find application is the modeling of the order arrival process. This topic has become ever more interesting with the diffusion of high- and ultrahigh-frequency data and with high-frequency trading. The availability of data has enabled the empirical study of the econometrics of high frequency data while high frequency trading has provided a powerful economic motivation for their study.
Ultrahigh-frequency data are tick-by-tick data. As orders and trading occur at random times, tick-by-tick data are not classical time series but point processes. The representation of tick-by-tick data includes a representation of the orderarrival process and a representation of the magnitude of the transaction.
数学代写|金融数学作业代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|ULTRAHIGH-FREQUENCY
Scalas et al. (2000) and Mainardi et al. (2000) were the first to apply tick-by-tick data to the formalism of Continuous-Time Random Walks (CTRW) developed in Montroll and Weiss. A CTRW is a random walk where both the length of the time between two steps and the magnitude of each step are random. Call $t_{i}, x_{i}$ the time and magnitude of the $i$-th transaction, call $\tau_{i}=t_{i+1}-t_{i}, \xi_{i}=x_{i+1}-x_{i}$ the waiting times and the magnitude of jumps, and call $\varphi(\xi, \tau)$ the joint density of jumps and waiting times and $p(x, t)$ the joint probability that the diffusing quantity be at position $x$ at time $t$. Montroll and Weiss (1965) demonstrated that the Laplace-Fourier transform of $p$ has the following form:
$$
\tilde{p}(\kappa, s)=\frac{1-\tilde{\psi}(s)}{s} \frac{1}{1-\tilde{\varphi}(\kappa, s)}
$$
where $\tilde{p}(\kappa, s)$ is the Laplace-Fourier transform of $p(x, t) ; \tilde{\psi}(s)$ is the Laplace transform of the waiting time pdf $\psi(\tau)=\int \varphi(\xi, \tau) d \xi$.
Scalas et al. (2000) demonstrated that in the hydrodynamic limit (i.e., long waiting times and long jumps), assuming that:
$$
\tilde{\varphi}(\kappa, s)=1-s^{\beta}-|\kappa|^{\alpha}, 0<\beta \leq 1,0<\alpha \leq 2
$$
the density $p(x, t)$ obeys the following fractional partial differential equation:
$$
\frac{\partial^{\beta} p(x, t)}{\partial t^{\beta}}=\frac{\partial^{\alpha} p(x, t)}{\partial|x|^{\alpha}}+\frac{t^{-\beta}}{\Gamma(1-\beta)} \delta(x)
$$
Empirical tests of the above formalism in different markets can be found in Scalas et al. (2004), Scalas (2006), Politi and Scalas (2007), Politi and Scalas (2008), and Sazuka et al. (2009).

数学代写|金融数学作业代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|ULTRAHIGH-FREQUENCY
分数流程应用的一个重要领域是订单到达流程的建模。随着高频和超高频数据的传播以及高频交易,这个话题变得越来越有趣。数据的可用性使得高频数据计量经济学的实证研究成为可能,而高频交易为他们的研究提供了强大的经济动力。
超高频数据是逐个滴答数据。由于订单和交易是随机发生的,逐笔交易数据不是经典的时间序列,而是点过程。逐笔交易数据的表示包括订单到达过程的表示和交易量的表示。
数学代写|金融数学作业代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|ULTRAHIGH-FREQUENCY
斯卡拉斯等人。2000和 Mainardi 等人。2000是第一个将逐个滴答数据应用于连续时间随机游走形式的人C吨R在在 Montroll 和 Weiss 开发。CTRW 是一种随机游走,其中两个步骤之间的时间长度和每个步骤的大小都是随机的。称呼吨一世,X一世的时间和幅度一世-th 交易,调用τ一世=吨一世+1−吨一世,X一世=X一世+1−X一世等待时间和跳跃幅度,并调用披(X,τ)跳跃和等待时间的联合密度和p(X,吨)扩散量在位置的联合概率X有时吨. 蒙特罗尔和韦斯1965证明了拉普拉斯-傅里叶变换p具有以下形式:
p~(ķ,s)=1−ψ~(s)s11−披~(ķ,s)
在哪里p~(ķ,s)是拉普拉斯-傅里叶变换p(X,吨);ψ~(s)是等待时间的拉普拉斯变换 pdfψ(τ)=∫披(X,τ)dX.
斯卡拉斯等人。2000证明在水动力极限一世.和.,一世○nG在一种一世吨一世nG吨一世米和s一种nd一世○nGj你米ps, 假如说:
披~(ķ,s)=1−sb−|ķ|一种,0<b≤1,0<一种≤2
密度p(X,吨)服从以下分数偏微分方程:
∂bp(X,吨)∂吨b=∂一种p(X,吨)∂|X|一种+吨−bΓ(1−b)d(X)
Scalas 等人在不同市场中对上述形式主义进行了实证检验。2004楼梯2006政治和斯卡拉斯2007政治和斯卡拉斯2008,和 Sazuka 等人。2009.

计量经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
微观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
宏观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写