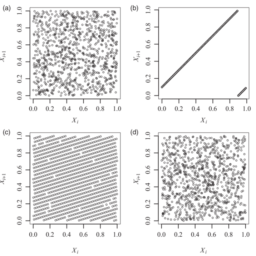
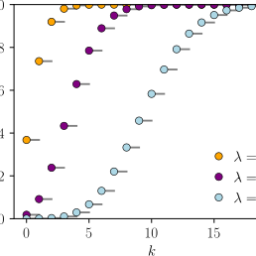
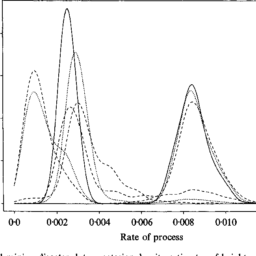
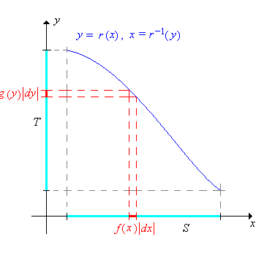
如果你也在 怎样统计计算Statistical Computing这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。统计计算Statistical Computing是统计学和计算机科学之间的纽带。它意味着通过使用计算方法来实现的统计方法。它是统计学的数学科学所特有的计算科学(或科学计算)的领域。这一领域也在迅速发展,导致人们呼吁应将更广泛的计算概念作为普通统计教育的一部分。与传统统计学一样,其目标是将原始数据转化为知识,[2]但重点在于计算机密集型统计方法,例如具有非常大的样本量和非同质数据集的情况。
许多统计建模和数据分析技术可能难以掌握和应用,因此往往需要使用计算机软件来帮助实施大型数据集并获得有用的结果。S-Plus是公认的最强大和最灵活的统计软件包之一,它使用户能够应用许多统计方法,从简单的回归到时间序列或多变量分析。该文本广泛涵盖了许多基本的和更高级的统计方法,集中于图形检查,并具有逐步说明的特点,以帮助非统计学家充分理解方法。
my-assignmentexpert™统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计计算Statistical Computing代写服务。我们的专家在统计计算Statistical Computing代写方面经验极为丰富,各种统计计算Statistical Computing相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的统计计算Statistical Computing及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 随机微积分 Stochastic calculus
- 随机分析 Stochastic analysis
- 随机控制理论 Stochastic control theory
- 微观经济学 Microeconomics
- 数量经济学 Quantitative Economics
- 宏观经济学 Macroeconomics
- 经济统计学 Economic Statistics
- 经济学理论 Economic Theory
- 计量经济学 Econometrics
统计代写
数学代写|统计计算作业代写Statistical Computing代考|Basic Monte Carlo
Assume that $X=\left(X_{t}\right){t \in[0, T]}$ is given as the solution of an SDE and that we want to compute $\mathbb{E}(f(X))$. In order to estimate this quantity using Monte Carlo integration, we generate independent samples $X^{(n, 1)}, X^{(n, 2)}, \ldots, X^{(n, N)}$, using numerical approximations to $X$, obtained by repeatedly solving a discretised SDE with discretisation parameter $n$. Then we can use the approximation $$ \mathbb{E}(f(X)) \approx \frac{1}{N} \sum{j=1}^{N} f\left(X^{(n, j)}\right)=Z_{n, N}
$$
Here we allow for the function $f$ to depend on the whole path of $X$ until time $T$. We can choose, for example,
$$
f(X)=\sup {t \in[0, T]} X{t}
$$
to get the maximum of a one-dimensional path, or $f(X)=\left|X_{T}\right|^{2}$ to get the second moment of the final point of the path.
As for all Monte Carlo methods, there is a trade-off between accuracy of the result and computational cost. One notable feature of Monte Carlo estimation for SDEs is that the result is not only affected by the Monte Carlo error, but also by discretisation error.
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|Variance reduction methods
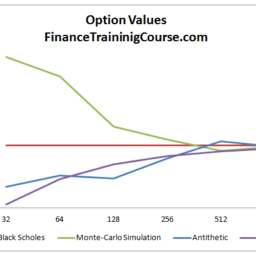
The error in Monte Carlo estimates such as (6.28) can be significantly reduced by employing the variance reduction techniques from Section 3.3.
