如果你也在 怎样代写光学Optics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。光学Optics始于古埃及人和美索不达米亚人对镜片的开发。最早的已知透镜由抛光的水晶制成,通常是石英,最早可追溯到公元前2000年的克里特岛(希腊赫拉克里翁考古博物馆)。罗德岛的镜片可追溯到公元前700年左右,亚述人的镜片也是如此,如尼姆鲁德的镜片。古代罗马人和希腊人将玻璃球装满水来制作透镜。在这些实践发展之后,古希腊和印度的哲学家们发展了关于光和视觉的理论,并在希腊-罗马世界中发展了几何光学。光学这个词来自古希腊词ὀπτική(optikē),意思是 “外观,看”。
光学Optics是研究光的行为和属性的物理学分支,包括它与物质的相互作用以及使用或探测它的仪器的构造。光学通常描述可见光、紫外光和红外光的行为。
my-assignmentexpert™ 光学Optics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的光学Optics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此光学Optics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理physics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的物理physics代写服务。我们的专家在光学Optics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种光学Optics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的光学Optics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 几何光学 Geometrical optics
几何光学,或称射线光学,是一种用射线来描述光的传播的光学模型。几何光学中的射线是一个抽象的概念,有助于近似地描述光线在某些情况下的传播路径。
- 波动光学
在物理学中,波动光学,或称波光学,是光学的一个分支,研究干涉、衍射、偏振和其他几何光学中的射线近似不成立的现象。
- 量子光学
量子光学是原子、分子和光学物理学的一个分支,处理单个光量子(称为光子)如何与原子和分子互动的问题。它包括研究光子的类似粒子的特性。
物理代写|光学作业代写Optics代考|Equations of motion for interacting optical waves in a dielectric medium
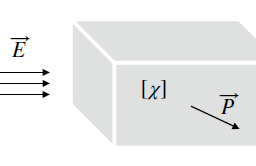
A physically meaningful coupled-wave formalism has been developed in the context of quantum Rayleigh coupling of photons for the operation of optical directional and counter-directional couplers, and other devices, in optically linear media as suggested in (Vatarescu [18-20]), for both homogeneous and inhomogeneous dielectric configurations. The resultant rate equations for the exchange of optical power $P_{j}=\hbar \omega N_{j}(j=1$ or 2$)$ or the corresponding numbers of photons $N_{j}$ between two interacting wavefronts and their corresponding phases $\varphi_{\mathrm{j}}$, are derived from equations (2.5) above, and have the following forms [18-20]:
where the gain coefficient $g$ includes a phase dependence and the coupling coefficient $\kappa$ is affected by the three-dimensional polarisation states of the two waves, that is, $\boldsymbol{e}{1}$ and $\boldsymbol{e}{2}$. The phase difference between the two waves is $\theta_{21}, \beta$ being the propagation constant and $z / t=\mathrm{v}{\mathrm{p}}$ is the phase velocity. In eq. ( $2.10 e), k{0}$ and $n$ specify the free-space wave vector and the effective refractive index, respectively. It should be noted that eqs. (2.10) describe the physically meaningful process of quantum Rayleigh conversion of photons [18-20]. The coupling coefficient of eq. (2.10e) indicates that the entire local value of the optically linear susceptibility $\chi^{(1)}$ is involved in the coupling process inside the dielectric medium at any point where the two spatial distributions $f_{l}$ and $f_{2}$ overlap, each having units of $\mathrm{m}^{-1}$, and the field squared $f^{2}$ being normalized to a dimensionless unit over the cross-section area. This is in contrast to the physically impossible coupling between two optical waveguides apparently induced by a perturbation of the dielectric constant $\Delta \varepsilon$ in the cladding which leads, physically, to random, classical Rayleigh scattering [21]. Once again, it is worthwhile reiterating that a correct identification of physical processes will enable improved design and operation of photonic devices.
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|Applications of the optically linear parametric interactions
As an application the optical power coupling of eqs. (2.10) underpinned by the physical process of quantum Rayleigh conversion of photons, we consider the optical directional coupler depicted in Fig. 2.1 as a crosssection of two waveguides of core indices $n_{1}$ and $n_{2}$ separated by a cladding of refractive index $n_{3}$. It is the overlap of modal fields in the cladding that brings about the exchange of optical power, with the coupling coefficient being proportional to the optically linear susceptibility $\chi^{(1)}$. The gain coefficient is phase- and polarisation- sensitive enabling selective amplification. Overall, it is possible to control the properties of a signal wave by adjusting the input values of a low-power pump wave because of the strong value of the optically linear susceptibility $\chi^{(1)}$. The relative phase (or phase-mismatch) can be controlled by adjusting the power ratio between the pump and the signal waves. Equations $(2.10 c-d)$ indicate the existence of a built-in mechanism for phase-matching between a strong pump and a weak signal through the parametrically induced phase shift. For converging or diverging $Y$-junctions, the coupling coefficient would have polarisation vectors projected onto each other.