6.5.2.1 Antithetic paths
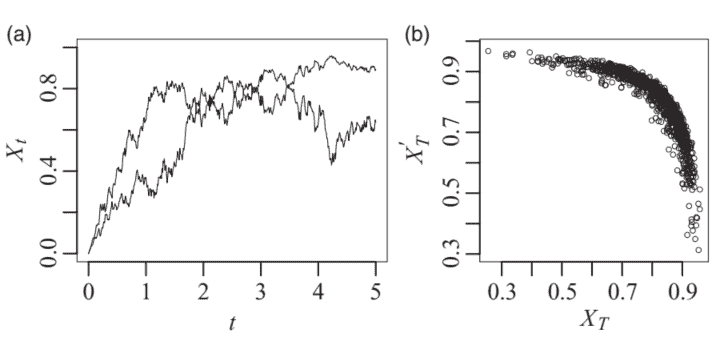
Pairs of antithetic paths can be easily generated for SDEs by using the fact that, if $B$ is a Brownian motion, $-B$ is also a Brownian motion (see lemma 6.5): thus, solving the SDE using the Brownian motions $B$ and $B^{\prime}=-B$ gives rise to two paths $X$ and $X^{\prime}$ of the SDE. Since $B_{t}$ and $B_{t}^{\prime}$ are negatively correlated, typically $X_{t}$ and $X_{t}^{\prime}$ will also be negatively correlated for all $t \in[0, T]$.
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|Multilevel Monte Carlo estimates
The variance reduction methods we have discussed so far are applications of the general methods from Section $3.3$ to the problem of estimating expectations for paths of SDEs. In contrast, the multilevel Monte Carlo approach, discussed in the rest of this section, is specific to situations where discretisation error is involved.
Multilevel Monte Carlo methods, by cleverly balancing the effects of discretisation error and Monte Carlo error, allow us to reduce the computational cost required to compute an estimate with a given level of error. Let $X$ be the solution of an SDE and let $\varepsilon>0$. In equation (6.34) we have seen that the basic Monte Carlo estimate for $\mathbb{E}\left(f\left(X_{T}\right)\right)$ requires computational cost of order $\mathcal{O}\left(1 / \varepsilon^{3}\right)$ in order to bring the root-mean squared error down to $\varepsilon>0$. We will see that multilevel Monte Carlo methods can reduce this cost to nearly $\mathcal{O}\left(1 / \varepsilon^{2}\right)$.
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|BASIC MONTE CARLO
假设 $X=\left(X_{t}\right){t \in[0, T]}$ is given as the solution of an SDE and that we want to compute $\mathbb{E}(f(X))$. In order to estimate this quantity using Monte Carlo integration, we generate independent samples $X^{(n, 1)}, X^{(n, 2)}, \ldots, X^{(n, N)}$, using numerical approximations to $X$, obtained by repeatedly solving a discretised SDE with discretisation parameter $n$. Then we can use the approximation $$ \mathbb{E}(f(X)) \approx \frac{1}{N} \sum{j=1}^{N} f\left(X^{(n, j)}\right)=Z_{n, N}
$$
Here we allow for the function $f$ to depend on the whole path of $X$ until time $T$. We can choose, for example,
$$
f(X)=\sup {t \in[0, T]} X{t}
$$
得到一维路径的最大值,或者F(X)=|X吨|2获得路径终点的第二个时刻。
对于所有蒙特卡罗方法,结果的准确性和计算成本之间存在权衡。SDE 的 Monte Carlo 估计的一个显着特点是,结果不仅受 Monte Carlo 误差的影响,而且还受离散化误差的影响。
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|VARIANCE REDUCTION METHODS
蒙特卡洛估计中的误差,例如6.28可以通过使用第 3.3 节中的方差减少技术来显着减少。
6.5.2.1
对立路径 通过使用以下事实,可以很容易地为 SDE 生成一对对立路径,如果乙是布朗运动,−乙也是布朗运动s和和一世和米米一种6.5:因此,使用布朗运动求解 SDE乙和乙′=−乙产生两条路径X和X′SDE 的。自从乙吨和乙吨′负相关,通常X吨和X吨′也将是负相关的所有吨∈[0,吨].
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|MULTILEVEL MONTE CARLO ESTIMATES
到目前为止,我们讨论的方差减少方法是第 1 节中的一般方法的应用。3.3估计 SDE 路径的期望问题。相比之下,本节其余部分讨论的多级蒙特卡罗方法特定于涉及离散化误差的情况。
多级蒙特卡罗方法通过巧妙地平衡离散化误差和蒙特卡罗误差的影响,使我们能够减少计算具有给定误差水平的估计所需的计算成本。让X是 SDE 的解并让e>0. 在等式中6.34我们已经看到,基本的蒙特卡罗估计和(F(X吨))需要计算订单成本○(1/e3)为了将均方根误差降低到e>0. 我们将看到多级蒙特卡洛方法可以将这个成本降低到几乎○(1/e2).

计量经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
微观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
宏观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写