By using the same optical frequency for an entire photonic circuit made up of dielectric waveguides, it should be possible to reduce the complexity associated with multiple waves and types of materials. Additionally, electro-optic waveguides provide connections between the electrical signals and optical ones.
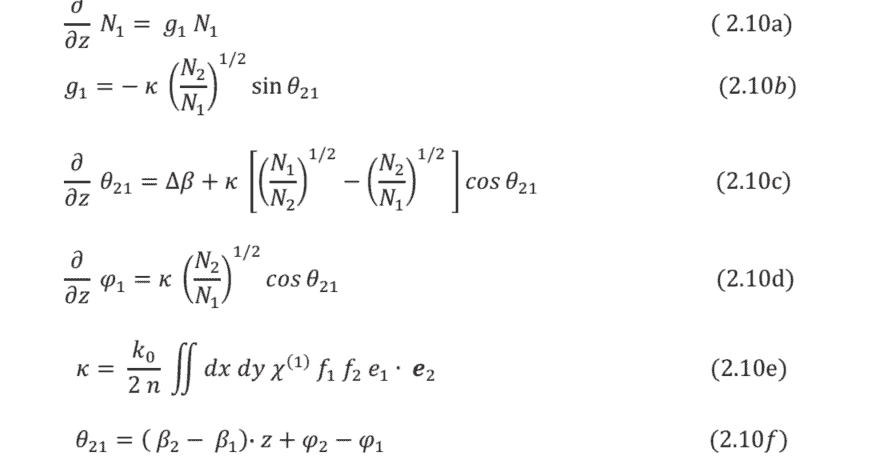
物理代写
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR INTERACTING OPTICAL WAVES IN A DIELECTRIC MEDIUM
在光子的量子瑞利耦合的背景下,一种物理上有意义的耦合波形式已被开发出来,用于在光学线性介质中操作光学定向和反向耦合器以及其他设备,如五一种吨一种r和sC你[18−20],对于均匀和不均匀的电介质配置。光功率交换的合成速率方程磷j=⁇ωñj(j=1或 2)或相应的光子数ñj在两个相互作用的波前及其相应的相位之间披j, 来自方程2.5上面,并有以下形式18−20:
其中增益系数G包括相位依赖性和耦合系数ķ受两个波的三维偏振态影响,即 $\kappa$ is affected by the three-dimensional polarisation states of the two waves, that is, $\boldsymbol{e}{1}$ and $\boldsymbol{e}{2}$. The phase difference between the two waves is $\theta_{21}, \beta$ being the propagation constant and $z / t=\mathrm{v}{\mathrm{p}}$ is the phase velocity. In eq. ( $2.10 e), k{0}$ and $n$ specify the free-space wave vector and the effective refractive index, respectively. It should be noted that eqs. (2.10) describe the physically meaningful process of quantum Rayleigh conversion of photons [18-20]. The coupling coefficient of eq. (2.10e) indicates that the entire local value of the optically linear susceptibility $\chi^{(1)}$ is involved in the coupling process inside the dielectric medium at any point where the two spatial distributions $f_{1}$ and $f_{2}$ overlap, each having units of $\mathrm{m}^{-1}$, and the field squared $f^{2}$ being normalized to a dimensionless unit over the cross-section area. This is in contrast to the physically impossible coupling between two optical waveguides apparently induced by a perturbation of the dielectric constant $\Delta \varepsilon$
在物理上导致随机的经典瑞利散射21. 再次重申,正确识别物理过程将有助于改进光子器件的设计和操作。
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|APPLICATIONS OF THE OPTICALLY LINEAR PARAMETRIC INTERACTIONS
作为一个应用,方程的光功率耦合。2.10以光子量子瑞利转换的物理过程为基础,我们将图 2.1 中描绘的光定向耦合器视为两个核心指数波导的横截面n1和n2由折射率的包层隔开n3. 正是包层中模态场的重叠导致了光功率的交换,耦合系数与光学线性磁化率成正比χ(1). 增益系数对相位和极化敏感,可以进行选择性放大。总的来说,由于光学线性磁化率的强值,可以通过调整低功率泵浦波的输入值来控制信号波的特性χ(1). 相对相位这rpH一种s和−米一世s米一种吨CH可以通过调节泵浦和信号波之间的功率比来控制。方程(2.10C−d)表明存在通过参数诱导的相移在强泵和弱信号之间进行相位匹配的内置机制。用于收敛或发散是-结,耦合系数将具有相互投影的极化矢量。
通过对由电介质波导组成的整个光子电路使用相同的光学频率,应该可以降低与多种波和材料类型相关的复杂性。此外,电光波导提供电信号和光信号之间的连接。

物理代写|光学作业代写Optics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。